Science News: Recent scientific discoveries and expert analysis
Read the latest science news and recent scientific discoveries on Live Science, where we've been reporting on groundbreaking advances for over 20 years. Our expert editors, writers and contributors are ready to guide you through today's most important breakthroughs in science with expert analysis, in-depth explainers and interesting articles, covering everything from space, technology, health, animals, planet Earth, and much more.

Explainers | Everything you need to know about the science news that matters.

Science Spotlight | Shining a light on new science transforming our world.
Latest news

AI is getting better and better at generating faces — but you can train to spot the fakes
By Sophie Berdugo published
Even the most skilled face recognizers are duped by AI-generated faces, a new study finds. But they can improve with training.

Spinosaurus relative longer than a pickup truck stalked Thailand's rivers 125 million years ago
By Patrick Pester published
A large fish-eating dinosaur died beside a river 125 million years ago in Cretaceous Thailand. Now, the remains of this ancient predator are helping researchers better understand Asia's enigmatic spinosaurids.

New electrochemical method splits water with electricity to produce hydrogen fuel — and cuts energy costs in the process
By Mason Wakley published
Scientists adapted a method that can produce double the amount of hydrogen when splitting water molecules with electricity.

Uranus and Neptune may be 'rock giants,' not 'ice giants,' new model of their cores suggests
By Mason Wakley published
A new computational model suggests that Uranus' and Neptune's cores may be less icy than their "ice giant" nickname suggests.
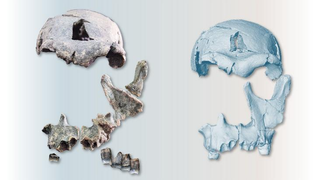
1.5 million-year-old Homo erectus face was just reconstructed — and its mix of old and new traits is complicating the picture of human evolution
By Skyler Ware published
A never-before-seen Homo erectus face reveals a complex picture of early human evolution.

Flat-headed cat not seen in Thailand for almost 30 years is rediscovered
By Patrick Pester published
Conservationists are celebrating the rediscovery of flat-headed cats in Thailand after camera traps recorded the endangered feline for the first time in almost 30 years.

Last of its kind dodo relative spotted in a remote Samoan rainforest
By Whitney Isenhower published
The manumea, a critically endangered ground pigeon and one of the closest living dodo relatives, has been spotted multiple times in a remote Samoan rainforest.

'What the heck is this?' James Webb telescope spots inexplicable planet with diamonds and soot in its atmosphere
By Elizabeth Howell published
Scientists using the James Webb telescope observed a distant exoplanet with an atmosphere of soot and diamonds, challenging all explanations.

First-ever 'superkilonova' double star explosion puzzles astronomers
By Sharmila Kuthunur published
A double explosion, in which a dying star split, then recombined, may be a long-hypothesized but never-before-seen "superkilonova."

'It won’t be so much a ghost town as a zombie apocalypse': How AI might forever change how we use the internet
By Roland Moore-Colyer published
AI slop, chatbots and agentic AI are changing the internet, and could transform it beyond recognition, experts say.
New tests could nearly halve the rate of late-stage cancers, some scientists say — is that true?
By RJ Mackenzie published
Blood tests that look for over a dozen cancers are being developed. But how soon will they help patients?

Earth's seasons vary wildly, even at the same latitude, new research finds
By Skyler Ware published
Earth's seasons look very different at locations not far from each other, 20 years' worth of satellite data reveals.

18,000 years ago, ice age humans built dwellings out of mammoth bones in Ukraine
By Owen Jarus published
Some people in Ukraine weathered the harshest moments of the last ice age by creating shelters made partly of mammoth bones and tusks.

Tiny implant 'speaks' to the brain with LED light
By Payal Dhar published
By directly communicating with the brain, a new wireless device could someday help restore lost senses or manage pain without medications, its developers say.

Cats meow more at men to get their attention, study suggests
By James Price published
A small study reveals that cats greet male owners more vocally than female ones. But the findings could be a result of cultural norms among the participants, rather than a universal cat behavior, scientists say.

NASA spacecraft takes milestone 100,000th image of Mars (photo)
By Brandon Specktor published
NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft has just taken its milestone 100,000th photo of the Red Planet using its high-definition camera. It reveals a dark region of moving sand dunes.

'A huge surprise': 1,500-year-old church found next to Zoroastrianism place of worship in Iraq
By Tom Metcalfe published
A 2,000-year-old palace in the Republic of Georgia and a 1,500-year-old church in Iraq suggest Zoroastrians coexisted with people of other religions.

Graphene supercapacitor breakthrough could boost energy storage in future EVs and other household devices
By Alan Bradley published
A new material called multiscale reduced graphene oxide could mean faster charging and power delivery than traditional batteries allow.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.