2011 Ties for Most Billion-Dollar Weather Disasters
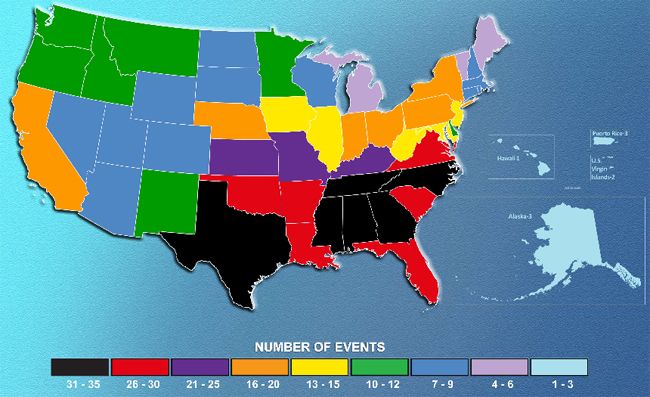
From fires to floods to tornadoes, 2011 has already racked up a record-tying nine weather disasters that caused at least $1 billion in damage each.
The costliest weather disasters in the United States since 1980 were analyzed in a report by the National Climatic Data Center, which normalized the damage amounts to 2011 values. According to the report, 108 weather-related disasters produced overall damages that reached or exceeded $1 billion. All together, those weather events caused more than $750 billion in damages.
Already in 2011, the number of billion-dollar weather disastershas matched the total from 2008, and hurricane season has yet to hit full stride. Could 2011 surpass the 2008 record?
"Impossible to predict," said the NCDC's Scott Stephens. "An active Atlantic hurricane season does not necessarily equate to hurricane landfalls or hits along the U.S. coastline."
That was the case last year, which saw 19 named storms (including tropical storms and hurricanes) but no hurricanes hitting the United States. On the flip side, in 1992 there were only seven storms, but one of those was Hurricane Andrew, the Category 5 hurricane that hit South Florida and one of the costliest disasters in U.S. history.
All it takes is one big storm hitting the wrong place to create tremendous damage, active season or not, Stephens told OurAmazingPlanet.
Here are the nine U.S. billion-dollar disasters of 2011, which so far have combined to cause $35 billion in damages:
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Upper Midwest flooding, summer: Melting of an above-average snowpack across the northern Rocky Mountains, combined with above-average precipitation, caused the Missouri and Souris rivers to swell beyond their banks across the Upper Midwest. An estimated 11,000 people were forced to evacuate Minot, N.D., due to the record high level of the Souris River. Numerous levees were breached along the Missouri River, flooding thousands of acres of farmland. The flooding, which is ongoing, has caused more than $2 billion in damages.
Mississippi River flooding, spring-summer: Persistent rainfall (nearly triple the normal precipitation amounts in the Ohio Valley), combined with melting snowpack, caused historical flooding along the Mississippi River and its tributaries. The region suffered $2 billion to $4 billion in losses. At least two people died.
Southern Plains/Southwest drought, heat wave and wildfires, spring-summer: Drought, heat waves, and wildfires scorched through Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, Arizona, southern Kansas, western Arkansas and Louisiana this year. In Texas and Oklahoma, respectively, 75 percent and 63 percent of range and pasture conditions were classified as "very poor" as of mid-August. Wildfire fighting costs for the region are about $1 million per day. Well over $5 billion in damage has been done so far, with over 2,000 homes and structures lost.
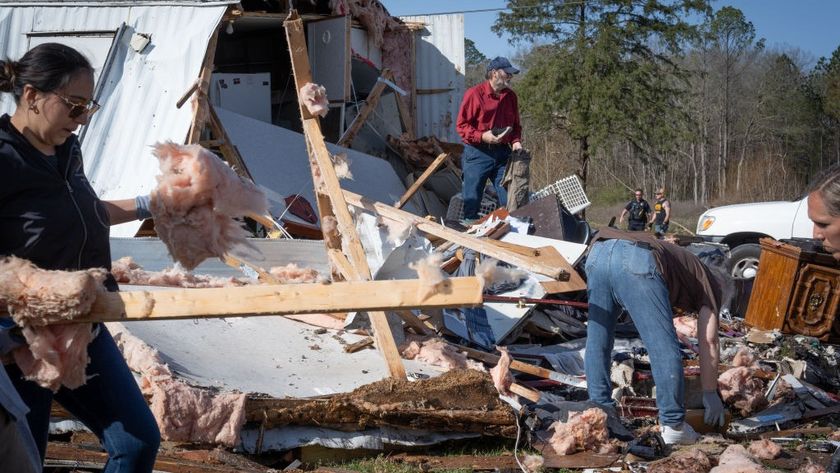
Midwest/Southeast tornadoes, May 22-27: Central and southern states saw approximately 180 twisters and 177 deaths within a week . A tornado rated EF-5 on the tornado damage scale struck Joplin, Mo., resulting in at least 141 deaths, making it the deadliest single tornado to strike the United States since modern tornado record keeping began in 1950. The total losses were greater than $7 billion.
Southeast/Ohio Valley/Midwest tornadoes, April 25-30: This outbreak of tornadoes over central and southern states led to 327 deaths. Of those fatalities, 240 occurred in Alabama. The deadliest of the estimated 305 tornadoes in the outbreak was an EF-5 that hit northern Alabama, killing 78 people. Several major metropolitan areas were directly affected by strong tornadoes, including Tuscaloosa, Birmingham and Huntsville, Ala., and Chattanooga, Tenn. Total losses exceeded $9 billion.
Midwest/Southeast tornadoes, April 14-16: An outbreak over central and southern states produced an estimated 160 tornadoes. Despite the large overall number of tornadoes, few were classified as intense, with just 14 EF-3 --and no EF-4 or EF-5 -- tornadoes identified. Total losses were greater than $2 billion. Thirty-eight people died, 22 of them in North Carolina.
Southeast/Midwest tornadoes, April 8-11: An outbreak of tornadoes over central and southern states saw an estimated 59 tornadoes. Total losses were greater than $2.2 billion.
Midwest/Southeast tornadoes, April 4-5: An outbreak of tornadoes over central and southern states saw an estimated 46 tornadoes. Total losses were greater than $2.3 billion. Nine people died.
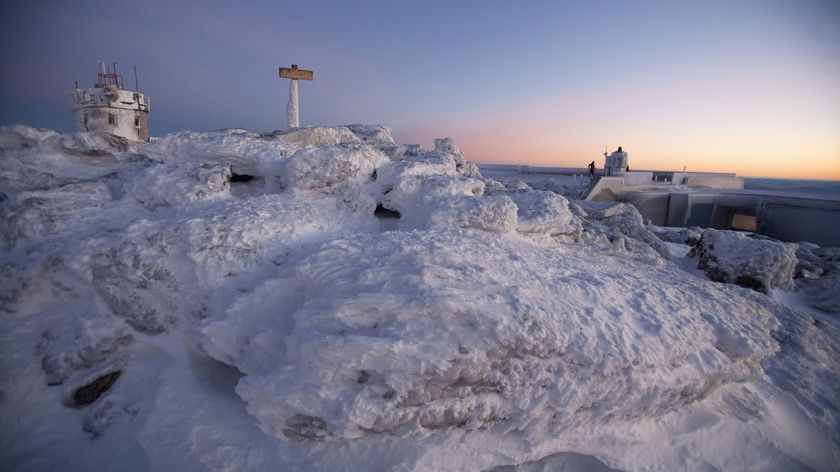
Groundhog Day blizzard, Jan 29-Feb 3: A large winter storm hit many central, eastern and northeastern states. Chicago was brought to a virtual standstill when 1 to 2 feet (0.3 to 0.6 meters) of snow fell across the city. Total losses were greater than $2 billion. The snowstorm killed 36 people.