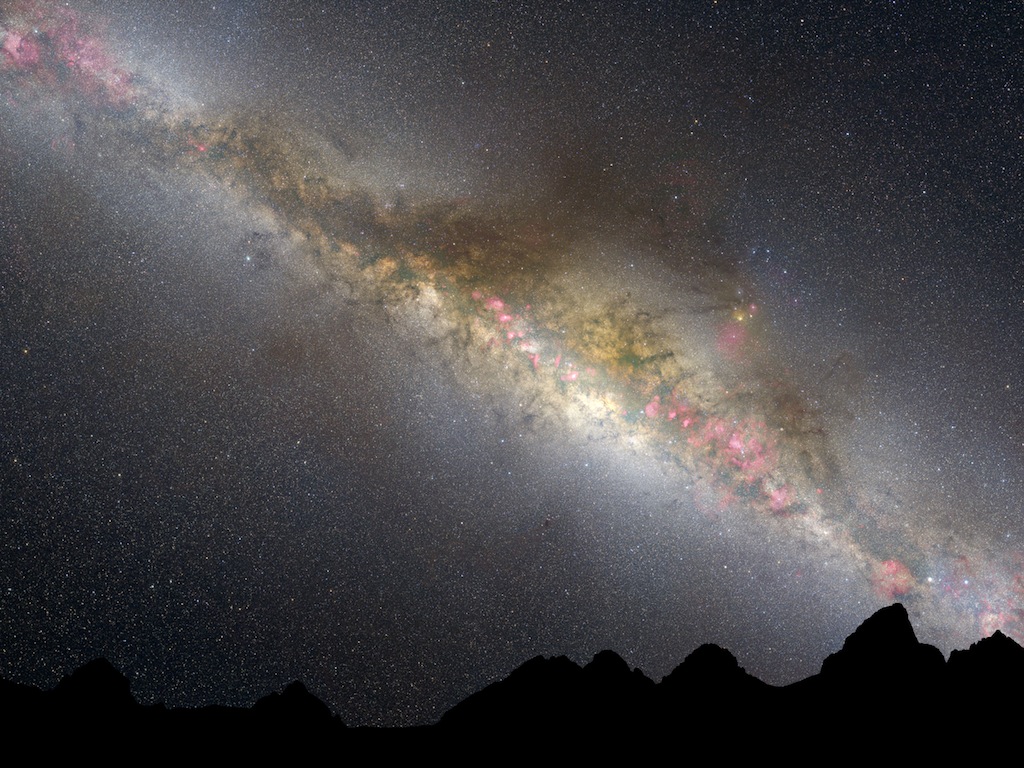
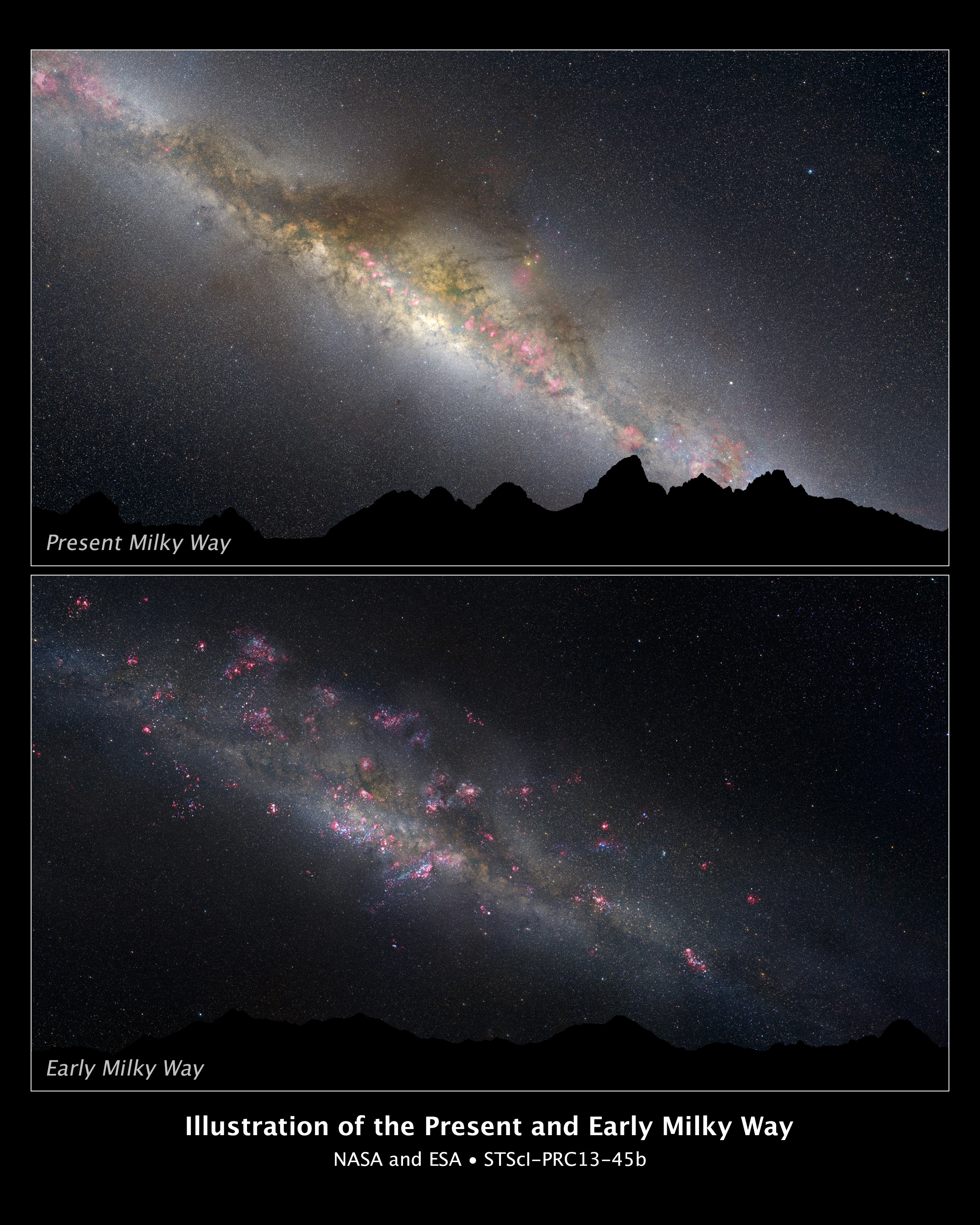
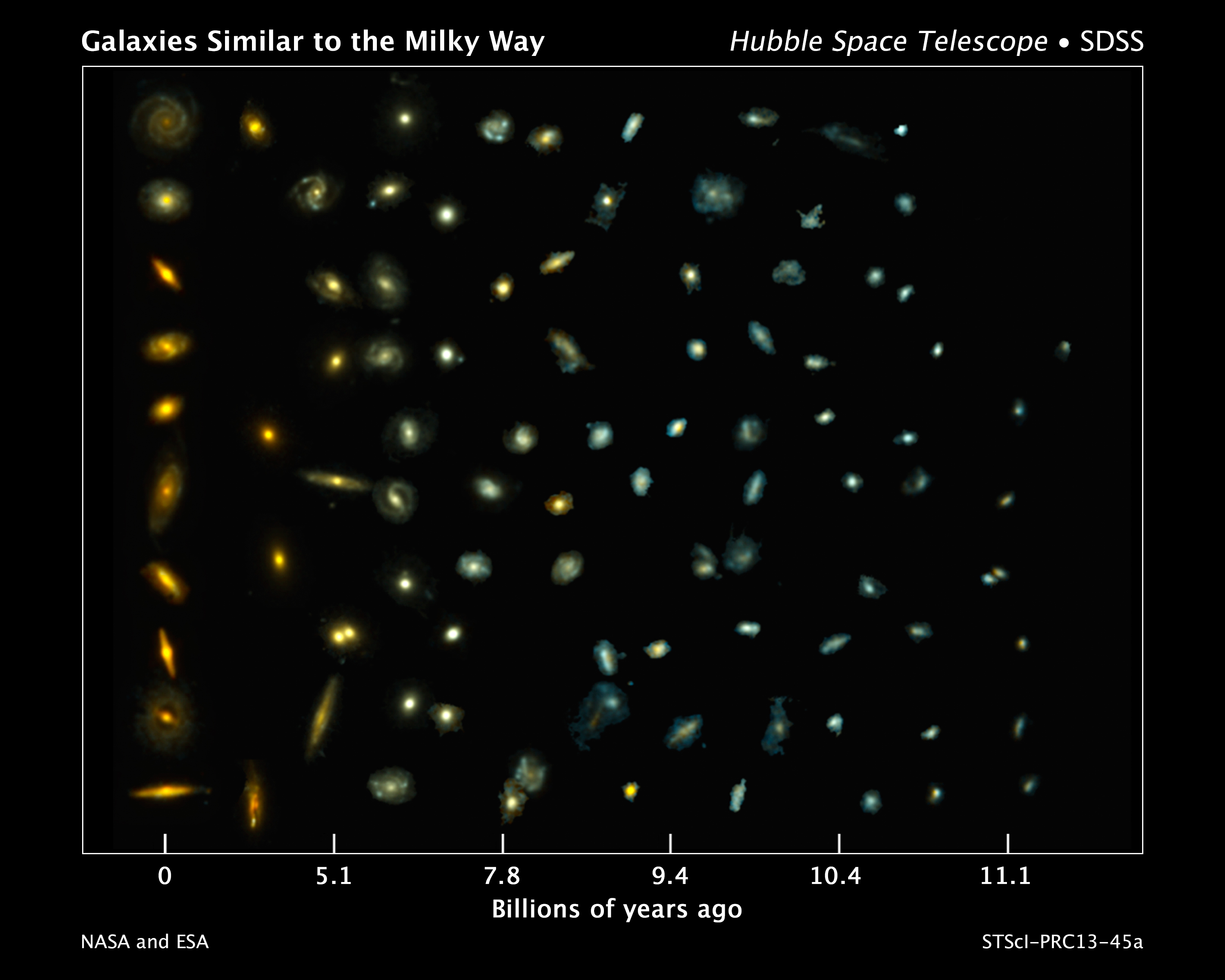
Astronomers have pieced together a detailed picture of how our Milky Way galaxy came together, using Hubble Space Telescope photos of 400 similar galaxies at various stages of evolution.
"For the first time we have direct images of what the Milky Way looked like in the past," study co-leader Pieter van Dokkum, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., said in a statement.
"Of course, we can't see the Milky Way itself in the past. We selected galaxies billions of light-years away that will evolve into galaxies like the Milky Way," van Dokkum added. "By tracing the Milky Way's siblings, we find that our galaxy built up 90 percent of its stars between 11 billion and 7 billion years ago, which is something that has not been measured directly before." [Stunning Photos of Our Milky Way Galaxy]
Hubble's images suggest that the Milky Way started out as a faint blue object with lots of gas, clouds of which eventually collapsed to form stars. At the time of peak star formation throughout the universe — about 4 billion years after the Big Bang— galaxies like the Milky Way were pumping out about 15 new stars per year, researchers said. (For comparison, the Milky Way produces just one star a year these days.)
The data further reveal that the Milky Way's flat disk and central bulge formed at about the same time, scientists said.
"You can see that these galaxies are fluffy and spread out," study co-leader Shannon Patel, of Leiden University in the Netherlands, said in a statement. "There is no evidence of a bulge without a disk, around which the disk formed later."
That's in contrast to huge elliptical galaxies, in which the bulge appears first, team members added. Further, galaxy mergers are thought to be important in the evolution of ellipticals, while spirals like the Milky Way likely grow primarily by star formation.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"These observations show that there are at least two galaxy-formation tracks," van Dokkum said. "Massive ellipticals form a very dense core early in the universe, including a black hole, presumably, and the rest of the galaxy slowly accretes around it, fueled by mergers with other galaxies. But from our survey we find that galaxies like our Milky Way show a different, more uniform path of growing into the majestic spirals we see today."
The researchers incorporated data from three different Hubble Space Telescope observing programs — the 3D-HST survey, the Cosmic Assembly Near-infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey and the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. Team members measured each of the 400 galaxies' distance and size, which they calculated using information about its brightness and color.
Part of the team's findings were published July 10 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, while a second paper appears in the Nov. 11 online edition of The Astrophysical Journal.