Dolphin Species Goes Extinct Due to Humans
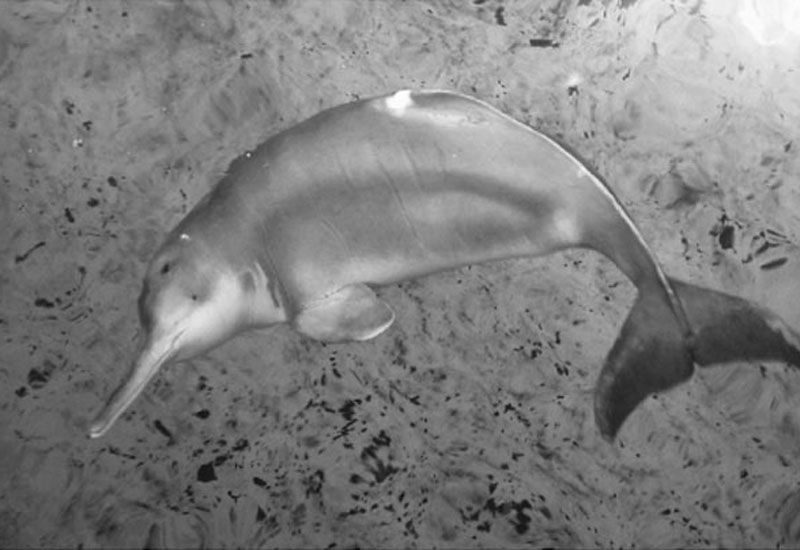

The Yangtze River dolphin is now almost certainly extinct, making it the first dolphin that humans drove to extinction, scientists have now concluded after an intense search for the endangered species.
The loss also represents the first global extinction of megafauna—any creature larger than about 200 pounds (100 kilograms)—for more than 50 years, since the disappearance of the Caribbean monk seal (Monachus tropicalis).
The Yangtze River dolphin or baiji (Lipotes vexillifer) of China has long been recognized as one of the world's most rare and threatened mammal species.
"It's a relic species, more than 20 million years old, that persisted through the most amazing kinds of changes in the planet," said marine biologist Barbara Taylor at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Fisheries Service. "It's been here longer than the Andes Mountains have been on Earth."
In 1999, the surviving baiji population was estimated to be as low as just 13 dolphins, compared to 400 known baiji in 1981. The last confirmed glimpse of a baiji was documented by a photo taken in 2002, although unverified sightings were reported as recently as 2006.
An international team of scientists conducted an intense six-week search for the dolphin in two research vessels during November and December 2006, covering the entire known range of the baiji in the 1,037-mile (1,669-kilometer) main channel of the Yangtze River. The researchers and their instruments failed to see or hear any evidence that the dolphin survives.
"It was a surprise to everyone on the expedition that we didn't have any sightings at all, that the extinction just happened so quickly," Taylor recalled.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
This would make the baiji the first cetacean—that is, dolphin, porpoise or whale—to go extinct because of humans.
The species was probably driven to extinction by harmful fishing practices that were not even devised to harm the dolphins, such as the use of gill nets, rolling hooks or electrical stunning. The findings are detailed Aug. 7 in the journal Biology Letters.
"In the past, you had this out-of-control whaling that still didn't result in any extinctions, but these accidental deaths, which are much less visible to people, are much more insidious," Taylor said.
Even if any baiji exist that scientists did not find, the continued deterioration of the Yangtze region's ecosystem—home to roughly 10 percent of the world's human population—means the species has no hope of even short-term survival as a viable population, the researchers added.
"To help save the endangered Yangtze finless porpoises (Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaeorientalis) that also live in the river, we'll likely have to keep them in lake preserves or raise them in captivity, because the situation in that river doesn't look like it can be controlled at this point," Taylor explained.
With the loss of the Yangtze River dolphin, the world's most critically endangered cetacean species now is the vaquita or Gulf of California porpoise (Phocoena sinus), of which 250 survive. The vaquita and other coastal dolphins around the world now face the same peril that claimed the baiji—accidental deaths from fishing.
"We have to find a way to let small-time fishermen put food on their tables that doesn't involve putting gill nets in the water that decimate these species," Taylor said. "Unless we figure out a way to deal with this problem, the baiji may be the first in quite a long line of animals to face extinction."
- IMAGE GALLERY: Endangered and Threatened Wildlife
- 10 Species Success Stories
- Top 20 Extinction Hot Spots

Most Popular