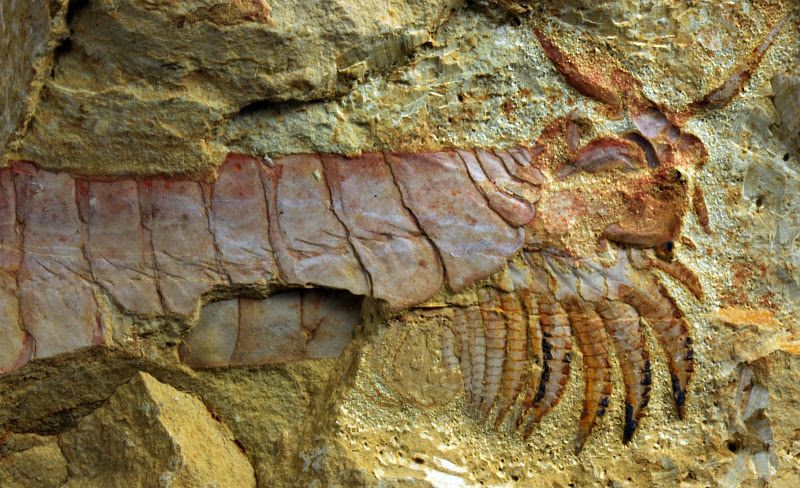
Scientists have unearthed extraordinarily preserved fossils of a 520-million-year-old sea creature, one of the earliest animal fossils ever found, according to a new study.
The fossilized animal, an arthropod called a fuxhianhuiid, has primitive limbs under its head, as well as the earliest example of a nervous system that extended past the head. The primitive creature may have used the limbs to push food into its mouth as it crept across the seafloor. The limbs may shed light on the evolutionary history of arthropods, which include crustaceans and insects.
"Since biologists rely heavily on organization of head appendages to classify arthropod groups, such as insects and spiders, our study provides a crucial reference point for reconstructing the evolutionary history and relationships of the most diverse and abundant animals on Earth," said study co-author Javier Ortega-Hernández, an earth scientist at the University of Cambridge, in a statement. "This is as early as we can currently see into arthropod limb development."
The findings were published today (Feb. 27) in the journal Nature.
Primordial animal
The fuxhianhuiid lived nearly 50 million years before animals first emerged from the sea onto land, during the early part of the Cambrian explosion, when simple multicellular organisms rapidly evolved into complex sea life. [See Images of the Wacky Cambrian Creatures ]
While paleontologists have unearthed previous examples of a fuxhianhuiid before, the fossils were all found in the head-down position, with their delicate internal organs obscured by a large carapace or shell.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
However, when Ortega-Hernández and his colleagues began excavating in a fossil-rich region of southwest China around Kunming called Xiaoshiba, they unearthed several specimens of fuxhianhuiid where the bodies had been flipped before fossilization. All told, the team unearthed an amazingly preserved arthropod, as well as eight additional specimens.
These primeval creatures probably spent most of their days crawling across the seabed trawling for food and may have also been able to swim short distances. The sea creatures, some of the earliest arthropods or jointed animals, probably evolved from worms with legs.
The discovery sheds light on how some of the earliest ancestors of today's animals may have evolved.
"These fossils are our best window to see the most primitive state of animals as we know them – including us," Ortega-Hernández said in a statement. "Before that there is no clear indication in the fossil record of whether something was an animal or a plant – but we are still filling in the details, of which this is an important one."
Follow Tia Ghose on Twitter @tiaghoseor LiveScience @livescience. We're also on Facebook & Google+.

Tia is the managing editor and was previously a senior writer for Live Science. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Wired.com and other outlets. She holds a master's degree in bioengineering from the University of Washington, a graduate certificate in science writing from UC Santa Cruz and a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin. Tia was part of a team at the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel that published the Empty Cradles series on preterm births, which won multiple awards, including the 2012 Casey Medal for Meritorious Journalism.