Massive 5,000-Year-Old Stone Monument Revealed in Israel
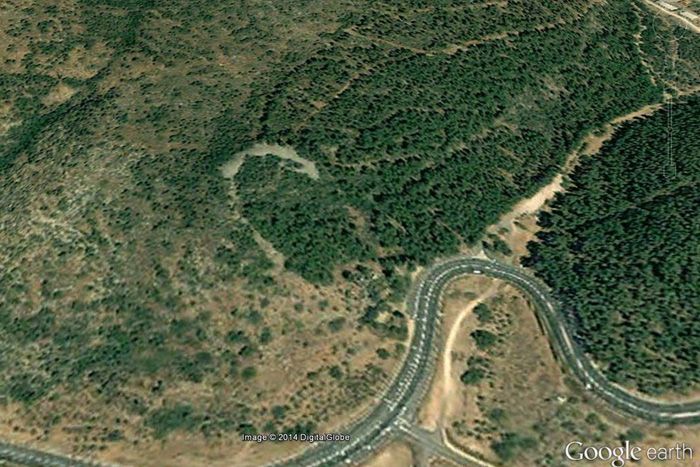

A lunar-crescent-shaped stone monument that dates back around 5,000 years has been identified in Israel.
Located about 8 miles (13 kilometers) northwest of the Sea of Galilee, the structure is massive — its volume is about 14,000 cubic meters (almost 500,000 cubic feet) and it has a length of about 150 meters (492 feet), making it longer than an American football field. Pottery excavated at the structure indicates the monument dates to between 3050 B.C. and 2650 B.C., meaning it is likely older than the pyramids of Egypt. It was also built before much of Stonehenge was constructed.
Archaeologists previously thought the structure was part of a city wall, but recent work carried out by Ido Wachtel, a doctoral student at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, indicates there is no city beside it and that the structure is a standing monument.
"The proposed interpretation for the site is that it constituted a prominent landmark in its natural landscape, serving to mark possession and to assert authority and rights over natural resources by a local rural or pastoral population," Wachtel wrote in the summary of a presentation given recently at the International Congress on the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East. [See Photos of the Crescent-Shaped Monument]
The structure's crescent shape stood out in the landscape, Wachtel told Live Science in an email. The shape may have had symbolic importance, as the lunar crescent is a symbol of an ancient Mesopotamian moon god named Sin, Wachtel said.
An ancient town called Bet Yerah (which translates to "house of the moon god") is located only a day's walk from the crescent-shaped monument Wachtel noted. As such, the monument may have helped mark the town's borders. While the monument is located within walking range of the city it is too far away to be an effective fortification.
Massive structure
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The structure is about 150 meters (492 feet) long and 20 m (66 feet) wide at its base, and is preserved to a height of 7 m (23 feet), Wachtel's research found.
"The estimation of working days invested in the construction [of] the site is between 35,000 days in the lower estimate [and] 50,000 in the higher," Wachtel said in the email.
If the lower estimate is correct, it means a team of 200 ancient workers would have needed more than five months to construct the monument, a task that would be difficult for people who depended on crops for their livelihood. "We need to remember that people were [obligated] most of the year to agriculture," Wachtel said.
Bet Yerah
At the time this monument was built, the site of Bet Yerah was located only 18 miles (29 km) away.
Bet Yerah was a large town with a grid plan and fortification system, according to a study detailed in 2012 in the Journal of Near Eastern Archaeology. Its inhabitants traded with the early kings of Egypt, as seen from several artifacts, including a jug with a hieroglyphic inscription.
The name Bet Yerah indicates that it was associated with the moon god. However, it's uncertain whether the town actually bore this name 5,000 years ago. In the 2012 journal article, researchers said the name "Bet Yerah" was recorded in 1,500-year-old Jewish rabbinic texts and may date back much earlier.
Megalithic landscape
Other large rock structures have been found not far from the crescent-shaped monument. One structure, called Rujum el-Hiri, isin the Golan Heights (an area to the east of the Sea of Galilee) and has four circles with a rock cairn at its center. The date of this structure is a matter of debate; recent research by Mike Freikman, an archaeologist with the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, suggests it may predate the crescent-shaped structure by several centuries.
Another stone monument, a giant cairn that weighs more than 60,000 tons, was discovered recently beneath the waters of the Sea of Galilee. Its date is unknown, but like the crescent-shaped structure, it is located close to Bet Yerah.
Wachtel's work at the crescent-shaped monument was conducted as part of his master's thesis.Today, people living in the area call the monument by its Arabic name, Rujum en-Nabi Shua'ayb, and it is sometimes referred to as the "Jethro Cairn," a reference to the Druze prophet Jethro, who plays an important role in local folklore.
Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on Live Science.

Owen Jarus is a regular contributor to Live Science who writes about archaeology and humans' past. He has also written for The Independent (UK), The Canadian Press (CP) and The Associated Press (AP), among others. Owen has a bachelor of arts degree from the University of Toronto and a journalism degree from Ryerson University.