Solar Eruptions Linked to Giant Loops of Super-Hot Plasma
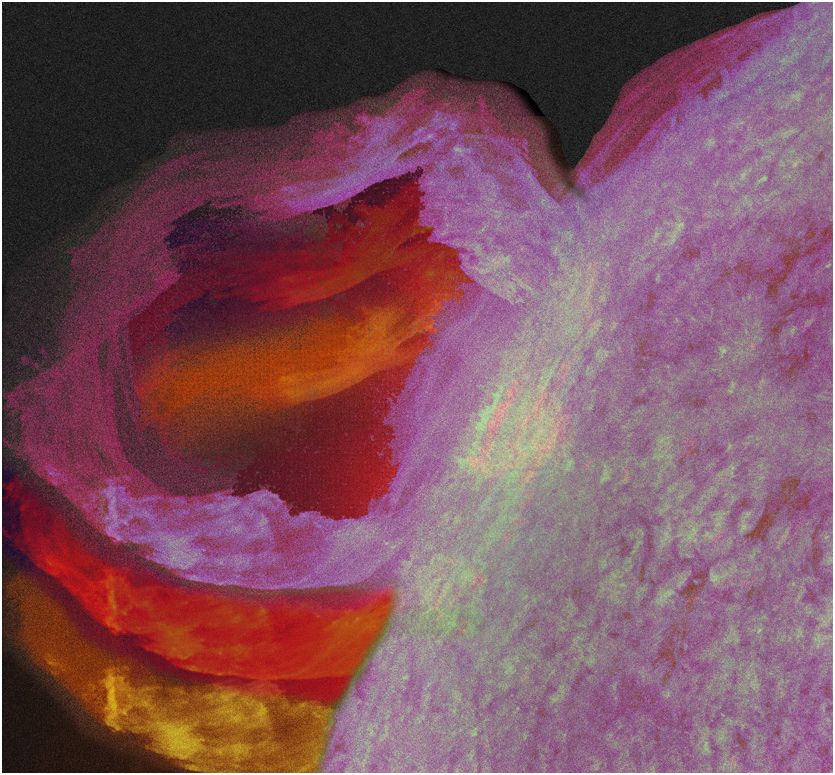
Giant unstable loops of plasma arcing from the surface of the sun may be the root of explosive solar flares and other solar eruptions, researchers find.
Astronomers have long noticed enormous arches of plasma emerging from the sun's surface. Known as magnetic flux ropes, these structures possess spiraling magnetic field lines, as if a huge bar magnet had been twisted into a corkscrew. A massive amount of electrical current typically runs through the core of each such tube.
Magnetic flux ropes (also known as coronal loops and solar prominences) sit on the surface of the sun, with matter and energy flowing through them, for hours or days. Scientists have long thought these structures are linked with solar explosions eruptions such as coronal mass ejections that can wreak havoc on satellites in space and power grids on Earth, but direct evidence of this remained elusive.
A year ago, however, researchers witnessed the formation and evolution of a magnetic flux rope on the surface of the sun before and during a solar eruption.
Scientists used the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly telescope on the orbiting Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) to study a solar eruption on March 8, 2011. Their findings suggest solar eruptions are triggered by instabilities in these structures. [Photos: Amazing Solar Flare Views]
"We can now watch how a solar storm is forming, developing and then erupting — it is like watching a combination of a tornado, volcano and tsunami wave in action," study lead author Jie Zhang, a solar physicist at George Mason University, told SPACE.com.

"The finding helps us understand the physical mechanisms that produce a solar eruption, and hopefully provide the capability for prediction in the future," Zhang said.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Multi-temperature images revealed the formation of a giant twisted crescent as hot as 18 million degrees Fahrenheit (10 million degrees Celsius), which rose at speeds of up to 223,000 mph (360,000 kilometers per hour) to become a more rounded arch. This structure apparently then became unstable, rising dramatically at speeds of more than 1.5 million mph (2.5 million kph), coinciding with the onset of a solar flare.
The researchers suggest the fast growth of the magnetic flux rope triggered the creation of a solar flarethrough a process called magnetic reconnection, where the energy within the magnetic fields of the structure were converted to kinetic energy. "The reconnection adds additional energy to the eruption," Zhang said.
This work should pave a new way of doing research on solar storms.
"We now know that the magnetic flux ropes — the engines of the storm — can be best viewed by imaging hot temperatures," Zhang said. "This explains why detection of the flux ropes was elusive in the past: Instrumentation before the SDO mission mostly observed the sun at cooler temperatures. In the future we will study and track more flux ropes and study their evolution. The ultimate goal is to develop the capability to predict solar storms."
The scientists detailed their findings online March 20 in the journal Nature Communications.
This story was provided by SPACE.com, a sister site to LiveScience. Follow SPACE.com for the latest in space science and exploration news on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.