Oops! Brain-Removal Tool Left in Mummy's Skull
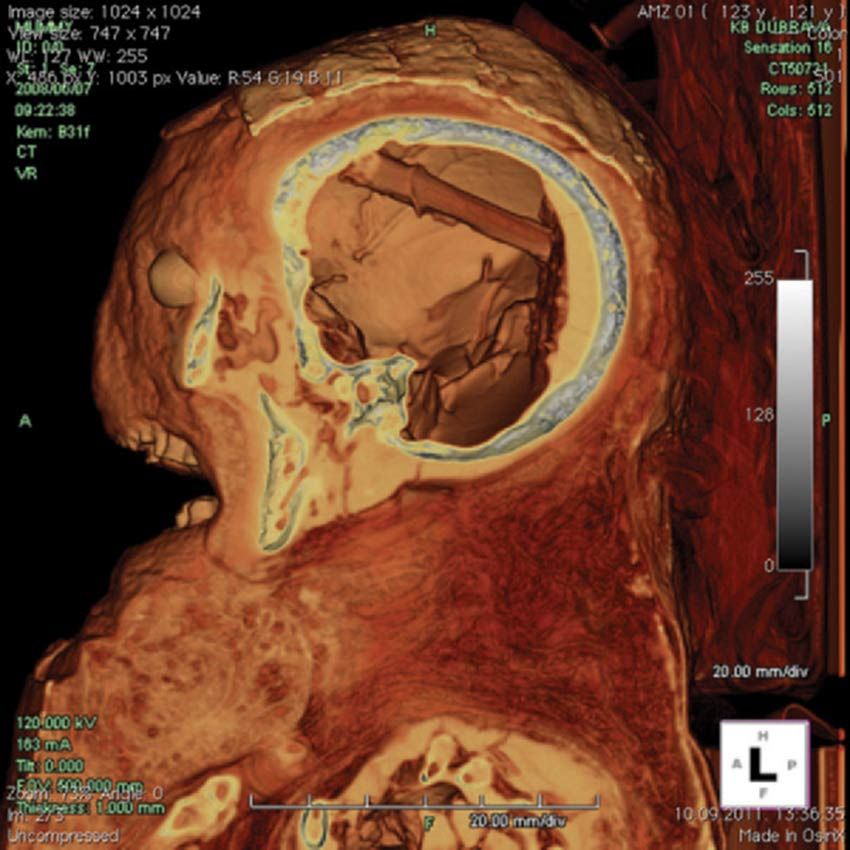
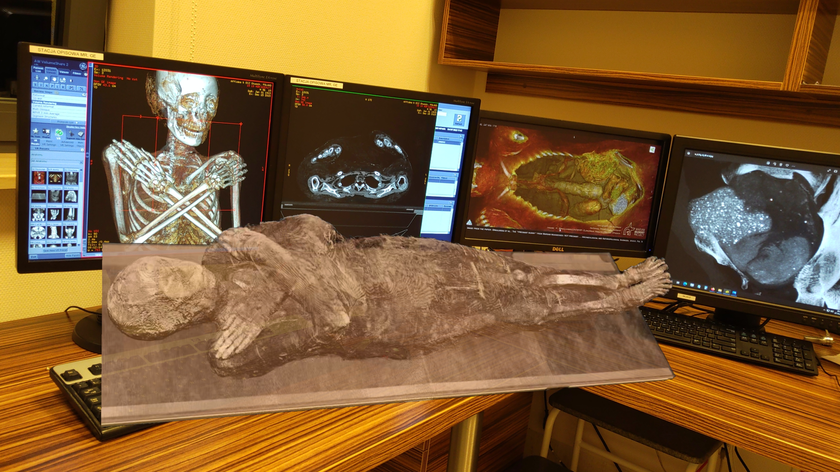
A brain-removal tool used by ancient Egyptian embalmers has been discovered lodged in the skull of a female mummy that dates back around 2,400 years.
Removal of the brain was an Egyptian mummification procedure that became popular around 3,500 years ago and remained in use in later periods.
Identifying the ancient tools embalmers used for brain removal is difficult, and researchers note this is only the second time that such a tool has been reported within a mummy's skull.
The discovery
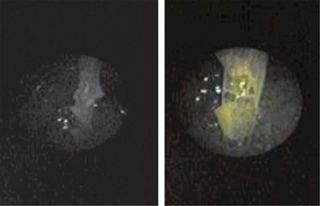
Located between the left parietal bone and the back of the skull, which had been filled with resin, the object was discovered in 2008 through a series of CT scans. Researchers then inserted an endoscope (a thin tube often used for noninvasive medical procedures) into the mummy to get a closer look and ultimately detach it from resin to which it had gotten stuck. [See Photos of Mummy & Brain-Removal Tool]
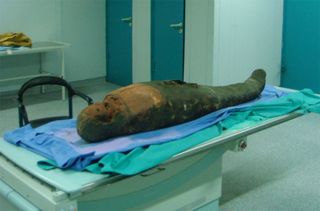
"We cut it with a clamp through the endoscope and then removed it from the skull," said lead researcher Dr. Mislav Čavka, of the University Hospital Dubrava in Zagreb Croatia, in an interview with LiveScience.
They found themselves peering at an object more than 3 inches (8 centimeters) long that would have been used for liquefying and removing the brain. "It almost definitely would have been used in excerebration [brain removal] of the mummy," Čavka said.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The instrument would have been inserted through a hole punched into the ethmoid bone near the nose. "Some parts [of the brain] would be wrapped around this stick and pulled out, and the other parts would be liquefied," Čavka said.
The Egyptian mummy could then be put on its abdomen and the liquid drained through the nose hole. "It is an error that [the] embalmers left this stick in the skull," said Čavka, adding the tool may have broken apart during the procedure.
This embalming accident, unfortunate for the ancient mummy, has provided researchers with a very rare artifact. Čavka's team point out in a paper they published recently in the journal RSNA RadioGraphics the only other brain-removal stick found inside a mummy's skull dates back 2,200 years.

"Probably in museums in Egypt there are many other evidences, but they were not found inside the skull," making it tricky to identify such artifacts as brain-removal tools, said Čavka.
The mummy is currently in the Archaeological Museum in Zagreb Croatia and is that of a woman who died around the age of 40. Brought to Croatia in the 19th century without a coffin, it's not known where she was found in Egypt. Radiocarbon dating and CT scans of the mummy determined its date to be around 2,400 years. Her cause of death is unknown. New insights
The stick is quite brittle and the team could not do as thorough of an analysis as they'd hoped. Looking at it under a microscope, botanical experts determined the tool is made from plants in the group Monocotyledon, which includes forms of palm and bamboo.
The most curious find came when the researchers compared their discovery with an ancient account of brain removal made by the Greek writer Herodotus in the fifth century B.C. A visitor to Egypt, he had this to say about how Egyptian brain removal worked (as translated by A. D. Godley, Cambridge, Harvard University Press, 1920, through Perseus Digital Library):
"Having agreed on a price, the bearers go away, and the workmen, left alone in their place, embalm the body. If they do this in the most perfect way, they first draw out part of the brain through the nostrils with an iron hook, and inject certain drugs into the rest."
The recent discovery suggests an organic stick, not an "iron hook," was used in at least some of these procedures, possibly for economic reasons. Researchers note that the tool found in the skull of the other mummy, dating from 2,200 years ago, was also made of an organic material.
"It is known that mummification was widely practiced throughout ancient Egyptian civilization, but it was a time-consuming and costly practice. Thus, not everyone could afford to perform the same mummification procedure," write the researchers in their journal article.
Follow LiveScience on Twitter @livescience. We're also on Facebook & Google+.

Owen Jarus is a regular contributor to Live Science who writes about archaeology and humans' past. He has also written for The Independent (UK), The Canadian Press (CP) and The Associated Press (AP), among others. Owen has a bachelor of arts degree from the University of Toronto and a journalism degree from Ryerson University.