Wearable Goose Bump Sensor May Detect Some Emotions
Could a tiny, flexible patch on your skin read your emotions and change things in your environment accordingly? Not yet, but it might know when you get the chills.
Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) in South Korea have developed a wearable sensor that can detect goose bumps, which are caused by sudden changes in body temperature or, sometimes, emotional states.
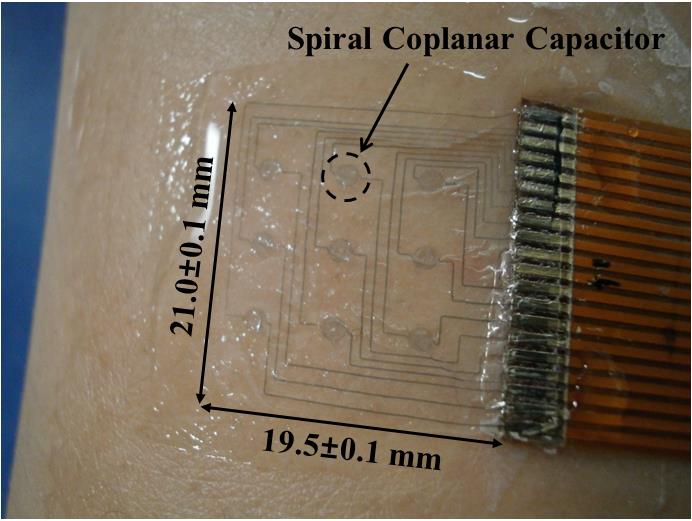
The flexible, electronic sensor is a small square patch, measuring less than 1 inch (2 centimeters) in height and width; it's made of conductive polymer material with embedded spiral-shape capacitors.
Goose bumps can change the shape of the patch, causing alterations in its capacitance, which is the patch's ability to store an electrical charge. By analyzing those alterations, the researchers can determine the height of the goose bumps and how long they persist. The scientists described their work Tuesday (June 24) in the journal Applied Physics Letters, a publication of the American Institute of Physics.
To test the device, the researchers attached the sensor to the inside of a person's arm and had him grab ice cubes to induce a sudden cold shock. The resulting goose bumps, which deformed the sensor's surface, caused the capacitance to notably decrease, the researchers said. [The 7 Biggest Mysteries of the Human Body]
The researcher said they plan to miniaturize the part of the device that processes electrical signals, so that it can be mounted on the skin along with the small patch.
It's not clear exactly how much goose bumps can tell about a person's emotional states, but they are often signs that someone is experiencing intense emotions. For example, goose bumps can happen involuntarily with feelings of extreme fear, shock and euphoria.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Beyond goose bumps, many emotional states have been shown to have other subtle, but measurable effects on the skin as well. For example, fear or anxiety can induce a slight increase in sweating, which would also change the skin's conductance. Devices to detect these changes exist, but are used primarily in science experiments.
But researchers say someday the technology could be integrated in wearable devices to detect users' emotions and relay them in real-time, for example, to advertisers or personalized music stations.
"In the future, human emotions will be regarded like any typical biometric information, including body temperature or blood pressure," study researcher Young-Ho Cho said in a statement.
Email Bahar Gholipour. Follow us @LiveScience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on Live Science.










