Man Develops Rare Reaction to Spider Bite

The strange rash a man in southern France developed on his arm, torso and thighs turned out to be a serious reaction to a spider bite from 10 days before, according to a new report of his case.
The 66-year-old patient first went to the hospital in Nice two days after his spider bite when he developed a fever and suffered from fatigue and lack of appetite. But doctors didn't find anything unusual when examining him, nor did they find the black, necrotic skin lesions typically seen in spider bites.
The man didn’t get better, and developed pinhead-sized bumps on his forearms. The bumps spread to cover most of his body, and the doctors diagnosed him with a condition called acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP).
AGEP is usually induced by taking antibiotics. However, "this was not the case in our patient, who received only acetaminophen, and had not shown prior reaction to this medication," the doctors wrote in the case report. [8 Strange Signs You're Having an Allergic Reaction]
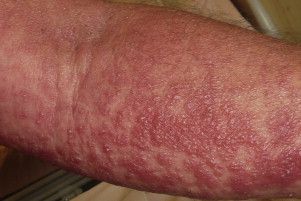
The patient also ran a high fever, and suffered from burning sensations and muscle pain.
Doctors worked to figure out what was wrong. Lab tests failed to find a viral disease that could explain the symptoms, but the results did show the man's kidney function was impaired. Further tests showed the patient's blood vessels were inflamed and necrotizing.
He was suffering from periarteritis nodosa (PAN), a serious blood vessel disease in which small arteries become swollen and damaged, according to the report.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The doctors realized that conditions similar to PAN have been seen in animals injected with the venom of brown recluse spider, the report said. Similarly, a few case reports have described people developing AGEP after a brown recluse spider bite.
However, there hadn't been a report of a patient developing both PAN and AGEP after a spider bite.
"To our knowledge, this is the first description of a case associating PAN-like signs and AGEP following a spider-bite," the doctors said.
Doctors treated the patient with high doses of oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and his condition rapidly improved. In five days, the rash disappeared and the man fully recovered, according to the report, published last month in the journal La Presse Médicale.
Email Bahar Gholipour. Follow us @LiveScience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on Live Science.

Most Popular

