Top 10 Ways to Destroy Earth
Not So Easy

Destroying the Earth is harder than you may have been led to believe.
You've seen the action movies where the bad guy threatens to destroy the Earth. You've heard people on the news claiming that the next nuclear war or cutting down rainforests or persisting in releasing hideous quantities of pollution into the atmosphere threatens to end the world.
Fools.
The Earth was built to last. It is a 4,550,000,000-year-old, 5,973,600,000,000,000,000,000-tonne ball of iron. It has taken more devastating asteroid hits in its lifetime than you've had hot dinners, and lo, it still orbits merrily.
So my first piece of advice to you, dear would-be Earth-destroyer: Do not think this will be easy.
( Editor's Note: This presentation was first published by Sam Hughes on his own website. Hughes' version is a living document that he updates as new information becomes available. This adapted version on LiveScience is presented with permission.)
Total existence failure

You will need: nothing
Method: No method. Simply sit back and twiddle your thumbs as, completely by chance, all 200,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 atoms making up the planet Earth suddenly, simultaneously and spontaneously cease to exist. Note: The odds against this actually ever occurring are considerably greater than a googolplex to one. Failing this, some kind of arcane (read: scientifically laughable) probability-manipulation device may be employed.
Utter, utter rubbish.
Gobbled up by strangelets

You will need: a stable strangelet
Method: Hijack control of the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider in Brookhaven National Laboratory, Long Island, N.Y. Use the RHIC to create and maintain a stable strangelet. Keep it stable for as long as it takes to absorb the entire Earth into a mass of strange quarks. Keeping the strangelet stable is incredibly difficult once it has absorbed the stabilizing machinery, but creative solutions may be possible.
A while back, there was some media hoo-hah about the possibility of this actually happening at the RHIC, but in actuality the chances of a stable strangelet forming are pretty much zero.
Earth's final resting place: a huge glob of strange matter.
Sucked into microscopic black hole

You will need: a microscopic black hole. Note that black holes are not eternal, they evaporate due to Hawking radiation. For your average black hole this takes an unimaginable amount of time, but for really small ones it could happen almost instantaneously, as evaporation time is dependent on mass. Therefore you microscopic black hole must have greater than a certain threshold mass, roughly equal to the mass of Mount Everest. Creating a microscopic black hole is tricky, since one needs a reasonable amount of neutronium, but may possibly be achievable by jamming large numbers of atomic nuclei together until they stick. This is left as an exercise to the reader.
Method: simply place your black hole on the surface of the Earth and wait. Black holes are of such high density that they pass through ordinary matter like a stone through the air. The black hole will plummet through the ground, eating its way to the center of the Earth and all the way through to the other side: then, it'll oscillate back, over and over like a matter-absorbing pendulum. Eventually it will come to rest at the core, having absorbed enough matter to slow it down. Then you just need to wait, while it sits and consumes matter until the whole Earth is gone.
Highly, highly unlikely. But not impossible.
Earth's final resting place: a singularity of almost zero size, which will then proceed to happily orbit the Sun as normal.
Source: "The Dark Side Of The Sun," by Terry Pratchett. It is true that the microscopic black hole idea is an age-old science fiction mainstay which predates Pratchett by a long time, he was my original source for the idea, so that's what I'm putting.
Blown up by matter / antimatter reaction

You will need: 2,500,000,000,000 tons of antimatter Antimatter - the most explosive substance possible - can be manufactured in small quantities using any large particle accelerator, but this will take some considerable time to produce the required amounts. If you can create the appropriate machinery, it may be possible - and much easier - simply to "flip" 2.5 trillion tons of matter through a fourth dimension, turning it all to antimatter at once.
Method: This method involves detonating a bomb so big that it blasts the Earth to pieces.
How hard is that? The gravitational binding energy of a planet of mass M and radius R is - if you do the lengthy calculations — given by the formula E=(3/5)GM^2/R. For Earth, that works out to roughly 224,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 Joules. The Sun takes nearly a WEEK to output that much energy. Think about THAT.
To liberate that much energy requires the complete annihilation of around 2,500,000,000,000 tonnes of antimatter. That's assuming zero energy loss to heat and radiation, which is unlikely to be the case in reality: You'll probably need to up the dose by at least a factor of ten. Once you've generated your antimatter, probably in space, just launch it en masse towards Earth. The resulting release of energy (obeying Einstein's famous mass-energy equation, E=mc^2) should be sufficient to split the Earth into a thousand pieces.
Earth's final resting place: A second asteroid belt around the sun.
Earliest feasible completion date: A.D. 2500. Of course, if it does prove possible to manufacture antimatter in the sufficiently large quantities you require - which is not necessarily the case - then smaller antimatter bombs will be around long before then.
Destroyed by vacuum energy detonation

You will need: a light bulb
Method: This is a fun one. Contemporary scientific theories tell us that what we may see as vacuum is only vacuum on average, and actually thriving with vast amounts of particles and antiparticles constantly appearing and then annihilating each other. It also suggests that the volume of space enclosed by a light bulb contains enough vacuum energy to boil every ocean in the world. Therefore, vacuum energy could prove to be the most abundant energy source of any kind. Which is where you come in. All you need to do is figure out how to extract this energy and harness it in some kind of power plant — this can easily be done without arousing too much suspicion — then surreptitiously allow the reaction to run out of control. The resulting release of energy would easily be enough to annihilate all of planet Earth and probably the sun too. [Wacky Physics: The Coolest Little Particles in Nature]
Slightly possible.
Earth's final resting place: a rapidly expanding cloud of particles of varying size.
Earliest feasible completion date: A.D. 2060 or so.
Sucked into a giant black hole

You will need: a black hole, extremely powerful rocket engines, and, optionally, a large rocky planetary body. The nearest black hole to our planet is 1,600 light-years from Earth in the direction of Sagittarius, orbiting V4641.
Method: After locating your black hole, you need get it and the Earth together. This is likely to be the most time-consuming part of this plan. There are two methods, moving Earth or moving the black hole, though for best results you'd most likely move both at once.
Very difficult, but definitely possible.
Earth's final resting place: part of the mass of the black hole.
Earliest feasible completion date: I do not expect the necessary technology to be available until AD 3000, and add at least 800 years for travel time. (That's in an external observer's frame of reference and assuming you move both the Earth and the black hole at the same time.)
Sources: "The Hitch Hiker's Guide To The Galaxy," by Douglas Adams (Image above shows a simulation of a gas cloud about to get gobbled up by a supermassive black hole.)
Meticulously and systematically deconstructed
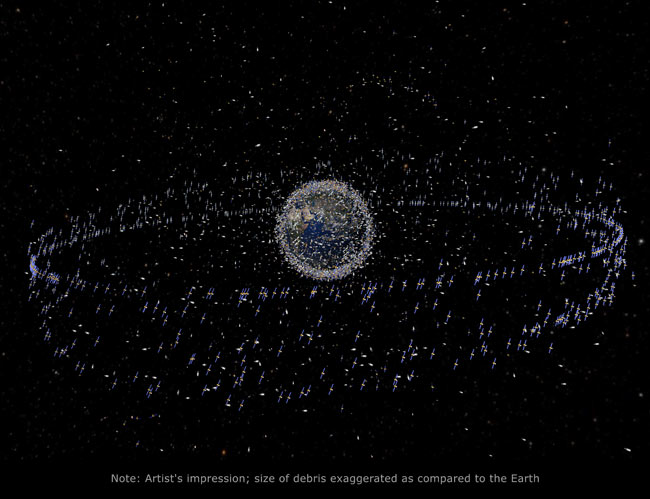

You will need: a powerful mass driver, or ideally lots of them; ready access to roughly 2*10^32J
Method: Basically, what we're going to do here is dig up the Earth, a big chunk at a time, and boost the whole lot of it into orbit. Yes. All 6 sextillion tons of it. A mass driver is a sort of oversized electromagnetic rail gun, which was once proposed as a way of getting mined materials back from the moon to Earth — basically, you just load it into the driver and fire it upwards in roughly the right direction. We'd use a particularly powerful model — big enough to hit escape velocity of 6.8 miles per second (11 kilometers per second) even after atmospheric considerations — and launch it all into the sun or randomly into space.
Alternate methods for boosting the material into space include loading the extracted material into space shuttles or taking it up via space elevator. All these methods, however, require a — let me emphasize this — titanic quantity of energy to carry out. Building a Dyson sphere ain't gonna cut it here. (Note: Actually, it would. But if you have the technology to build a Dyson sphere, why are you reading this?) See No. 6 for a possible solution.
If we wanted to and were willing to devote resources to it, we could start this process RIGHT NOW. Indeed, what with all the gunk left in orbit, on the moon and heading out into space, we already have done. (Orbital debris shown in image)
Earth's final resting place: Many tiny pieces, some dropped into the sun, the remainder scattered across the rest of the solar system.
Earliest feasible completion date: Ah. Yes. At a billion tons of mass driven out of the Earth's gravity well per second: 189,000,000 years.
Sources: This method arose when Joe Baldwin and I knocked our heads together by accident.
Pulverized by impact with blunt instrument

You will need: a big heavy rock, something with a bit of a swing to it ... perhaps Mars.
Method: Essentially, anything can be destroyed if you hit it hard enough. ANYTHING. The concept is simple: find a really, really big asteroid or planet, accelerate it up to some dazzling speed, and smash it into Earth, preferably head-on but whatever you can manage. The result: an absolutely spectacular collision, resulting hopefully in Earth (and, most likely, our "cue ball" too) being pulverized out of existence - smashed into any number of large pieces which if the collision is hard enough should have enough energy to overcome their mutual gravity and drift away forever, never to coagulate back into a planet again.
A brief analysis of the size of the object required can be found here. Falling at the minimal impact velocity of 11 kilometers per second and assuming zero energy loss to heat and other energy forms, the cue ball would have to have roughly 60 percent of the mass of the Earth. Mars, the next planet out, "weighs" in at about 11 percent of Earth's mass, while Venus, the next planet in and also the nearest to Earth, has about 81 percent. Assuming that we would fire our cue ball into Earth at much greater than 6.8 miles/second, or 11 km/s, (I'm thinking more like 31 mi/s, or 50 km/s), either of these would make great possibilities.
Obviously a smaller rock would do the job, you just need to fire it faster. A 10,000,000,000,000-tonne asteroid at 90 percent of light speed would do just as well. See the Guide to moving Earth for useful information on maneuvering big hunks of rock across interplanetary distances.
Pretty plausible.
Earth's final resting place: a variety of roughly moon-sized chunks of rock, scattered haphazardly across the greater solar system.
Earliest feasible completion date: Ah. Yes. At a billion tons of mass driven out of the Earth's gravity well per second: 189,000,000 years.
Sources: This method arose when Joe Baldwin and I knocked our heads together by accident.
Eaten by von Neumann machines

You will need: a single von Neumann machine.
Method: A von Neumann machine is any device that is capable of creating an exact copy of itself given nothing but the necessary raw materials. Create one of these that subsists almost entirely on iron, magnesium, aluminum and silicon, the major elements found in Earth's mantle and core. It doesn't matter how big it is as long as it can reproduce itself exactly in any period of time. Release it into the ground under the Earth's crust and allow it to fend for itself. Watch and wait as it creates a second von Neumann machine, then they create two more, then they create four more. As the population of machines doubles repeatedly, the planet Earth will, terrifyingly soon, be entirely eaten up and turned into a swarm of potentially sextillions of machines. Technically your objective would now be complete — no more Earth — but if you want to be thorough then you can command your VNMs to hurl themselves, along with any remaining trace elements, into the sun. This hurling would have to be achieved using rocket propulsion of some sort, so be sure to include this in your design.
So crazy it might just work.
Earth's final resting place: the bodies of the VNMs themselves, then a small lump of iron sinking into the sun.
Earliest feasible completion date: Potentially 2045-2050, or even earlier.
Sources: "2010: Odyssey Two," by Arthur C. Clarke
Hurled into the Sun

You will need: Earthmoving equipment.
Method: Hurl the Earth into the sun. Sending Earth on a collision course with the sun is not as easy as one might think; even though you don't actually have to literally hit the sun (send the Earth near enough to the sun (within the Roche limit), and tidal forces will tear it apart), it's surprisingly easy to end up with Earth in a loopy elliptical orbit which merely roasts it for four months in every eight. But careful planning can avoid this.
This is impossible at our current technological level, but will be possible one day, I'm certain. In the meantime, may happen by freak accident if something comes out of nowhere and randomly knocks Earth in precisely the right direction.
Earth's final resting place: a small globule of vaporized iron sinking slowly into the heart of the sun.
Earliest feasible completion date: Via act of God: 25 years' time. Any earlier and we'd have already spotted the asteroid in question. Via human intervention: given the current level of expansion of space technology, 2250 at best.
Sources: "Infinity Welcomes Careful Drivers," by Grant Naylor
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.