Far Out! Meteorites From Mars & Moon Going Up For Sale
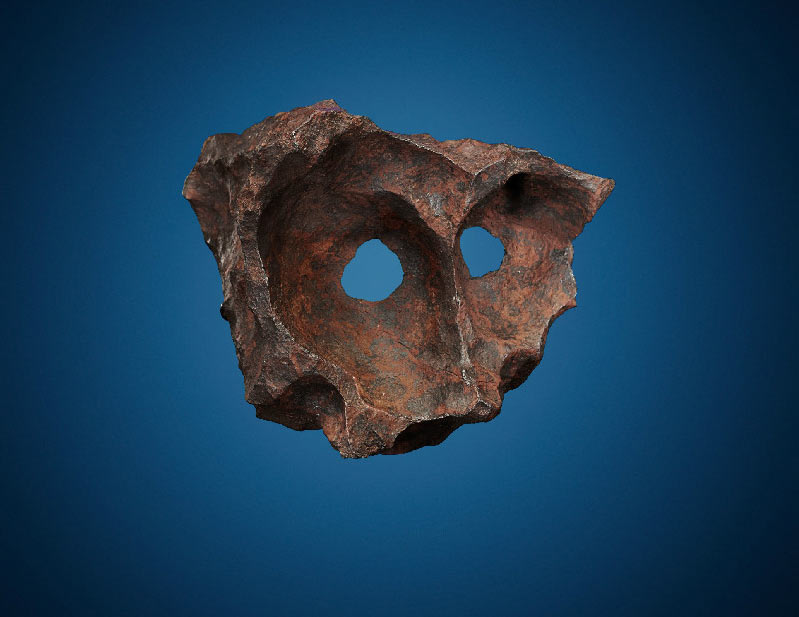

If you've ever yearned to own something from out of this world, here's your chance.
On Oct. 14 in Manhattan, fragments of Mars, the moon and asteroids that have fallen to Earth go up for sale, in what auction house Heritage Auctions is billing as the largest public meteorite auction ever held.
More than 125 items are for sale, a number of which have no minimum bid attached.
The growing market for meteorites has driven the emergence of a meteorite prospecting industry in northwestern Africa and Oman, but even as people scour the deserts for meteorites, rocks from space remain among the most rare things on Earth.
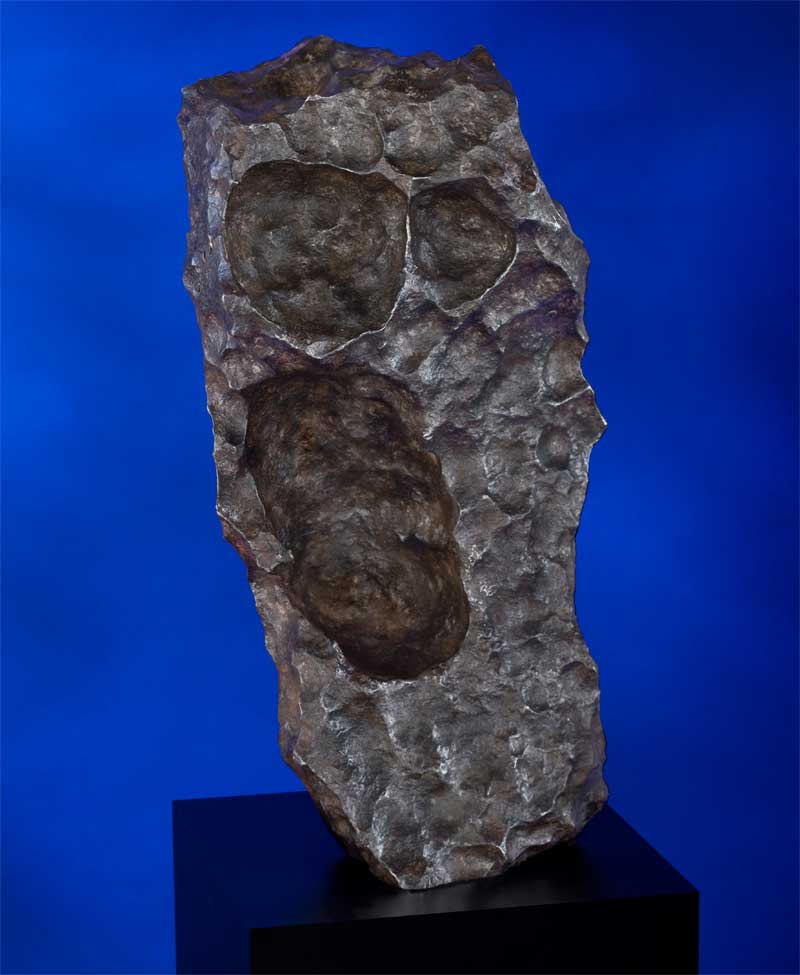

Taken together, every single meteorite known to exist would weigh significantly less than the world’s annual output of gold, said Darryl Pitt, the meteorite consultant for the auction.
Nearly all known meteorites originate in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, and research tied a few back to the large asteroid Vesta. Vesta's surface bears evidence of collisions, including a large crater near its southern pole that could have ejected rocks onto paths that intersected with Earth’s. [See Photos of Meteorites for Sale]
This sale includes material from six meteorites that originated on Vesta.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Bits of Mars and the moon are much more rare, but they, too, have been launched by asteroid impacts. About 150 pounds (68 kilograms) of moon meteorites are known to exist, and none has been found in Europe or the Americas. About one-quarter, however, have been found by scientists on the cold desert of Antarctica, according to auction materials.
Mars' rocks present a particular challenge to identify, because humans haven't been able to bring Martian rocks back to Earth, as has happened with moon rocks. However, scientists do know the composition of Mars' atmosphere, and they have matched it to the composition of pockets of gas contained in some meteorites, confirming their Martian origin.
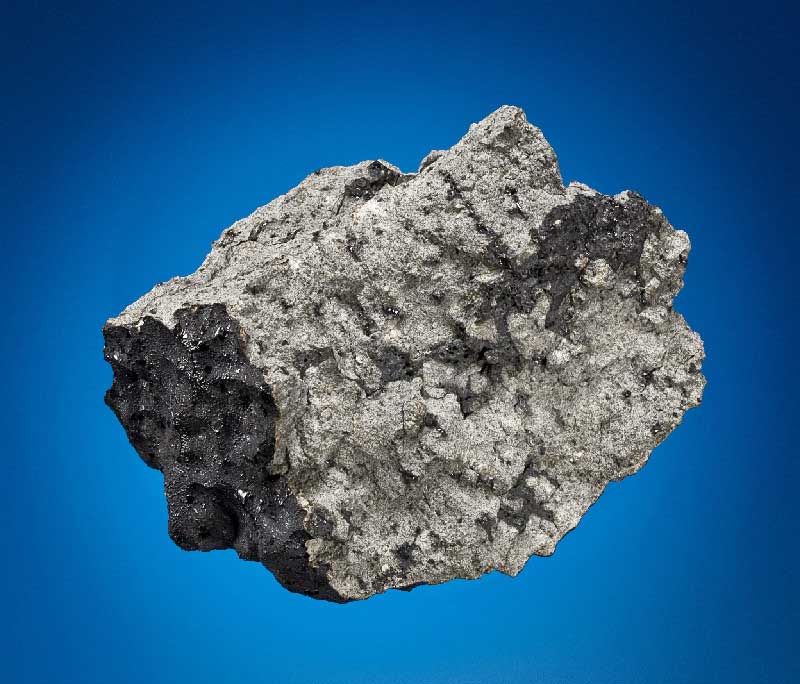

Next month's auction is slated to feature meteorites from both places, including a fragment of the Tissint meteorite, which fell in Morocco in July 2011; the fragment came from a larger specimen owned by the Natural History Museum of London. The auction also includes two halves from a 4-pound (1.8-kilogram) lunar meteorite that is the fourth largest available for private ownership.
Exotic origins and scientific interest aside, meteorites can also be beautiful. Some can look like abstract sculptures or are dotted with yellow peridot, the August birthstone. In some cases, slices reveal the metallic patterns hidden within the meteorite.
This Mars meteorite landed in July 2011 as part of a shower in the vicinity of Tissint, Morocco, the location that gives the meteorite its name. Collectors and institutions have since snapped up Tissint meteorites. This meteorite, which weighs 0.75 pounds (327 grams), locks into a larger specimen now owned by London's Natural History Museum.
A meteorite has no value until it has been authenticated by meteoriticist, a scientist who studies meteorites. To examine a meteorite, a meteoriticist must look at the rock's internal matrix by cutting away a piece. As a result, all meteorites must be cut, except those that fall as part of the same meteor shower, Pitt said. A description of the meteorite and its name are then published. [Facts About Meteorites]
A backstory can also make a meteorite more valuable to collectors; for instance, meteorites seen falling from the sky are more valuable than those discovered only after they are on the ground, Pitt said.
The auction is scheduled to take place on Sunday (Oct. 14) at the Fletcher-Sinclair Mansion at 2 East 79th Street, Manhattan. The public can view the meteorites on Thursday (Oct. 11) from noon to 8 p.m. ET, on Friday and Saturday (Oct. 12 and 13) from 10 a.m. to 6 p.m., and on Sunday (Oct. 14) from noon to 3:30 p.m.
Follow LiveScience on Twitter @livescience. We're also on Facebook & Google+.