Ancient Carving Shows Stylishly Plump African Princess
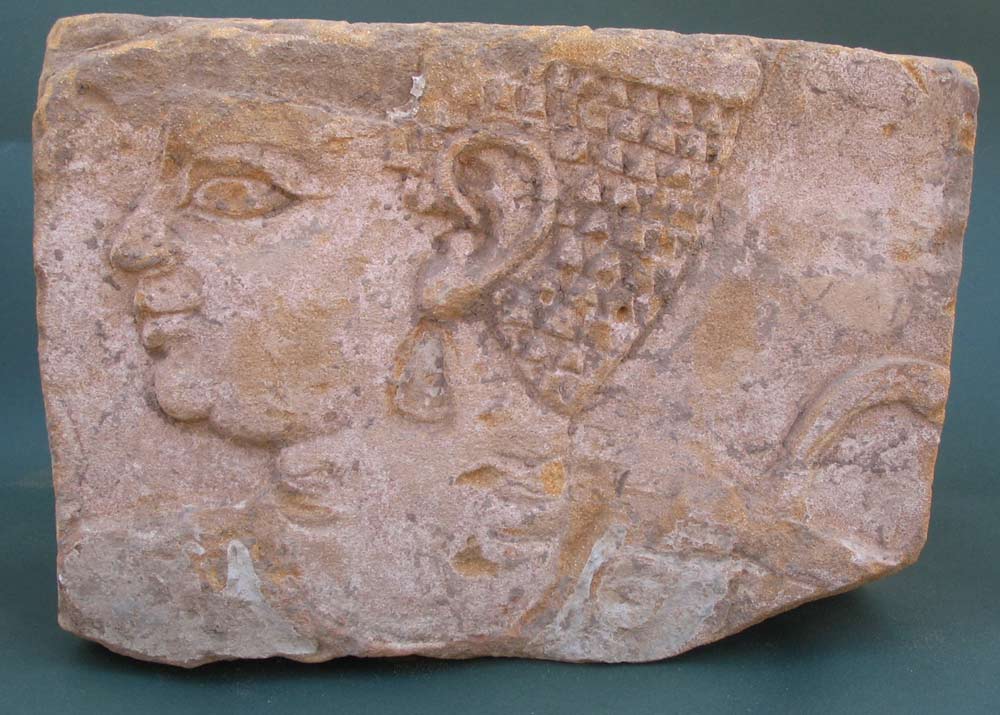

A 2,000-year-old relief carved with an image of what appears to be a, stylishly overweight, princess has been discovered in an "extremely fragile" palace in the ancient city of Meroë, in Sudan, archaeologists say.
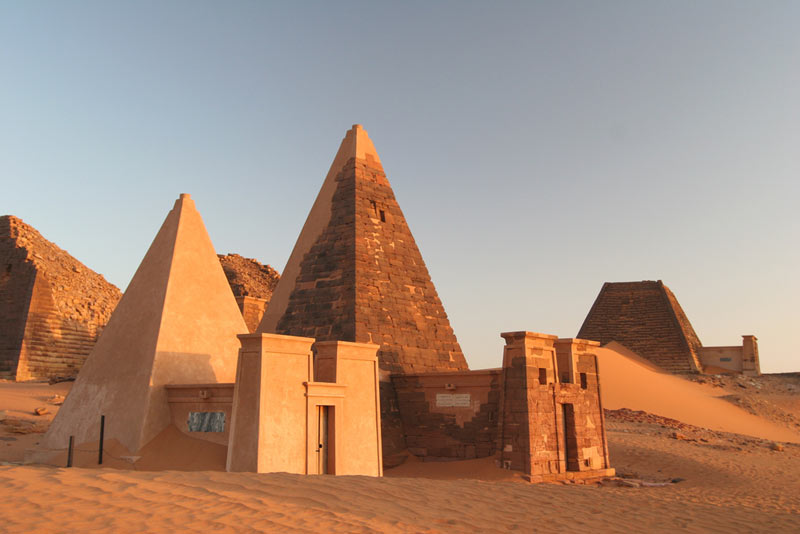
At the time the relief was made, Meroë was the center of a kingdom named Kush, its borders stretching as far north as the southern edge of Egypt. It wasn't unusual for queens (sometimes referred to as "Candaces") to rule, facing down the armies of an expanding Rome.
The sandstone relief shows a woman smiling, her hair carefully dressed and an earring on her left ear. She appears to have a second chin and a bit of fat on her neck, something considered stylish, at the time, among royal women from Kush.
Team leader Krzysztof Grzymski presented the relief, among other finds from the palace at Meroë, at an Egyptology symposium held recently at the Royal Ontario Museum in Toronto.

Researchers don't know the identity of the woman being depicted, but based on the artistic style the relief appears to date back around 2,000 years and show someone royal. "It's similar to other images of princesses," Grzymski told LiveScience in an interview. He said that the headdress hasn't survived and it cannot be ruled out that it actually depicts a queen. [Image Gallery: Amazing Egyptian Discoveries]
Why royal women in Kush preferred to be depicted overweight is a long-standing mystery. "There is a distinct possibility that the large size of the Candaces represented fertility and maternity," wrote the late Miriam Ma'at-Ka-Re Monges, who was a professor at California State University, Chico, and an expert on Kush, in an article published in The Encyclopedia of Black Studies (Sage Publications, 2005).
An ancient palace
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The discovery occurred in 2007 as Grzymski's team was exploring a royal palace in the city, trying to determine its date. The sandstone blocks that made up its foundation were "extremely fragile," according to Grzymski, and the team found that the palace dated to late in the life of Kush's existence. The blocks were re-used in antiquity by the palace's builders and were originally from buildings that stood in earlier times.
When they found the relief it "was loose and falling apart so we just took it out," Grzymski said. It was brought to a museum in Khartoum, Sudan's modern capital, for safekeeping. "There's always a danger of robbers coming and taking [them] out, so many of those decorated blocks were in danger."
They found many other decorated blocks as well, Grzymski said. Because they had been re-used in antiquity the blocks were out of order and presented researchers with a giant jigsaw puzzle.
"Ideally, I would like to dismantle this whole wall, this foundation wall, and take out the decorated blocks and see if we would be able reconstruct some other structures from which the blocks came," Grzymski told the Toronto audience.
It's one of many, many, tasks that need to be done in the ancient city. "It's considered one of the largest archaeological sites in Africa," Grzymski said of Meroë. "This site will be worked on for a hundred years perhaps before it's fully explored."
Grzymski is a curator at the Royal Ontario Museum and the symposium was organized by the Society for the Study of Egyptian Antiquities and the museum's Friends of Ancient Egypt group.
"Ideally, I would like to dismantle this whole wall, this foundation wall, and take out the decorated blocks and see if we would be able reconstruct some other structures from which the blocks came," Grzymski told the Toronto audience.
It's one of many, many, tasks that need to be done in the ancient city. "It's considered one of the largest archaeological sites in Africa," Grzymski said of Meroë. "This site will be worked on for a hundred years perhaps before it's fully explored."
Grzymski is a curator at the Royal Ontario Museum and the symposium was organized by the Society for the Study of Egyptian Antiquities and the museum's Friends of Ancient Egypt group.
Follow LiveScience on Twitter @livescience. We're also on Facebook & Google+.

Owen Jarus is a regular contributor to Live Science who writes about archaeology and humans' past. He has also written for The Independent (UK), The Canadian Press (CP) and The Associated Press (AP), among others. Owen has a bachelor of arts degree from the University of Toronto and a journalism degree from Ryerson University.