Ancient Reptile Dined on Dinosaurs
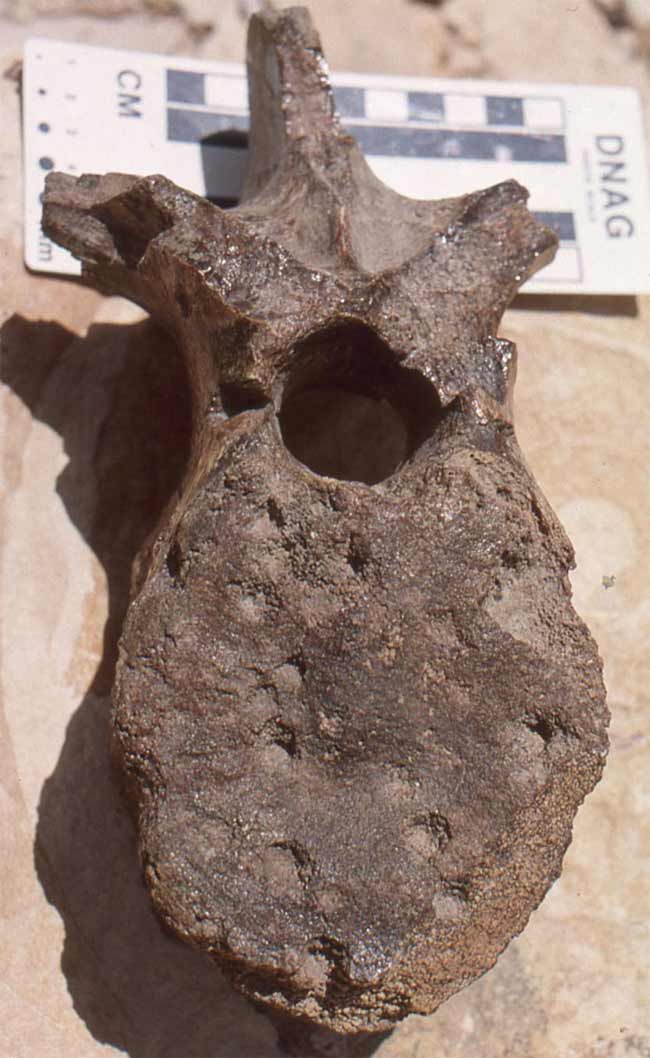

An ancient crocodile-like animal, about twice the length of an SUV, probably dined on sea turtles and dinosaurs, suggests bite-mark evidence and dung droppings.
The giant reptile called Deinosuchus was up to 29 feet long (nearly 9 meters), and likely adorned Georgia's shores, in the United States, about 79 million years ago, much as modern crocodiles dot the shores of the West Nile, the researchers say.
While the animals weren't true crocodiles, they were members of the crocodilian group and more closely related to alligators than crocs (alligators and crocodiles are closely related but distinct species). Either way, the new findings show the beast was tough, taking down dinosaurs its own size.
"We're sure (Deinosuchus) ate a lot of sea turtles, but it's evident it liked to prey on dinosaurs too," said David Schwimmer, a Columbus State paleontologist, who recently completed two studies on the giant crocodile with one of his students, Samantha Harrell.
The team analyzed various specimens of dinosaurs and sea turtles, along with the crocodilian's teeth, which were typically broken at the tips. Schwimmer said the breakage suggests a diet that included hard foods, like bone material.
"These things had very thick blunt teeth, built like little hub caps, especially the back teeth," Schwimmer said.
Several dinosaur bones showing the distinctive bite marks, including the tailbones of duck-billed dinosaurs found in the western United States, and the leg bone of a small carnivorous dinosaur, whose remains are stored at a New Jersey museum.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"The [leg] bone was so chewed that it was distorted, and it looked like a chew toy, like a dog had been working on it," Schwimmer told LiveScience. "It was covered with crocodilian bites."
Similar marks were found on turtle shells.
Fossilized feces were also collected along the banks of the Hannahatchee Creek in Stewart County, a major tributary of the Chattahoochee River, in Georgia. Poop analyses provided some support for their predator-prey conclusions. The so-called coprolites were each about a half-foot long (15 centimeters) and 2 to 3 inches (5 to 7.6 cm) in diameter, or "about the size we'd expect to come out of one of these animals," Schwimmer said, referring to the crocodilians.
The feces showed no sign of bones, which is what would be expected even if the animals were chowing on dinosaur bones. "Crocodilians have very strong digestive acids and bones get dissolved," he said.
Within the coprolites, Harrell found sand and lots of shell fragments. The results indicated the ancient crocs lived in a shallow, warm-water environment, perhaps near the mouth of a river where there may have been an abundance of sea turtles.
Jeanna Bryner is managing editor of Scientific American. Previously she was editor in chief of Live Science and, prior to that, an editor at Scholastic's Science World magazine. Bryner has an English degree from Salisbury University, a master's degree in biogeochemistry and environmental sciences from the University of Maryland and a graduate science journalism degree from New York University. She has worked as a biologist in Florida, where she monitored wetlands and did field surveys for endangered species, including the gorgeous Florida Scrub Jay. She also received an ocean sciences journalism fellowship from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. She is a firm believer that science is for everyone and that just about everything can be viewed through the lens of science.