Rosy Complexion Is Sign of Health
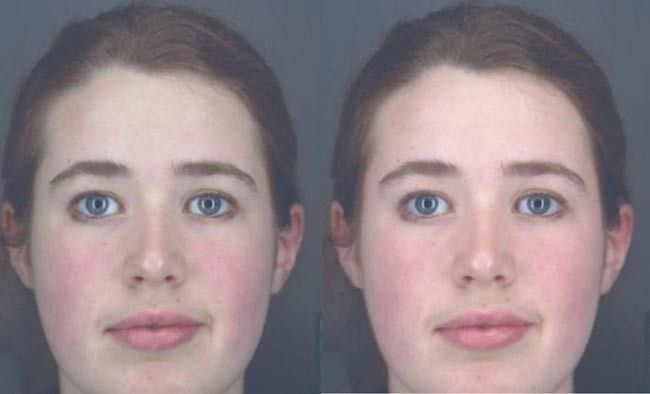
Don't blush when you read this … or maybe do: A new study finds that we perceive people with rosier complexions as being healthier, and therefore more attractive.
Perceived healthiness is a strong mate attractor in the animal kingdom and can be signaled to potential paramours by a variety of physical traits.
Scientists have known that several monkey species (some of our closest evolutionary relatives) use redness in their faces or other skin to advertise their health status to attract mates.
A team of researchers at the University of St Andrews in Scotland wanted to discover if similar mate-attracting mechanisms were at work in humans.
They did this by first measuring how skin color varies with the amount of blood present and with the oxygen in the blood.
These measurements were used with computer graphics to allow research participants — all college-aged — to change the color of the faces in photographs of other young people to look as healthy as possible. The team found that, for all faces, participants added more oxygen-rich blood color to improve the healthy appearance.
"Our skin contains many tiny blood vessels that carry blood laden with oxygen to the skin cells, allowing them to 'breathe,' and allowing us to lose heat during exercise," said lead researcher Ian Stephen. "People who are physically fit or have higher levels of sex hormones have more of these blood vessels and flush easier than people who are unhealthy, unfit, elderly or smokers. Physically fit people also have more oxygen in their blood than people who are unfit or have heart or lung illnesses."
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
A study detailed in a December issue of the journal Psychological Science demonstrated that men's faces tend to be redder, while women's tend to have a greener tint.
But faces can only get so red before they are judged to be unhealthy again, which researchers said could be the result of having the wrong kind of blood circulating through the skin.
"It's not just the amount of blood that's important; it's the type of blood that determines healthy looks," said study team member Dave Perrett. "Our evaluators all thought that bright red blood with lots of oxygen looked healthier than darker, slightly bluer blood with lower oxygen levels. It is remarkable is that people can see this subtle difference."
The research, detailed in the April 1 edition of the online journal PLoS One, shows that humans do indeed use the color of a person's skin to judge their healthiness, and perhaps by extension, attractiveness.
"Since your attractiveness relies upon how healthy you look, you might be able to make yourself more attractive by being kind to your heart and lungs in doing more exercise or quitting smoking," Stephen said.
The study was funded by BBSRC and Unilever Research.
- Video – Sex and the Senses
- The Sex Quiz: Myths, Taboos, and Bizarre Facts
- Men Are Red-Faced, Women Greenish
Most Popular
