See Jupiter and Moon Pair Up on St. Patrick's Day
On Sunday evening, revelers can cap their St. Patrick’s Day by enjoying a view of a rendezvous involving two of the brightest objects in the night sky: the moon and the planet Jupiter.
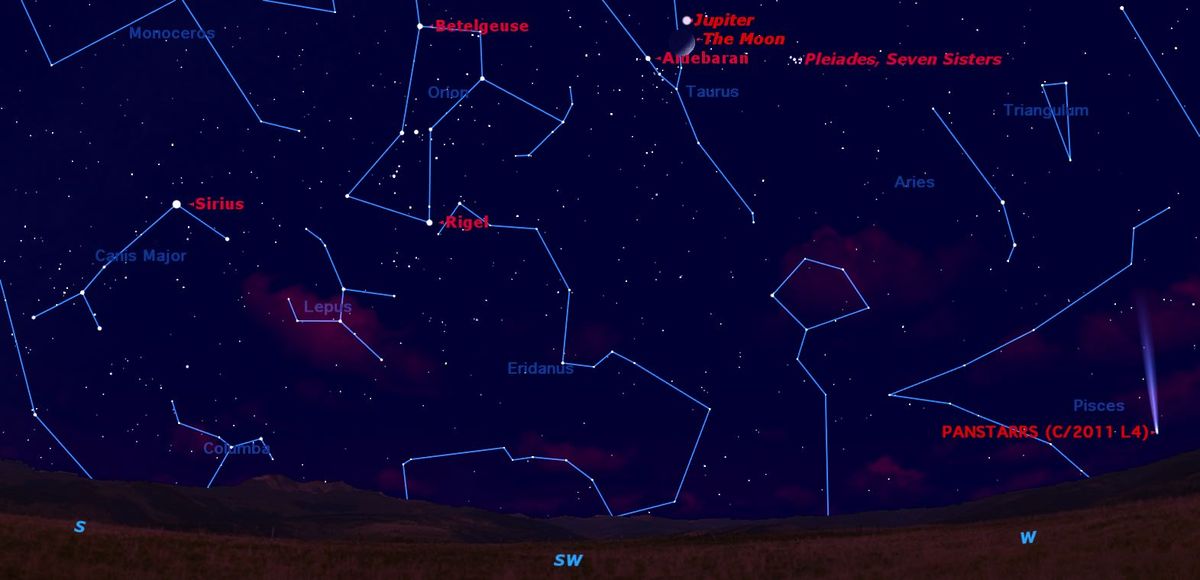
About 45 minutes after sunset on Sunday (March 17), the eye-catching celestial duo will be visible in the southwest sky, roughly two-thirds up from the horizon to the point directly overhead (called the zenith).
The moon will be a wide crescent at the time, 34 percent illuminated by the sun, and will sit below Jupiter. At its closest pass — which will occur at around 10:30 p.m. local daylight time along the U.S. East Coast, and around 7:00 p.m. local time for the West Coast — Earth's natural satellite will be just 2 degrees from the giant planet. (For reference, your clenched fist held at arm's length measures about 10 degrees.)
After its closest approach, the moon, moving at its own apparent diameter per hour, will appear to slowly move away from Jupiter to the east (left). [Amazing Night Sky Photos by Stargazers (March 2013)]
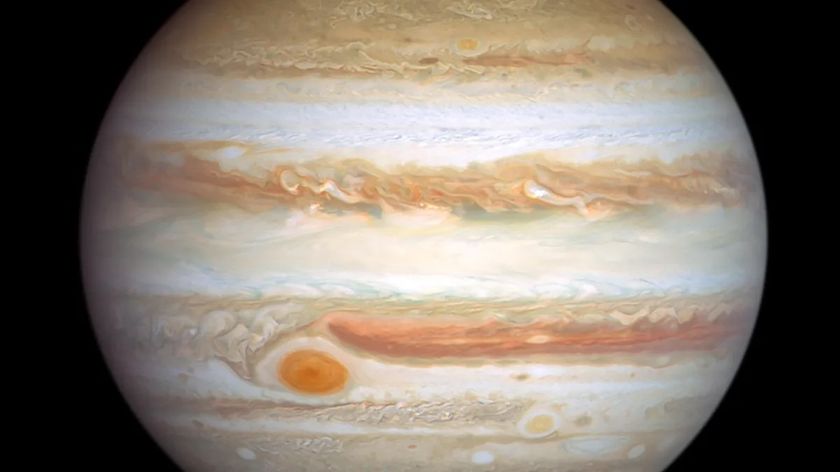
Even without the moon, Jupiter readily attracts attention. It’s the brightest "star" of the night, coming into view high in the southwest during the early stages of twilight. The first-magnitude star Aldebaran flickers into view next, about 5 degrees to the lower left of Jupiter, its orange color helping it to stand out from the deepening dark-blue sky.
Last to appear are the famous Pleiades and Hyades star clusters as the sky darkens from purple to black. The entire array of the moon, planet, bright star and star clusters sits within the constellation of Taurus (The Bull).
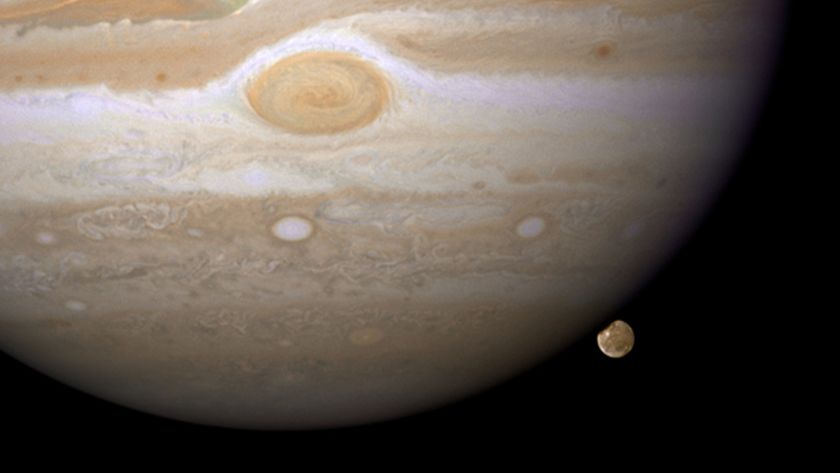
Binoculars are perfect for observing the whole Taurus get-together. Even the most ordinary pair will show dozens of Pleiades and Hyades stars, and at least one, two, or three of Jupiter’s four bright Galilean moons (Ganymede, Callisto, Io and Europa).
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Be sure to check out Jupiter on the evening of March 24, when any small telescope will show it closely flanked above and below by two seventh-magnitude background stars in Taurus, masquerading as an extra pair of renegade Galilean satellites.
In a telescope, Jupiter is best observed during early evening when it’s still high and its image reasonably calm. Viewing at such times shows the king of planets as a great big belted ball with tantalizing glimpses of detail.
As the evening grows late, the whole assemblage wheels lower in the west and sets soon after midnight.
Editor's note: If you snap an amazing photo of Jupiter and the moon in the night sky, or any other celestial object, and you'd like to share for a possible story or image gallery, please send images and comments, including location information, to managing editor Tariq Malik at spacephotos@space.com
Joe Rao serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for The New York Times and other publications, and he is also an on-camera meteorologist for News 12 Westchester, New York. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on SPACE.com.