8 Ways Global Warming Is Already Changing the World
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Warming world
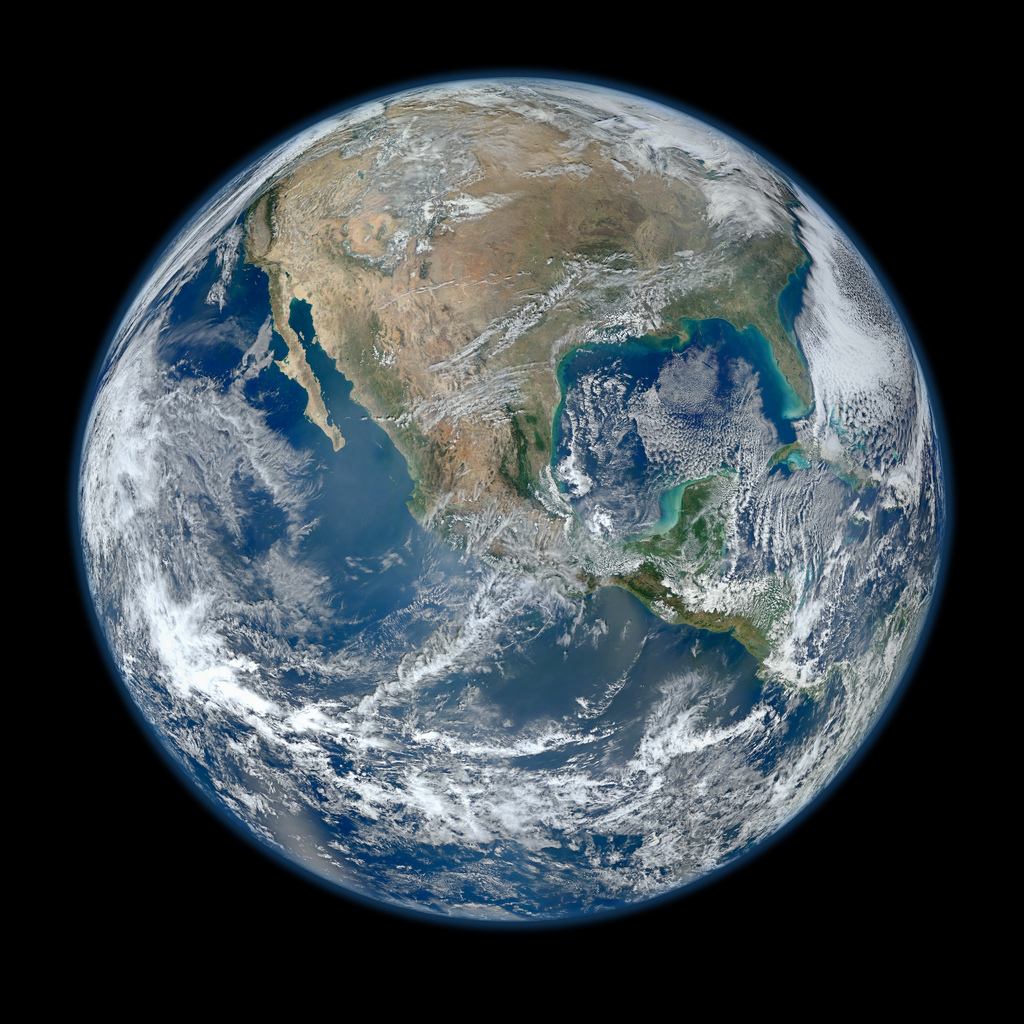

Over the last 100 years, global temperatures have warmed by about 1.33 degrees Fahrenheit (0.74 degrees Celsius) on average. The change may seem minor, but it's happening very quickly — more than half of it since 1979, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
Though it can still be difficult to tease out how much climate change plays in any given weather event, changes are occurring.
In the spirit of Earth day, here's a look at our marvelous blue marble and the ways people and other living things are responding to global warming. [50 Amazing Facts About Earth]
Moving the military northward
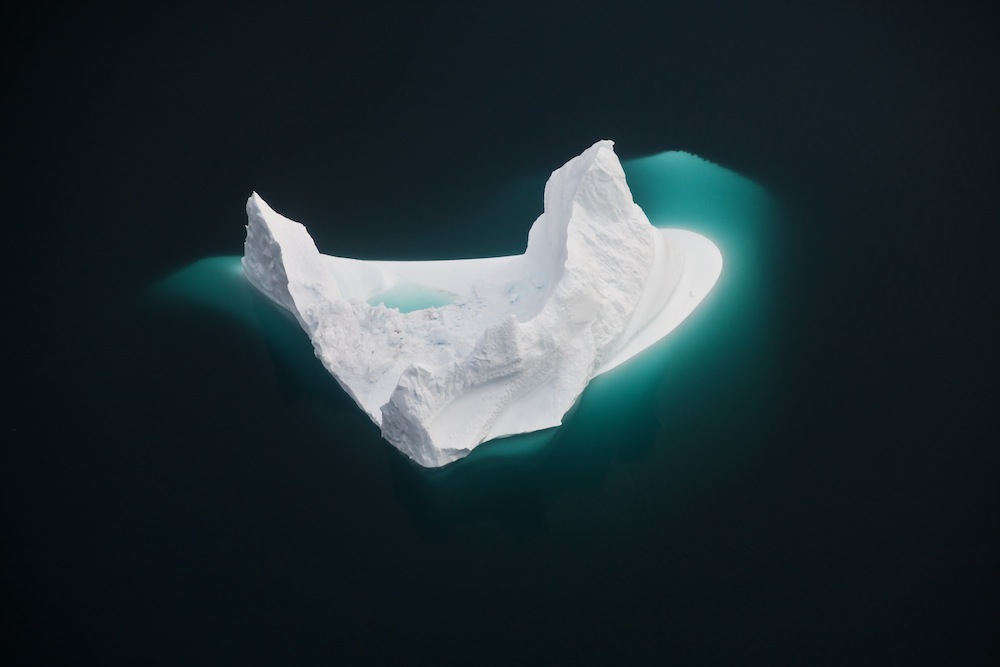

As the Arctic ice opens up, the world turns its attention to the resources below. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, 30 percent of the world's undiscovered natural gas and 13 percent of its undiscovered oil are under this region. As a result, military action in the Arctic is heating up, with the United States, Russia, Denmark, Finland, Norway, Iceland, Sweden and Canada holding talks about regional security and border issues. Several nations, including the U.S., are also drilling troops in the far north, preparing for increased border patrol and disaster response efforts in a busier Arctic.
Altering breeding seasons
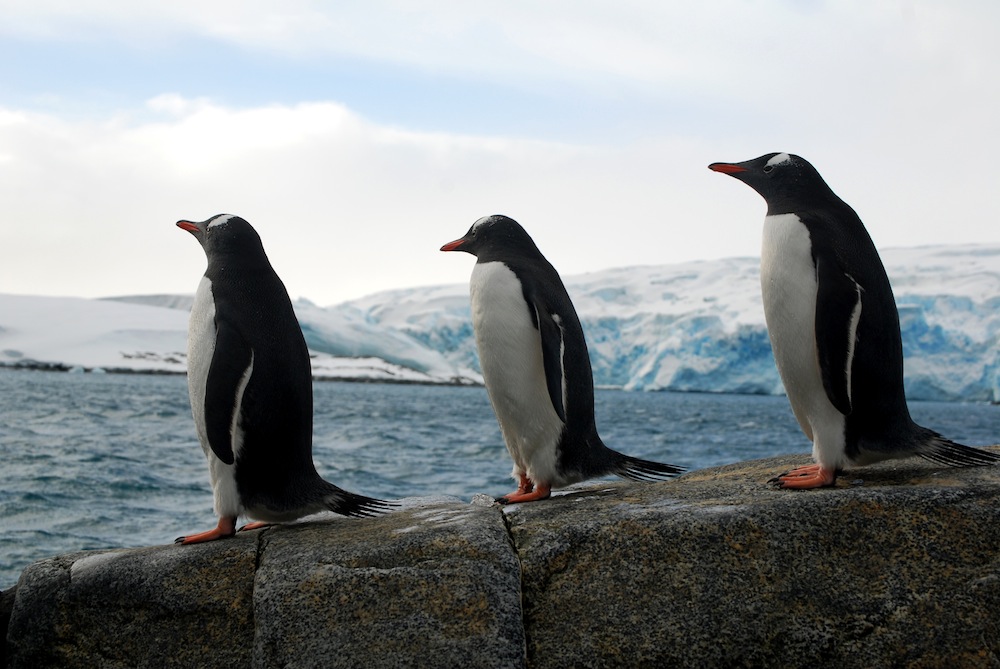

As temperatures shift, penguins are shifting their breeding seasons, too. A March 2012 study found that gentoo penguins are adapting more quickly to warmer weather, because they aren't as dependent on sea ice for breeding as other species.
It's not just penguins that seem to be responding to climate change. Animal shelters in the U.S. have reported increasing numbers of stray cats and kittens attributed to a longer breeding season for the felines.
High-country changes

Decreased winter snowfall on mountaintops is allowing elk in northern Arizona to forage at higher elevations all winter, contributing to a decline in seasonal plants. Elk have ravaged trees such as maples and aspens, which in turn has led to a decline in songbirds that rely on these trees for habitat.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Altered Thoreau's stomping grounds

The writer Henry David Thoreau once lovingly documented nature in and around Concord, Mass. Reading those diaries today has shown researchers just how much spring has changed in the last century or so.
Compared to the late 1800s, the first flowering dates for 43 of the most common plant species in the area have moved forward an average of 10 days. Other plants have simply disappeared, including 15 species of orchids.
Changed high season at national parks

When's the busiest time to see the Grand Canyon? The answer has changed over the decades as spring has started earlier. Peak national park attendance has shifted forward more than four days, on average, since 1979. Today, the highest number of visitors now swarm the Grand Canyon on June 24, compared with July 4 in 1979.
Changing genetics
Even fruit flies are feeling the heat. According to a 2006 study, fruit fly genetic patterns normally seen at hot latitudes are showing up more frequently at higher latitudes. According to the research, the gene patterns of Drosophila subobscura, a common fruit fly, are changing so that populations look about one degree closer in latitude to the equator than they actually are. In other words, genotypes are shifting so that a fly in the Northern Hemisphere has a genome that looks more like a fly 75 to 100 miles (120 to 161 kilometers) south.
Hurting polar bears

Polar bear cubs are struggling to swim increasingly long distances in search of stable sea ice, according to a 2011 study. The rapid loss of sea ice in the Arctic is forcing bears to sometimes swim up to more than 12 days at a time, the research found. Cubs of adult bears that had to swim more than 30 miles (48 kilometers) had a 45 percent mortality rate, compared with 18 percent for cubs that had to swim shorter distances.
More mobile species
Species are straying from their native habitats at an unprecedented rate: 11 miles (17.6 km) toward the poles per decade. Areas where temperature is increasing the most show the most straying by native organisms. The Cetti's warbler, for example, has moved north over the last two decades by more than 90 miles (150 km).

Stephanie Pappas is a contributing writer for Live Science, covering topics ranging from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and behavior. She was previously a senior writer for Live Science but is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and regularly contributes to Scientific American and The Monitor, the monthly magazine of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie received a bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










