The Facts on Moms & Breast-Feeding (Infographic)
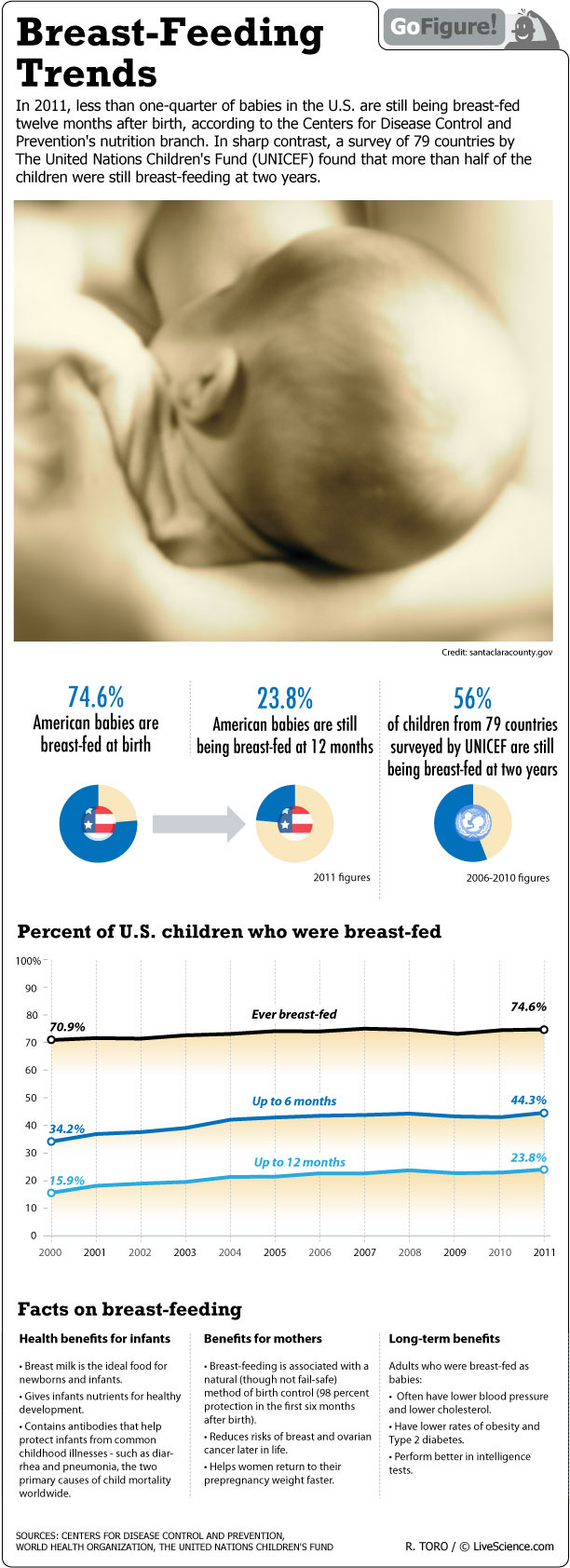
Less than one-quarter of babies in the U.S. are still being breast-fed 12 months after birth, according to a 2011 study by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's nutrition branch. In sharp contrast, a survey of 79 countries by The United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) found that more than half of the children were still breast-feeding at 2 years. Multiple studies show that breast-feeding is beneficial for both mother and infant. Breast milk reduces allergies, colds, infections and other health problems. It also boosts the baby’s immune system, protecting them from illnesses. Breast-fed babies have lower rates of ear infections, eczema, diarrhea, lower respiratory tract infections, sudden infant death syndrome, obesity, leukemia and childhood diabetes. Mothers who breast-feed have lower rates of breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends exclusive breast-feeding for the first six months of a baby's life, followed by breast-feeding in combination with the introduction of complementary foods until at least 12 months of age, and continued breast-feeding as long as mother and baby chose to do so. However, most mothers in the U.S. do not breast-feed the recommended six months, which researchers theorize may contribute to more health issues in the future.
- That's Incredible! 9 Brainy Baby Abilities
- 11 Facts Every Parent Should Know About Their Baby's Brain
- Blossoming Body: 8 Odd Changes That Happen During Pregnancy
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Man gets sperm-making stem cell transplant in first-of-its-kind procedure
'Love hormone' oxytocin can pause pregnancy, animal study finds
