
Clouds Contributed to Record Greenland Ice Melt
The culprit behind the record-shattering level of ice melting in Greenland in 2012 may have been low, thin clouds, new research suggests.
These novel findings, detailed in the April 4 issue of the journal Nature, may help answer climate mysteries elsewhere in the Arctic, the researchers said.
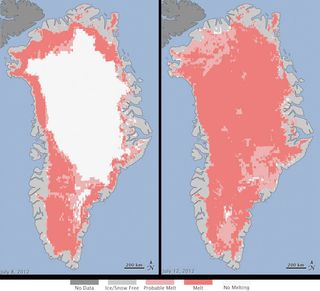
If the sheet of ice covering Greenland were to completely melt, such destruction of 720,000 cubic miles (3 million cubic kilometers) of ice would raise global sea levels by 24 feet (7.3 meters). In summer 2012, Greenland saw an extraordinarily large amount of melting across nearly its entire ice sheet. In fact, it was the largest ice melt seen in Greenland since scientists began tracking melt rates there in 1979. Ice-core records suggest melting events so extreme have only happened once every 150 years or so over the past 4,000 years.
"The July 2012 event was triggered by an influx of unusually warm air, but that was only one factor," said study researcher Dave Turner, a physical scientist at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Severe Storms Laboratory. "We show that low-level clouds were instrumental in pushing temperatures up above freezing."
Thin clouds
Turner and his colleagues discovered the role these clouds played by analyzing temperature data from the ICECAPS experiment run at Summit Station atop the Greenland Ice Sheet at about 10,500 feet (3,200 m) above sea level. Melting occurred even all the way up there on July 11, 2012. [Images of Melt: Earth's Vanishing Ice]
The idea that low clouds might help melt ice might seem mistaken at first, since they usually reflect solar energy back into space. (Cloudy days tend to be cooler than sunny ones.) However, the research team's computer models suggest these clouds can be both thin enough to allow sunlight to pass through to heat the surface and thick enough to trap thermal radiation emitted upward by the surface. (This thermal radiation is a form of light but comes in longer wavelengths than visible light and is invisible to the human eye. The Earth's surface absorbs the sun's rays and then re-emits this thermal radiation.)
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Climate models often underestimate the occurrence of these clouds, thus limiting their ability to predict Arctic climate change and other phenomena. This new research suggests this kind of cloud is present about 30 percent to 50 percent of the time over both Greenland and across the Arctic, said Ralf Bennartz, lead author of the study and an atmospheric physicist at the University of Wisconsin at Madison.
More observations needed
"A very narrow range of cloud thickness allows for amplification of surface warming," Bennartz told OurAmazingPlanet. "This shows how well we have to understand individual components of the climate system, such as clouds, in order to accurately understand the system as a whole."
More observations are key to a better understanding of these components, he added.
"We need to continue detailed observational studies at Summit Station in Greenland in order to better understand processes leading to melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet and help improve the representation of these processes in global climate models," Bennartz said.
Follow OurAmazingPlanet @OAPlanet, Facebook and Google+.Original article at LiveScience's OurAmazingPlanet.

Most Popular


