Fungus Among Us! Body's Microbes Mapped
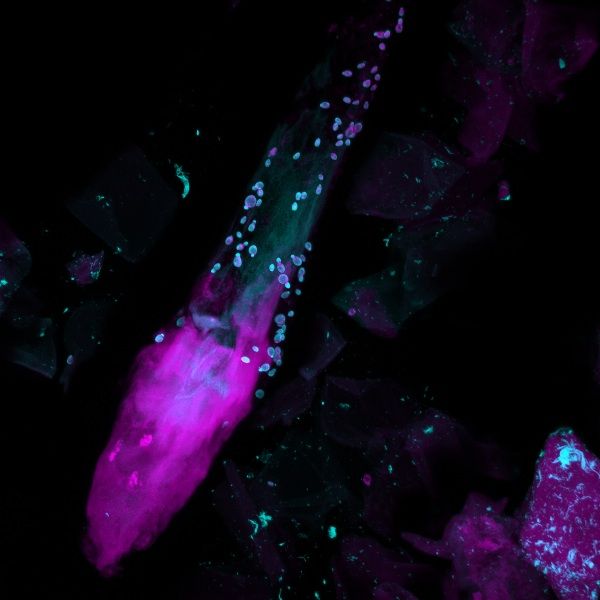
A new map of the fungal species lurking on human skin reveals the most diverse communities can be found on — you guessed it — the bottom of the feet.
Genetic sequencing found the fungal genus Malassezia dominated on most of the core body regions and arms. The heel, toenail and toe web (skin between the toes), by contrast, supported highly varied fungal communities. Imbalances in these populations may lead to athlete's foot and other fungal diseases, the researchers say.
The skin serves as a barrier to pathogenic microorganisms, but is also home to a rich array of harmless microbes. Until now, most efforts to study the skin's microorganisms have focused on bacterial species, but fungi (which are a distinct biological group) form a significant part of these skin communities. [Microscopic Worlds Gallery: Fascinating Fungi]
Feet love fungi
In the study, scientists took skin scrapings from 10 healthy adults at 14 different sites on the body. They sequenced the DNA from the swabs. In addition, the researchers isolated more than 130 fungal strains from the genera Malassezia, Penicillium and Aspergillus, and grew them in the lab.
The genus Malassezia, which may cause dandruff, was the most abundant type of fungus at all 11 core-body and arm sites, results showed. These areas included the inner elbow, palm, space between the eyebrows, back of the head, nostril and forearm, among other spots. Core-body sites, such as the chest and abdomen, had the fewest types of fungi, ranging from two to 10 genera.
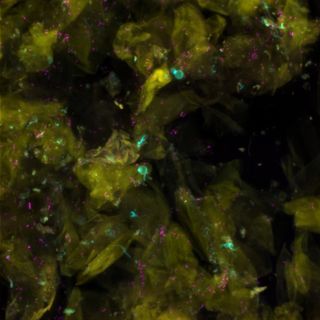
The three foot sites — heel, toenail and toe web — contained much greater fungal diversity, with populations of Malassezia¸ Aspergillus, Cryptococcus, Rhodotorula and Epicoccum, among others. Overall, the heel had the most diverse fungal makeup, with about 80 fungal genera.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
One study participant had an especially diverse array of fungi. This person had taken a course of oral antifungal medication for a toenail infection seven months prior to the study. The unusual fungal diversity suggests that either an imbalance in the fungal community was causing the stubborn toenail infections, or that changes in the microbe composition due to the medication continued even seven months after stopping treatment, the researchers say. The results demonstrate that human skin is capable of harboring a highly varied fungal population.
When fungi go awry
The researchers also sequenced bacteria on the skin. The results confirmed previous findings for skin bacterial makeup in healthy people. In contrast to fungal populations, the most diverse bacterial populations were found on the arms. The person with abnormal fungal diversity appeared to have a normal distribution of bacteria.
The study of the skin's native fungi has important implications for infection and disease. About 20 percent of the study participants showed signs of possible foot fungal infections, and previous studies have shown up to 60 percent of healthy people may harbor such infections.
Fungal infections affect 29 million North Americans. Several factors influence the prevalence of fungal infections, including population and climate. Antifungal medications can have dangerous side effects, and new treatments that target fungal imbalances are needed, the researchers say.
The findings were reported online today (May 22) in the journal Nature.
Follow Tanya Lewis on Twitter and Google+. Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.com.

Most Popular