Caribbean Beauties: Two New Orchid Species Found
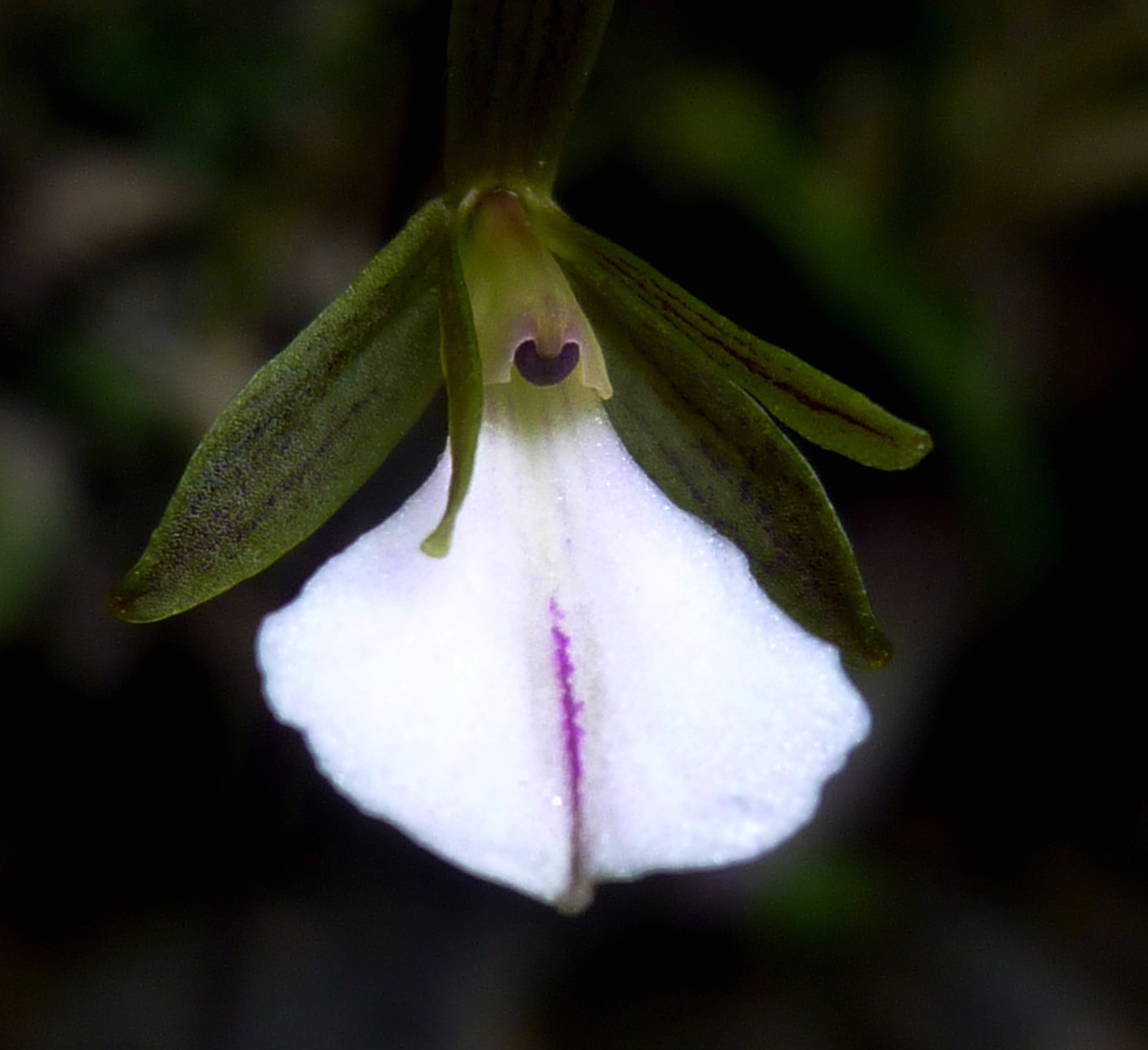

One of the world's newest orchid species is also its most delicate, with tiny white flowers smaller than a dime. Yet the flower finds its home amid boulders near the banks of rushing streams in Cuba's remote eastern mountains.
The orchid is one of two new species identified by botanists in Cuba, a hotbed for orchids — the largest and most diverse plant family in the world. The islands of the Caribbean have more the 25,000 species of orchids tucked into their forests and rivers.
The new species was named Tetramicra riparia, a nod to its discovery along stony streams in the mountains of Baracoa, one of the rainiest and least explored areas in Cuba, Ángel Vale, a researcher at the University of Vigo in Spain, said in a statement. The plant has an unusually broad, sturdy base: Its pedicel is almost four times as large as its column, Vale and his co-authors report.
The second new orchid, from the western tip of the island, dwarfs its neighbor in size. The flower's showy purple and green petals are similar to a daffodil in appearance, spreading more than 2.5 inches (7 centimeters), with up to 20 blooms on one plant.
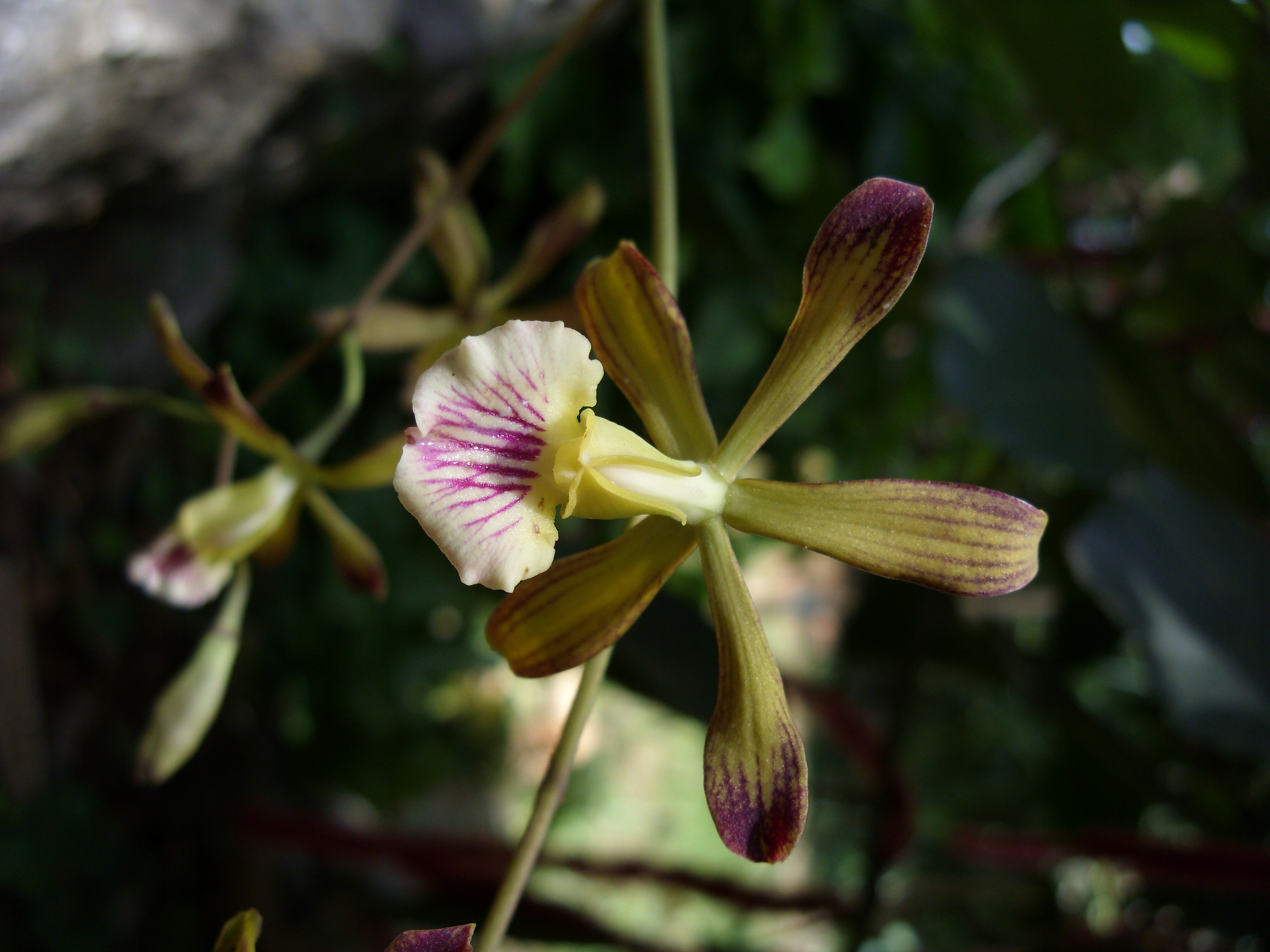

Like many orchids, the flower, dubbed Encyclia navarroi, is epiphytic, meaning it grows on other plants for support, but not for nutrients. Along the western coast, the species preferred to perch on plumeria and ficus, the researchers discovered.
Both new species are deceit pollinators, Vale said, enticing bees to spread their pollen without a reward. "Contrary to most plants, many orchids do not produce nectar or other substances to compensate insects and birds that visit them," he said.
Vale and his colleagues are studying orchids throughout the Greater Antilles (Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico) to reconstruct their evolutionary history and analyze the effect of pollinators in their development. One of the mysteries they aim to solve is whether deceit orchids have greater diversity than other nectar-producing species.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"Despite the fact that T. riparia's flowers have a complete central petal, just like other species that make up a subgenre endemic to Cuba; the way they grow is very similar to a more widespread group that seems to have diverged on the neighboring island of Hispaniola," Vale said. "Our work provides molecular evidence of the greater relationship of T. riparia with these species on the neighboring island."
The findings were detailed in the October 2012 issue of the journal Systematic Botany and the April 2012 issue of the journal Annales Botanici Fennici.
Reach Becky Oskin at boskin@techmedianetwork.com. Follow her on Twitter @beckyoskin. Follow OurAmazingPlanet on Twitter @OAPlanet. We're also on Facebook and Google+.