Cavemen Bones Yield Oldest Modern Human DNA
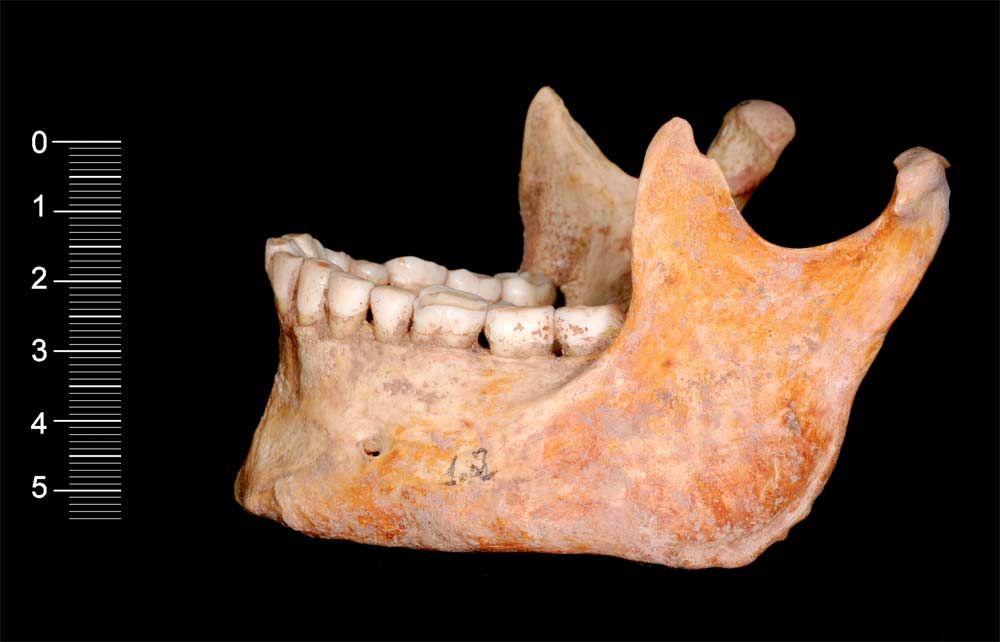
What may be the oldest fragments of the modern human genome found yet have now been revealed — DNA from the 7,000-year-old bones of two cavemen unearthed in Spain, researchers say.
These findings suggest the cavemen there were not the ancestors of the people found in the region today, investigators added.
Scientists have recently sequenced the genomes of our closest extinct relatives, the Neanderthals and the Denisovans. When it came to our lineage, the oldest modern human genomes recovered yet came from Ötzi the Iceman, a 5,300-year-old mummy found in the Alps in 1991. Researchers have salvaged DNA from even older human cells, but this comes from the mitochondria that generate energy for our bodies, and not from the nucleus where our chromosomes are housed. (Mitochondrial DNA is passed down only by mothers.)
Now researchers have rescued fragments of genomes from the remains of two cavemen unearthed in northern Spain.
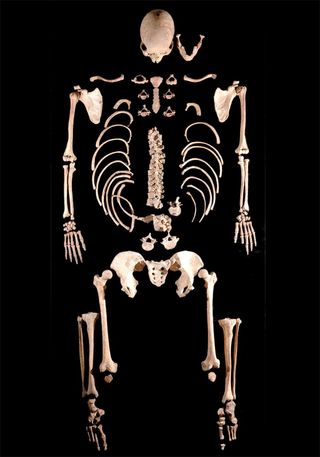
"These are the oldest partial genomes from modern human prehistory," researcher Carles Lalueza-Fox, a paleogeneticist at the Spanish National Research Council, told LiveScience. [Image Gallery: Our Closest Human Ancestor]
The skeletons of two young adult males were discovered by chance in 2006 by cave explorers in a cavern high in the Cantabrian mountain range, whose main entrance is found at 4,920 feet (1,500 meters) altitude. Winters there are notably cold, which helped preserve the DNA in the bones.
These bones date back to the Mesolithic period, before agriculture spread to the Iberian Peninsula with Neolithic settlers from the Middle East. These cavemen were hunter-gatherers, judging by the ornament that one was found with of red-deer canines embroidered onto a cloth.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The scientists recovered 1.34 percent and 0.5 percent of the human genomes from the bones of these two cave men. Analyses revealed that current populations of the Iberian Peninsula, which includes Spain, Portugal and Andorra, are not genetically linked with these ancient hunter-gatherers. Instead, these cavemen were closer genetically to the current populations of northern Europe.
"There are many works that claim the Basques [of the Iberian Peninsula] could be descendants from Mesolithics that became isolated in the Basque country," Lalueza-Fox said. "We found the modern Basques are genetically not related to these two individuals."
The scientists also recovered the complete mitochondrial DNA of one of these cavemen. This revealed that European populations during the Mesolithic were very uniform genetically.
"Despite their geographical distance, individuals from the regions corresponding to the current England, Germany, Lithuania, Poland and Spain shared the same mitochondrial lineage," Lalueza-Fox said. "These hunters-gatherers shared nomadic habits and had a common origin."
The researchers now aim to complete the genomes of both cavemen. Such data could help "explore genes that have been modified with the arrival of the Neolithic in the European populations," Lalueza-Fox said.
The scientists detailed their findings online today (June 28) in the journal Current Biology.
Follow LiveScience on Twitter @livescience. We're also on Facebook & Google+.