Leading Causes of Death in the US: 1900 - Present (Infographic)
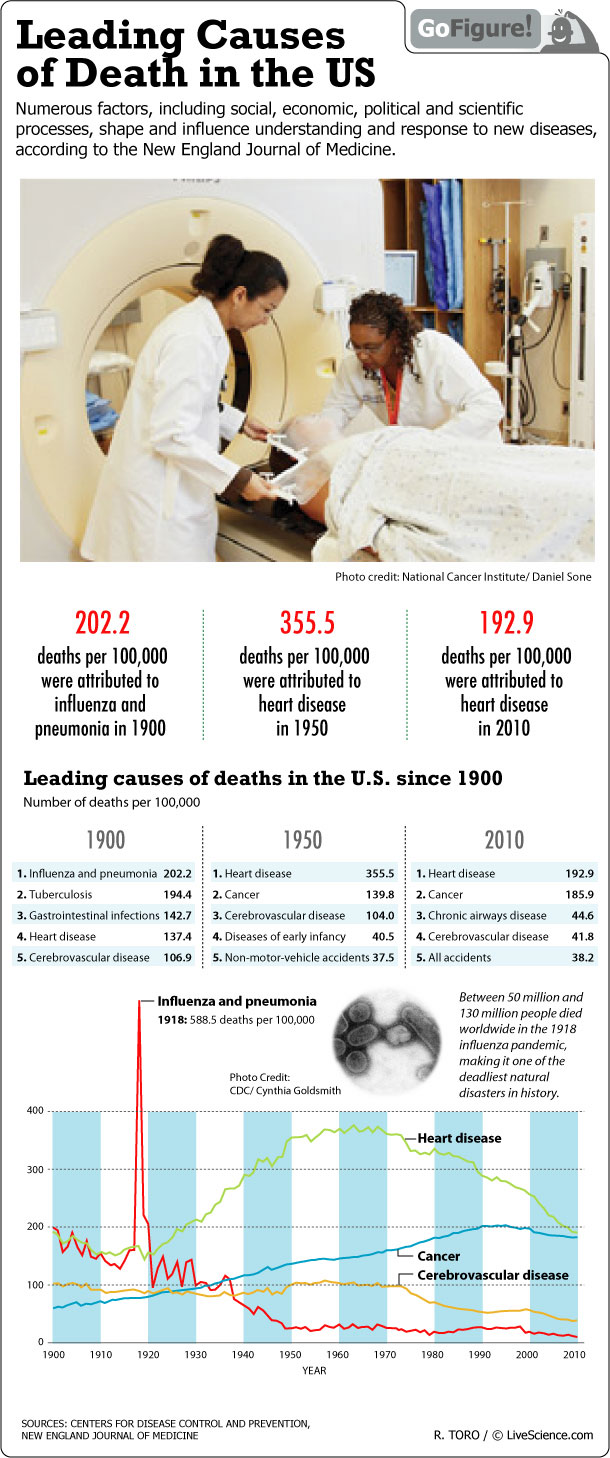
Numerous factors, including social, economic, political and scientific processes, shape and influence understanding and response to new diseases, according to the New England Journal of Medicine.
By categorizing the ways illness develop and analyzing the many new diseases that have appeared over the past two centuries, medical historians found that new environmental conditions and ecological changes, human factors like population growth, changing social mores and sexual behavior, migration, war, intravenous drug use and even the consequences of new therapies can produce new diseases and increase the prevalence of once-obscure ailments.
Developing diagnostic technologies and criteria can reveal previously unrecognized conditions such as hypertension and expand the scope and understanding of a disease such as depression. HIV–AIDS emerged as the result of conscious advocacy by interested parties, in addition to many of these modes of emergence.
In battling emerging disease, the medical community hopes to use these factors and processes along with an integrated policy under which health care and health programs can address the complexities and ever-changing burden of disease.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

