Space photo of the week — Extraordinary images of our sublime universe

Space photos remind us that, around every corner of our vast universe, something spectacular awaits. From the newest James Webb Space Telescope images to historic photos of groundbreaking space missions, join us every Sunday as we explore the wonders of the universe, and humanity's place in it.
See more incredible space photos:
Latest about space photo of the week

Space photo of the week: Hubble hunts a stellar 'imposter' hiding in the Great Bear
By Jamie Carter published
The legendary Hubble Space Telescope has turned its gaze to the Ursa Major-adjacent galaxy UGC 5460, revealing spiral arms, star clusters and a possible supernova "imposter".

Space photo of the week: The last view of the 'Great Comet of 2025' for half a million years
By Shreejaya Karantha published
Beautifully captured against a starry sky, Comet C/2024 G3 (ATLAS) — dubbed by some as the "Great Comet of 2025" — shines brightly after its last approach to the sun for hundreds of thousands of years.

Space photo of the week: James Webb telescope reveals mysterious 'light echo' in the broken heart of Cassiopeia
By Shreejaya Karantha published
Beautifully captured by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), this image shows interstellar gas and dust lit up by a dead star in Cassiopeia.

Space photo of the week: James Webb telescope shocks scientists with image of ancient galaxy roaring back to life
By Jamie Carter published
The James Webb Space Telescope has zoomed in on Leo P, a tiny galaxy with some big things to say about star formation.

Space photo of the week: Dry ice 'geysers' erupt on Mars as spring hits the Red Planet
By Jamie Carter published
NASA shares an iconic image of carbon dioxide ice erupting in geysers when Martian winter turns to spring.

Space photo of the week: James Webb and Hubble telescopes unite to solve 'impossible' planet mystery
By Jamie Carter published
New James Webb Space Telescope observations of a star cluster called NGC 346 are shedding light on how, when and where planets formed in the early universe.

Space photo of the week: Galaxies teeter toward collision in the sparkling depths of Virgo
By Jamie Carter published
An ultra-deep image from the National Science Foundation's Dark Energy Camera reveals a wide variety of galaxies in the unusual Antlia Cluster.
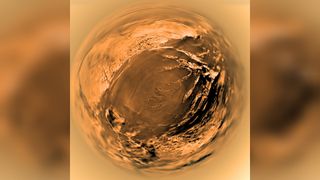
Space photo of the week: Look into Titan's 'eye,' 20 years after the Huygens spacecraft's historic landing on Saturn's largest moon
By Shreejaya Karantha published
Twenty years ago, the Huygens probe achieved humanity's first landing on a moon in the outer solar system when it touched down on Titan.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.