China Unveils Astronaut Crew, 1st Female Spaceflyer, for Saturday Launch
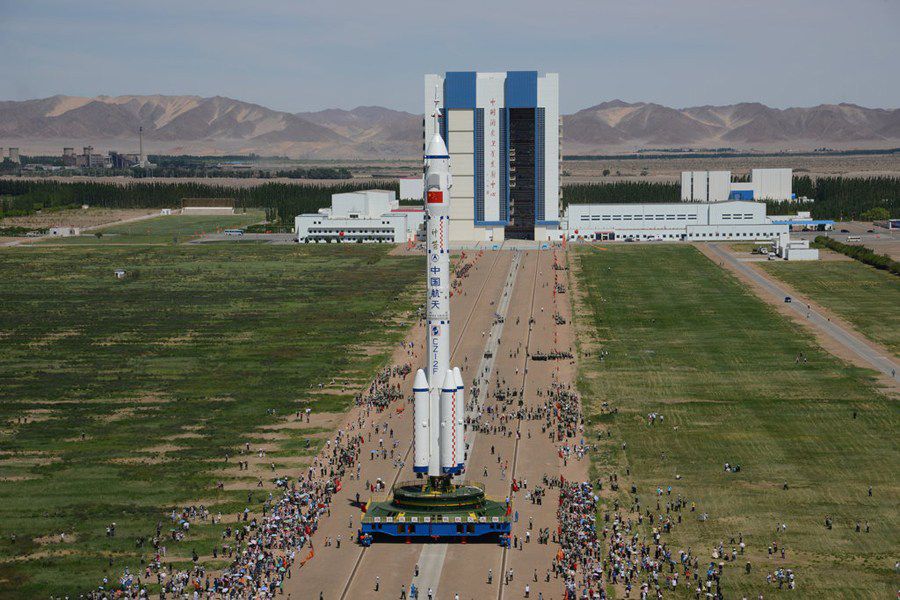

China has unveiled the three-person crew for its first manned docking spaceflight set to launch Saturday (June 16) — a mission that will send the country's first female astronaut into orbit in the process.
The crew of China's Shenzhou 9 space docking mission met reporters today (June 15) at the country's Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center ahead of Saturday's planned launch at 6:37 p.m. local time (6:37 a.m. EDT or 1037 GMT). The three astronauts, or taikonauts as China's spaceflyers are known, include male crewmembers Jing Haipeng, Liu Wang and the country's first woman to fly in space: the 34-year-old Liu Yang.
"I am grateful to the motherland and the people," Liu Yang said in a press conference according to the state-run Xinhua news agency. "I feel honored to fly into space on behalf of hundreds of millions of female Chinese citizens."
Liu and her crewmates will blast off atop a Long March 2F rocket and fly their Shenzhou 9 space capsule to China's Tiangong 1 laboratory module, which is a prototype space station that has been orbiting Earth since last September. It is China's fourth human spaceflight since 2003 and the first to actually rendezvous with a target in orbit.
The Shenzhou 9 astronauts are expected to perform at least two docking tests, one manual and the other automatic, and spend several days living and working inside the Tiangong 1 lab, said Wu Ping, spokeswoman for the China Manned Space Engineering Office that oversees China's human spaceflight program. [China's Shenzhou 9 Docking Mission Pictures]

China's fourth space crew revealed
Liu and her two crewmates are all former pilots with the People's Liberation Army and members of the Communist Party of China, Xinhua reported.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
As China's first woman to fly in space, Liu was selected from a field female military pilots to join China's astronaut corps. She joined China's Air Force in 1997 and served in the Wuhan Flight Unit before being selected for the astronaut program.
Another female Chinese pilot, Wang Yaping, was also in the running to fly on the Shenzhou 9 crew. Liu currently holds the rank of major, Xinhua reported. [Women in Space: A Gallery of Firsts]
"China's first female astronaut in space … will be the 56th woman to fly into space out of the more than 500 people that have made it into orbit worldwide," said space history and artifacts expert Robert Pearlman, editor of collectSPACE.com, a SPACE.com partner site. "The first woman in space, Soviet cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova was launched on June 16, 1963. If Shenzhou 9 launches on Saturday, it will be exactly 49 years to the day after Tereshkova's historic first flight."

Liu has about 1,680 hours of flying experience, served as the deputy head of a PLA flight unit, and is married — a requirement for all China's female astronauts, according to media reports.
Of the three Shenzhou 9 astronauts, only Jing Haipeng, 46, has flown in space before. He served on the three-man crew of Shenzhou 7 in 2008, a mission that featured China's first spacewalk.
Rounding out the Shenzhou 9 mission team is Liu Wang, 43, a senior colonel in the PLA with 1,000 hours of flight time under his belt.
Major space docking test
Performing the first manned docking is the next step toward China's ultimate goal of establishing a crewed space laboratory by 2020. China is the third country, after Russia and the United States, to launch its own astronauts to space.
Fueling of the Long March 2F rocket set to launch Shenzhou 9 will begin at about 5:30 p.m. local time today at Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwest China's Gansu Province.
"The launch of the Shenzhou 9 is a highly influential event that marks an important milestone for the development of China's space technology," Cui Jijun, director of the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, said on Wednesday, according to Xinhua.
While the upcoming mission is China's first crewed flight to dock two spacecraft, it follows an unmanned docking mission that went smoothly last November when the robotic Shenzhou 8 craft linked with Tiangong 1 after its launch.
"In the Russian and USA space programs, the most serious docking problems have been caused by automatic docking systems, more so than by manual docking," Xinhua quoted Pat Norris, chairman of the Royal Aeronautical Society Space Group, as saying. "China has taken the prudent course of verifying new space technology in robotic flights before applying it to human space missions."
China's first astronaut, Yang Liwei, launched on the Shenzhou 5 mission in 2003. Two more missions followed, with the second including the nation's first spacewalk.
This story was provided by SPACE.com, a sister site to LiveScience. Follow Clara Moskowitz on Twitter @ClaraMoskowitz or SPACE.com @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook & Google+.