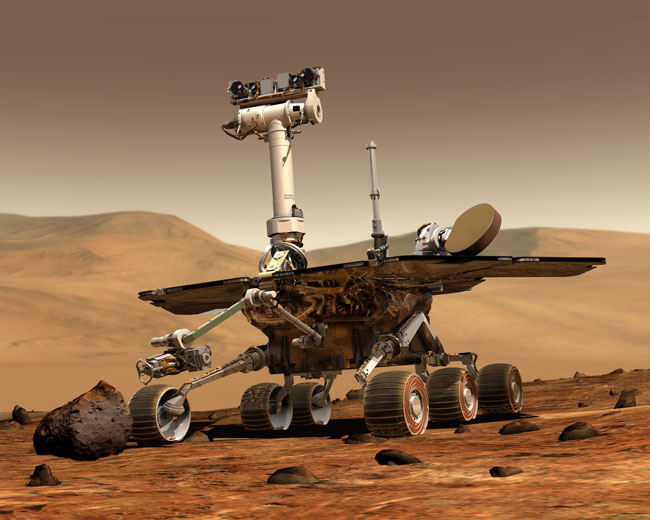
NASA's long-lived Opportunity Mars rover has gone into a self-imposed standby mode on the Red Planet, the robot's handlers say.
Mission controllers for Opportunity, which landed on Mars in January 2004, first learned of the issue on Saturday (April 27). On that day, the rover got back in touch after a nearly three-week communication moratorium caused by an unfavorable planetary alignment called a Mars solar conjunction, in which Mars and Earth are on opposite sides of the sun.
The Opportunity rover apparently put itself into standby on April 22 after sensing a problem during a routine camera check, mission managers said.
"Our current suspicion is that Opportunity rebooted its flight software, possibly while the cameras on the mast were imaging the sun," Opportunity project manager John Callas, of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., explained in a statement Monday (April 29).
"We found the rover in a standby state called automode, in which it maintains power balance and communication schedules, but waits for instructions from the ground," Callas added. "We crafted our solar conjunction plan to be resilient to this kind of rover reset, if it were to occur."
Opportunity's handlers prepared new commands Monday designed to spur the rover into resuming operations, mission team members said.
The golf-cart-size Opportunity landed on Mars more than nine years ago along with its twin, Spirit, on a three-month mission to search for signs of past water activity on the Red Planet. The two rovers found plenty of such evidence, and then kept trundling across Mars. Spirit was declared dead in 2010, but Opportunity is still going strong.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Mars solar conjunctions occur every 26 months, so Opportunity's team knows how to weather them. This most recent conjunction, in fact, is the fifth that the rover has endured.
Mars solar conjunctions affect NASA's entire fleet of robotic Red Planet explorers. Mission controllers resumed sending commands to the agency's venerable Mars Odyssey orbiter Monday and plan to do the same with the Mars rover Curiosity on Wednesday (May 1), officials said.
This story was provided by SPACE.com, a sister site to Live Science. Follow Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on SPACE.com.