Diagram of the Human Nervous System (Infographic)
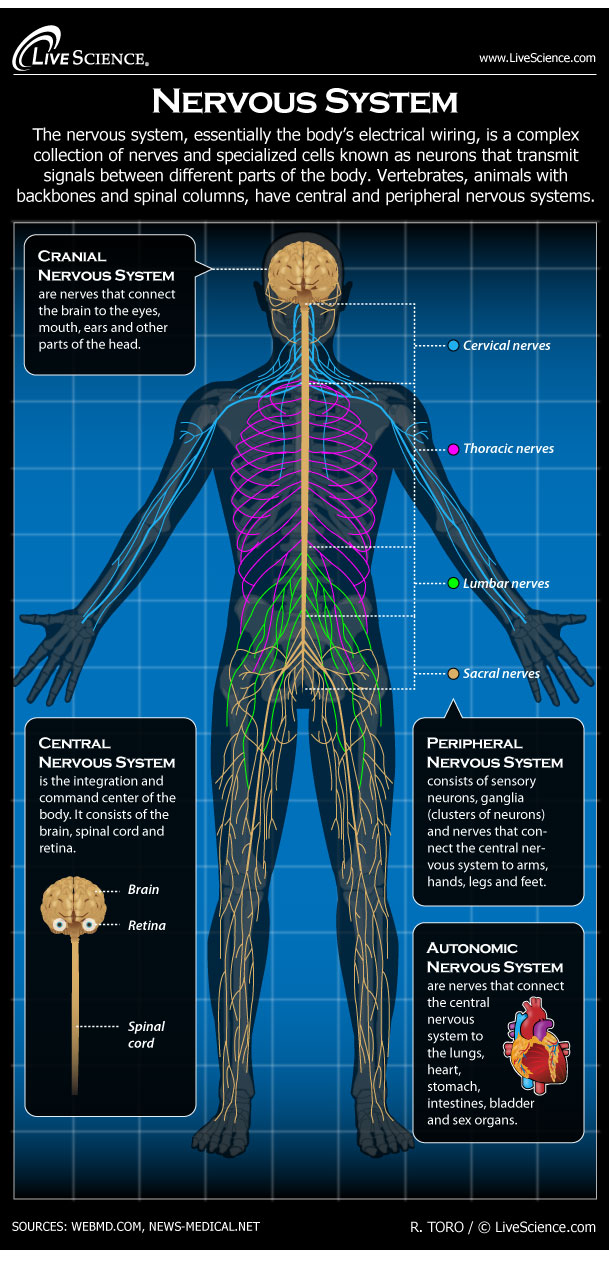
The nervous system, essentially the body’s electrical wiring, is a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body. Neurons signal to other cells through fibers called axons. Chemicals called neurotransmitters are released at gaps called synapses. These communications take only a fraction of a millisecond. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as light and sound. Motor neurons carry activation signals to muscles and glands. Neurons are supported and fed by glial cells. “Glial” derives from the Greek word for “glue.” Vertebrates, animals with backbones and spinal columns, have central and peripheral nervous systems. The Central Nervous System is the integration and command center of the body. It consists of the brain, spinal cord and the retinas of the eyes. The Peripheral Nervous System consists of sensory neurons, ganglia (clusters of neurons) and nerves that connect the central nervous system to arms, hands, legs and feet. The Cranial Nervous System nerves connect the brain to the eyes, mouth, ears and other parts of the head. The Autonomic Nervous System nerves connect the central nervous system to the lungs, heart, stomach, intestines, bladder and sex organs. The branch of medicine that studies the nervous system is called neurology. Doctors who treat the nervous system are neurologists.
Related:
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

