Image Gallery: Small Sea Monsters
Encope aberrans

Sand dollars, like this one, may be found in sediment depths of 30 cm or more. Members of the genus Encope, typically have commensal relationships with Dissodactylus crabs. In this association the crab receives food, shelter, and means of transportation and the sand dollar receives no harm or benefit.
Oxyurostylis smithi

Cumaceans, like this one, generally reside at the sediment-water interface, and as a result, are an important component of the diets of benthic-dwelling fishes.
Cirrophorus ilvana
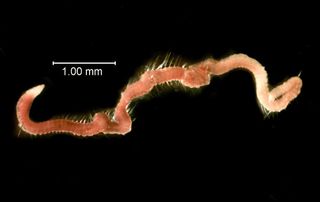
Relatively little is known about Cirrophorus ilvana. This species is a deposit feeder that resides solely within the sediment, either actively burrowing, or living within the interconnected tubes it builds out of its own mucus.
Sipuncula

Sipunculids, or peanut worms, may be epi- or infaunal. Above the sediment they may bore into rock, or are found in mollusc shells, foraminiferan tests, crevices, or in polychaete tubes. Below the sediment, they occupy soft mucus burrows that may extend 50 cm into the sediment.
Tubulanus sp.

This sipunculid genus is found in hard mucus burrows deep within the sediment, in rock crevices, and attached to tunicates. It is a predatory carnivore and scavenger that uses a feeding apparatus called an introvert to capture its prey.
Nephtys simoni

Nephtys simoni is an errant, predatory worm that can burrow up to 10 cm beneath the sediment. It is a popular food of numerous benthic fishes, and humans even use it as "bait" on their fishing hooks.
Bhawania heteroseta

Little is known about the two species of Bhawania that live at Gray's Reef. They have an epi- or infaunal lifestyle, are carnivorous, have no obvious symbiotic relationships, and have typical polychaete reproductive habits.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Sigalion arenicola

Sigalion arenicola, also referred to as a "scaleworm," is an epi- and infaunal errant polychaete, typically associated with rocky areas. It is a predatory carnivore that uses its eversible proboscis to capture small invertebrate prey.
Acteocina sp.

Acteocina species are deep-dwelling, carnivorous and deposit feeding gastropods. They feed on small invertebrates, and are an important food item for benthic fishes.