Astronomy Teacher Finds Hubble Telescope's Hidden Treasure
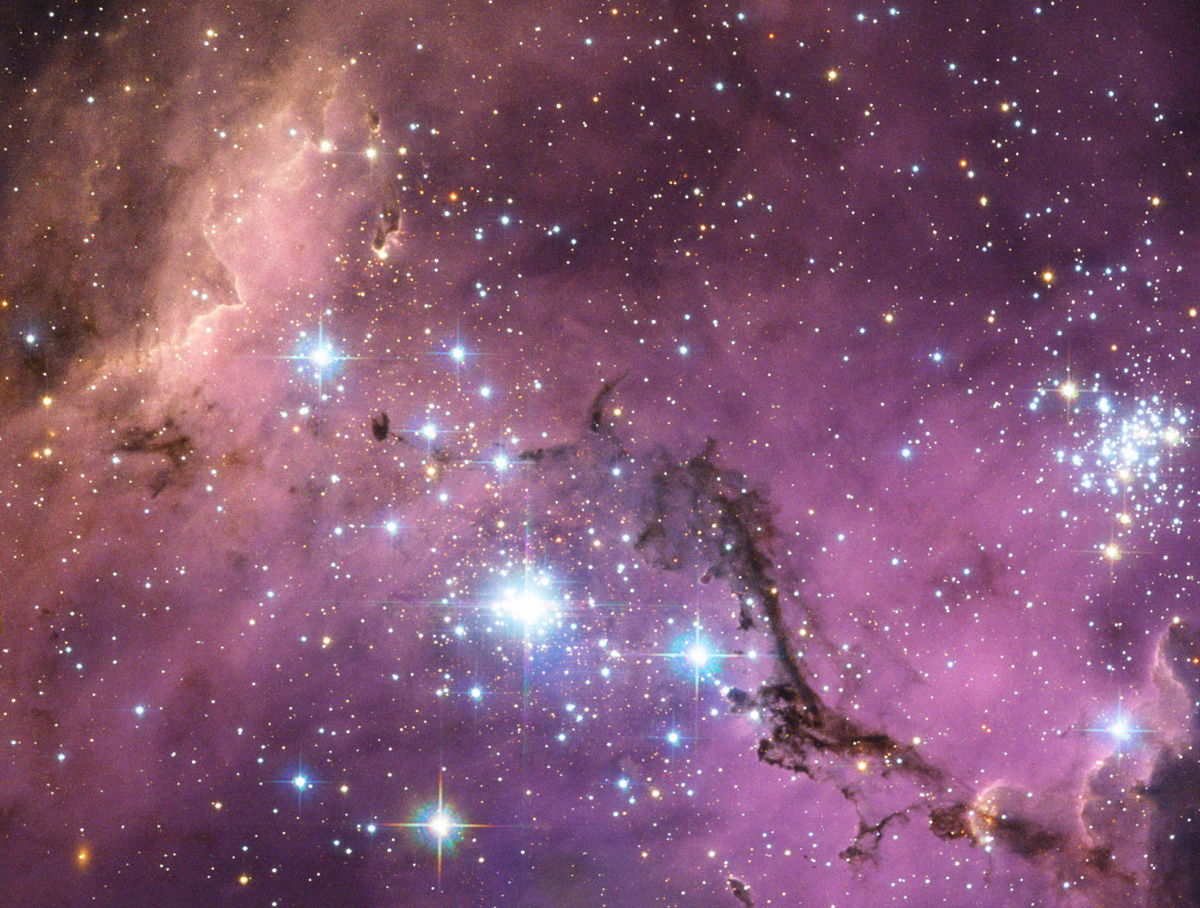

A Connecticut astronomy teacher has uncovered a dazzling view of a satellite galaxy to the Milky Way while exploring the "hidden treasures" of the Hubble Space Telescope.
The new Hubble photo, released Thursday (Jan. 17), shows an intriguing star nursery dotted with dark dust lanes in the Large Magellanic Cloud about 200,000 light-years from Earth. The Hubble observation used to create the image was discovered in the telescope's archives by Josh Lake, a high school astronomy teacher at Pomfret School in Pomfret, Conn., as part of the "Hubble Hidden Treasures" contest that challenged space fans to find unseen images from the observatory.
Hubble officials also released an eye-popping video tour of the Large Magellanic Cloud, which zooms in on the region highlighted in Lake's photo.
Lake won first prize in the Hubble photo contest with an image of the LHA 120-N11 (N11) region of the Large Magellanic Cloud. Hubble officials combined Lake's image with more observations of the N11 region in blue, green and near-infrared light wavelengths to create the new view.
"In the center of this image, a dark finger of dust blots out much of the light," Hubble officials said in an image description. "While nebulae are mostly made of hydrogen, the simplest and most plentiful element in the universe, dust clouds are home to heavier and more complex elements, which go on to form rocky planets like the Earth." [Hubble Telescope's Hidden Treasures: Winning Photos
The interstellar dust in N11 is extremely fine, much more so than household dust on Earth. It is more similar to smoke, researchers explained.
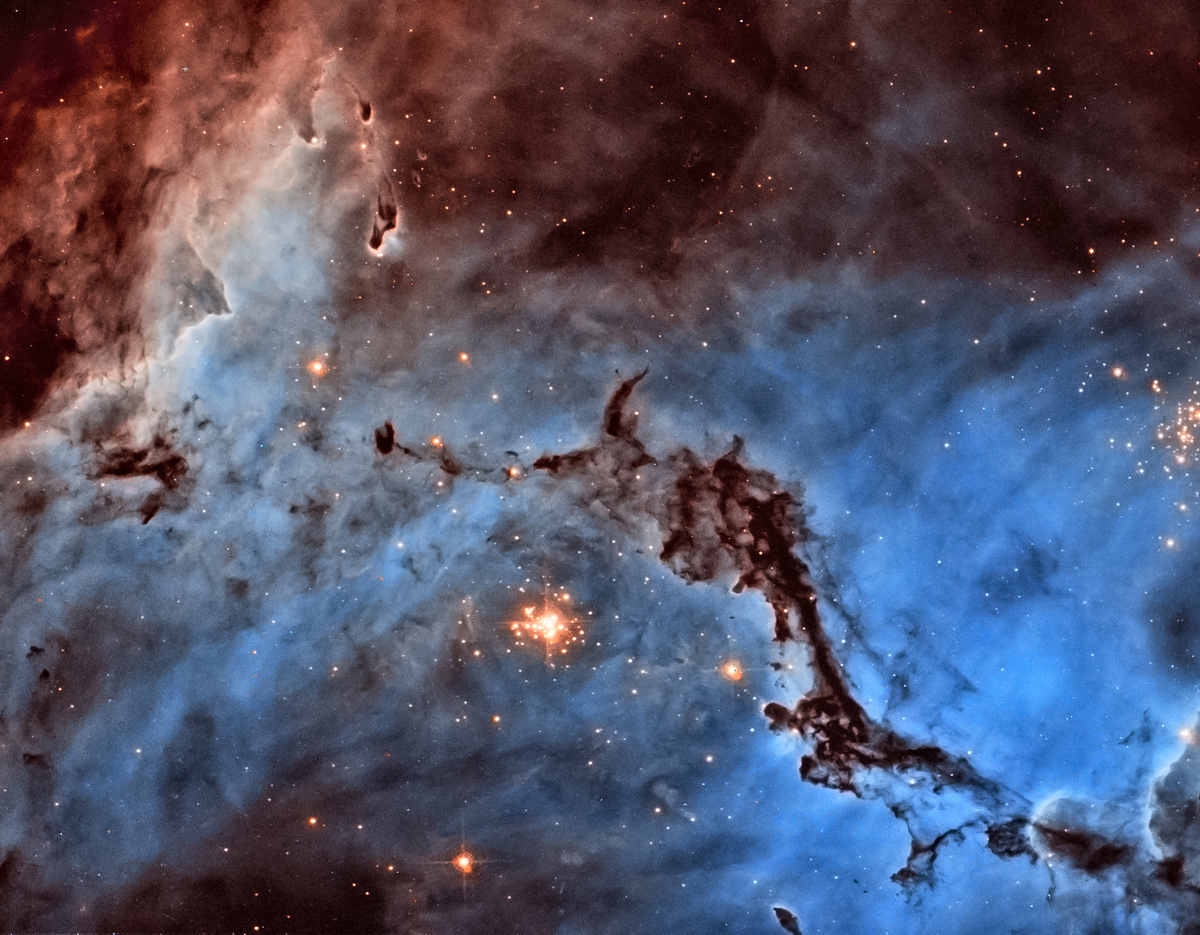

The Large Magellanic Cloud, or LMC, is one of two small satellite galaxies of the Milky Way (the other is the smaller, aptly named Small Magellanic Cloud). Because of its relatively close proximity, the Large Magellanic Cloud has long been used as a sort of cosmic laboratory to study how stars form in other galaxies.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"It lies in a fortuitous location in the sky, far enough from the plane of the Milky Way that it is neither outshone by too many nearby stars, nor obscured by the dust in the Milky Way’s center," Hubble officials said in a statement. "It is also close enough to study in detail … and lies almost face-on, giving us a bird’s eye view."
In addition to the N11 region, the Large Magellanic Cloud is also home to the spectacular Tarantula nebula, the brightest nearby star nursery, Hubble officials said.
The Hubble Space Telescope has been snapping spectacular photos of the universe since 1994 and is a joint project by NASA and the European Space Agency. This month, NASA officials said the long-lived space observatory could potentially last through 2018.
This story was provided by SPACE.com, a sister site to Live Science. You can follow SPACE.com Managing Editor Tariq Malik on Twitter @tariqjmalik. Follow SPACE.com for the latest in space science and exploration news on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.

Tariq is the editor-in-chief of Live Science's sister site Space.com. He joined the team in 2001 as a staff writer, and later editor, focusing on human spaceflight, exploration and space science. Before joining Space.com, Tariq was a staff reporter for The Los Angeles Times, covering education and city beats in La Habra, Fullerton and Huntington Beach. He is also an Eagle Scout (yes, he has the Space Exploration merit badge) and went to Space Camp four times. He has journalism degrees from the University of Southern California and New York University.