What are the systems of the body? Fast facts about the human body and how it works
Learn all about the human body's many systems and some of its individual organs, both vital and vestigial.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
The human body is a complex network of systems that work together to keep life-sustaining processes running smoothly. These systems break down food for fuel, clear away waste, repair damaged tissues and DNA, fight infectious germs and monitor the outside world so we can move through it safely.
Many scientists spend their days working to understand how each bodily system performs its jobs, how the systems interact, and what can happen when one or more of them falter. Such malfunctions can stem from aging or disease, for instance, and through medical care, doctors aim to get derailed systems back on track.
Here's a quick rundown of the systems of the human body, its vital organs and its "vestigial" organs, as well as a few fascinating facts about how the body works.
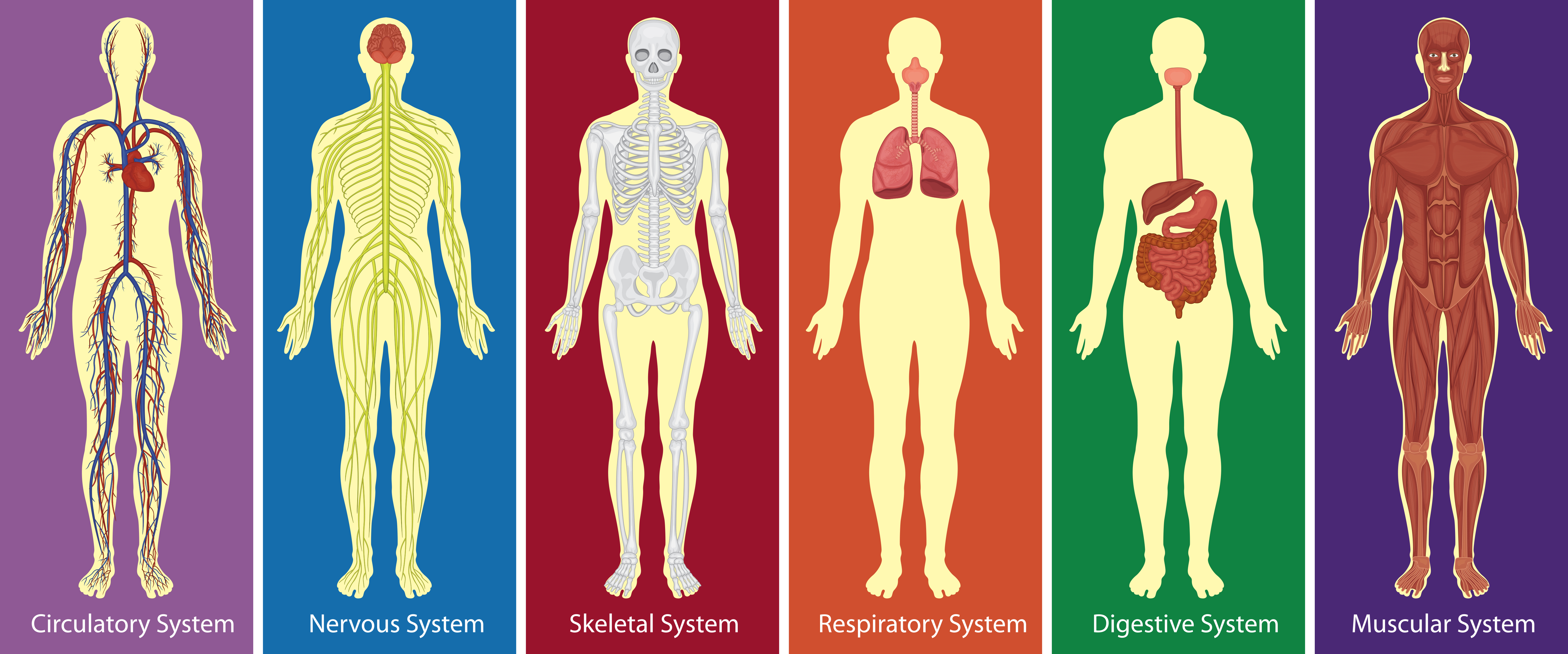
What are the different systems of the human body?
Our bodies consist of a number of biological systems that carry out specific functions necessary for everyday living. Some organs and tissues play roles in multiple systems at once.
Related: Strange, two-faced brain cells confirmed to exist, and they may play a role in schizophrenia
Circulatory: The job of the circulatory system is to move blood, nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide and hormones around the body. It consists of the heart, blood, blood vessels, arteries and veins. According to the Cleveland Clinic, the adult human body's network of blood vessels is more than 60,000 miles (around 100,000 kilometers) long.
Digestive: The digestive system consists of a series of connected organs that together allow the body to break down and absorb nutrients from food and remove waste. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus. The large intestine is home to microorganisms that are collectively called the gut microbiome and influence our health in various ways. The liver and pancreas also have roles in the digestive system because they produce digestive juices filled with enzymes to break down the components of food, such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Endocrine: The endocrine system consists of a network of glands that secrete hormones — long-range chemical messengers that regulate how cells and tissue function — into the blood. These hormones, in turn, travel to different tissues and regulate many bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth and sexual function, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine. For example, the pancreas releases the hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar. Conditions like diabetes and insulin resistance arise from the body having too little insulin or not responding to it adequately.
Related: Meet the 'exclusome': A mini-organ just discovered in cells that defends the genome from attack
Immune: The immune system is the body's defense against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens that may be harmful. Components of the system include the lymph nodes, which contain infection-fighting cells called lymphocytes. These lymphocytes are one of many types of leukocyte, or white blood cell. The immune system also includes the spleen, the bone marrow and a gland called the thymus. The immune system can learn to recognize antigens — proteins on the surface of bacteria, fungi and viruses — and alert the body to their presence. Some immune cells make proteins called antibodies that attach to these antigens and mark invaders for destruction.
Lymphatic: The lymphatic system includes the lymph nodes, lymph ducts and lymph vessels and is considered part of the immune system. Its main job is to make and move lymph, a clear fluid that contains white blood cells. The lymphatic system also removes excess lymph fluid from the body's tissues and returns it to the blood.
Nervous: The nervous system controls both voluntary actions, such as conscious movements, and involuntary actions,like breathing, and it sends signals to and detects signals from different parts of the body. Conscious actions are controlled by the somatic nervous system, while involuntary actions are controlled by the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system dictates whether we're in "rest and digest" or "fight or flight" mode. The nervous system can further be split up into the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, or the nerves connecting the CNS to every other part of the body.
Muscular: The body's muscular system consists of hundreds of muscles that aid movement, blood flow and other bodily functions, according to the Library of Congress. There are three types of muscle: skeletal, which is connected to bone and helps with voluntary movement; smooth, which is found inside organs and helps to move substances through them; and cardiac, which is found in the heart. The body's largest muscle by mass is the gluteus maximus, but the two latissimus dorsi are the largest in terms of surface area.
Related: Why is it harder for some people to build muscle than others?
Reproductive: The reproductive system allows humans to produce offspring. The male reproductive system includes the penis and the testes, which produce sperm. The female reproductive system includes the vagina, uterus and ovaries, which produce eggs. During fertilization, a sperm cell will fuse with an egg cell that, in a successful pregnancy, will then implant in the uterus. The fertilized egg will then mature into what's called a blastocyst, then an embryo and, finally, a fetus. A placenta forms to support this process.

Skeletal: Our bodies are supported by the skeletal system, which contains between 206 and 213 bones in an adult human body, due to slight variations in people's anatomy, according to the medical resource StatPearls. These bones are connected by tissues called tendons, ligaments and cartilage. As infants, humans have about 300 bones, but some fuse together as the child grows. The skeleton not only helps us move but is also involved in the production of blood cells and the storage of calcium. The teeth are also part of the skeletal system, but they aren't considered bones. The smallest bones in the body are found in the ear, and the largest is the femur, or thigh bone, which is also one of the heaviest body parts.
Respiratory: The respiratory system allows us to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide through breathing. It includes the lungs; trachea, or windpipe; and the diaphragm, a muscle that pulls air into and pushes air out of the lungs.
Urinary: The urinary system helps eliminate a waste product called urea, which is produced when certain foods are broken down. The system includes the two kidneys; two ureters, or tubes leaving the kidneys; the bladder; two sphincter muscles; and the urethra. The kidneys filter blood in the body to make urine that then travels down the ureters to the bladder and exits the body through the urethra.
Integumentary: The skin, hair and nails make up the integumentary system. Skin is the body's largest organ. It protects our innards from the outside world, serving as our first defense against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens, for instance. Our skin also helps regulate body temperature and eliminate waste through perspiration, or sweat.
Related: Scientists discover new way humans feel touch
What are the body's vital organs?
Click the purple circles to learn about the body's vital organs, including the brain, lungs, heart, liver and kidneys. They're considered vital because you need a functioning brain, heart, liver, at least one kidney and at least one lung to survive. That said, there are medical devices and treatments that can make up for a loss of function in these organs, at least temporarily — for example, ECMO machines can do the work of the heart and lungs, and dialysis can filter the blood of people with kidney failure.
Fast facts
- The average adult male body contains about 36 trillion cells, the average adult female body contains 28 trillion cells and a 10-year-old has about 17 trillion.
- It's often said that there are 78 organs in the human body, but the number actually differs depending on whom you ask.
- There's a popular idea that the body replaces itself every seven years. But that's not really true, because tissues renew themselves at different rates.
- Oxygen is the most common element in the human body, followed by carbon.
- The average adult body contains about 1.2 to 1.5 gallons (4.5 to 5.5 liters) of blood.
- Humans' average body temperature has fallen slightly over time, so it's no longer 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (37 degrees Celsius).
- The most detailed map of the human brain to date contains more than 3,300 types of brain cells.
What are vestigial organs?
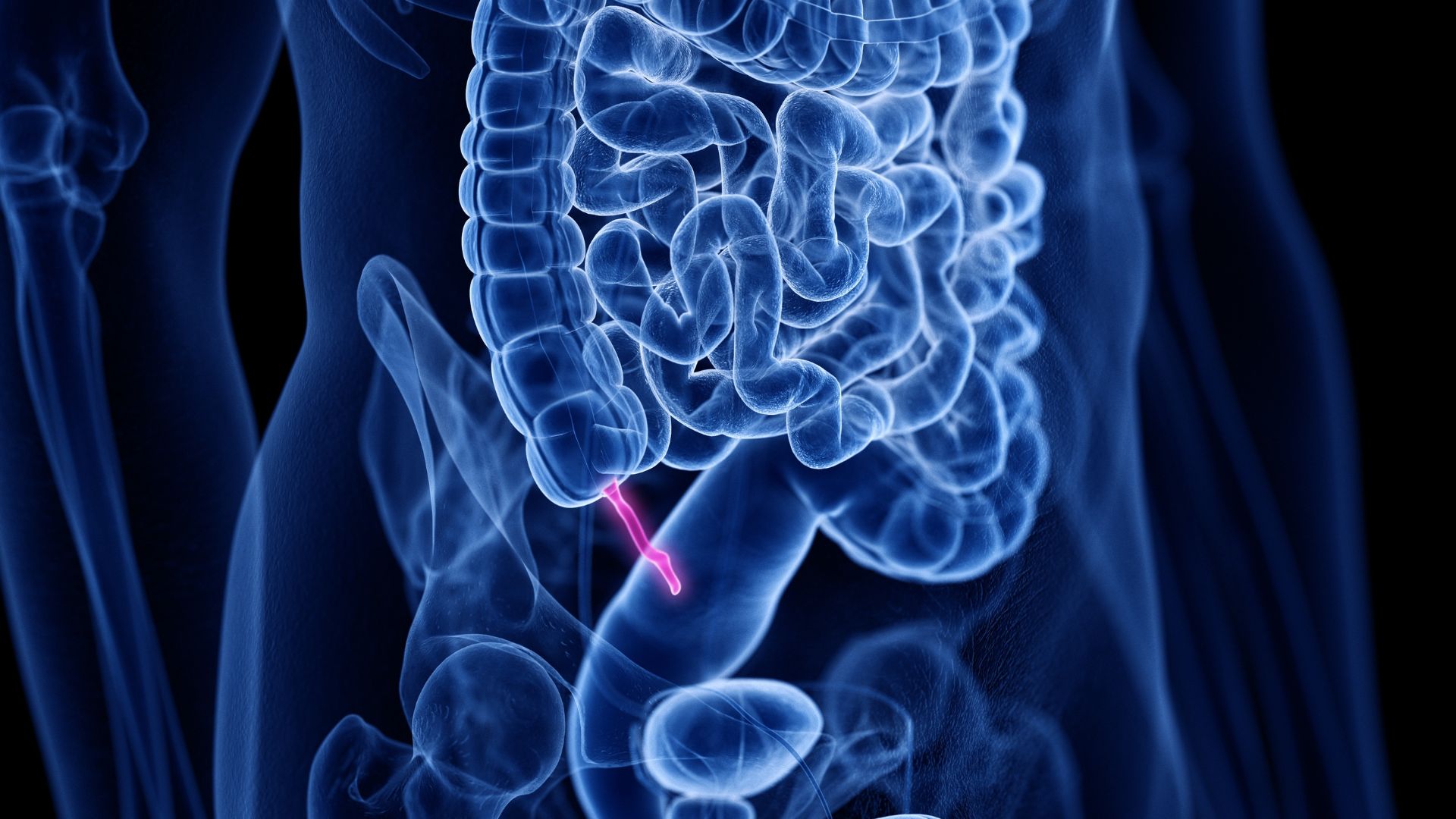
There are arguably some parts of the human body that don't serve any useful purpose, such as the male nipple. That said, the usefulness of some organs is still up for debate, as scientists have often judged the worth of body parts before discovering their purposes.
Broadly speaking, vestigial body parts are defined as those that have lost their original physiological significance to humans over the course of evolutionary history. The idea is that, while we inherited them from an ancient ancestor, we could really do without them in the modern day.
Wisdom teeth are held up as one example of a vestigial body part, as the modern human jaw is often too small to accommodate a third set of molars. Some people also carry remnants of a vomeronasal organ that is largely thought to be nonfunctional in humans; animals use equivalent organs to detect each other's pheromones.
Some scientists consider the human tailbone, or coccyx, vestigial because it's no longer a full-blown tail. But it's far from useless, as it still anchors many muscles, ligaments and tendons. And the appendix has gotten a bad rap for supposedly being both vestigial and useless, but more recently, scientists have uncovered possible functions for the long-maligned body part.
Ever wonder why some people build muscle more easily than others or why freckles come out in the sun? Send us your questions about how the human body works to community@livescience.com with the subject line "Health Desk Q," and you may see your question answered on the website!
Editor's note: This page was last updated on April 5, 2024.

Rachael is a Live Science contributor, and was a former channel editor and senior writer for Live Science between 2010 and 2022. She has a master's degree in journalism from New York University's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program. She also holds a B.S. in molecular biology and an M.S. in biology from the University of California, San Diego. Her work has appeared in Scienceline, The Washington Post and Scientific American.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus