Diagram of the Human Integumentary System (Infographic)
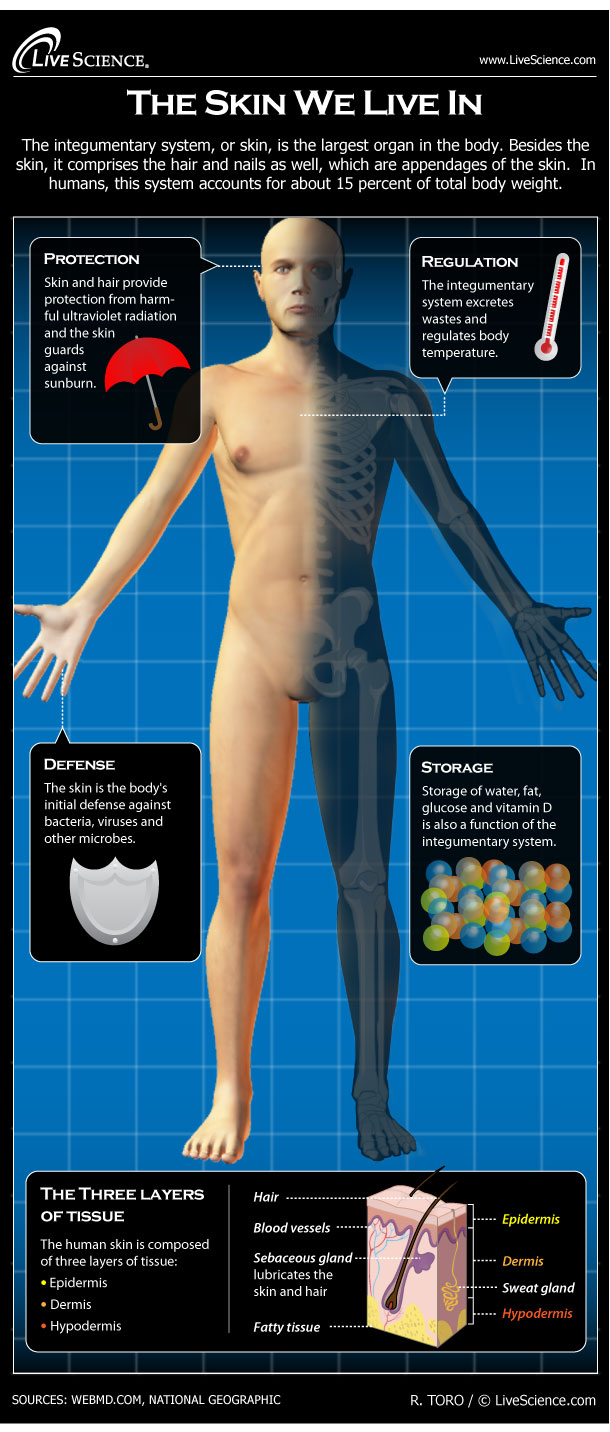
The integumentary system, or skin, is the largest organ in the body. Besides the skin, it comprises the hair and nails as well, which are appendages of the skin. In humans, this system accounts for about 15 percent of total body weight. Skin and hair provide protection from harmful ultraviolet radiation and the skin guards against sunburn. It also waterproofs, cushions and protects the body from infection. The integumentary system excretes wastes and regulates body temperature. The skin is the body's initial defense against bacteria, viruses and other microbes. Human skin color is determined by the interaction of melanin, carotene and hemoglobin.
((VideoProviderTag|jwplayer|Ams60mDN|100%|100%))
Storage of water, fat, glucose and vitamin D is also a function of the integumentary system. The human skin is composed of three layers of tissue: • Epidermis: the top layer of skin. It does not contain blood vessels. The epidermis is about one-tenth of a millimeter thick. • Dermis: the middle layer of skin is composed of the Papillary layer and the Reticular layer. These layers provide elasticity. • Hypodermis: the deepest layer of skin helps insulate the body and cushion internal organs. The hypodermis is composed of adipose tissue that stores excess energy as fat.
Related:
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

