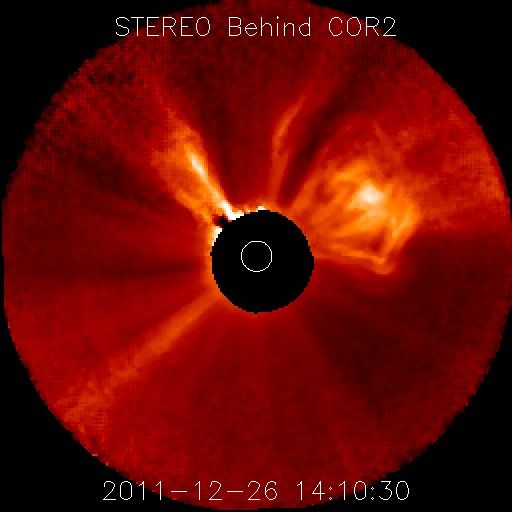
Particles ejected by recent solar storms are due to slam into Earth over the next few days, possibly causing super-charged northern lights displays and temporary radio blackouts in some areas, experts say.
On Monday (Dec. 26), the sun unleashed a massive eruption of solar plasma known as a coronal mass ejection (CME). The CME's fast-moving charged particles should squarely strike Earth's magnetic field at about 3:20 p.m. EST (2020 GMT) Wednesday, give or take seven hours, according to the website Spaceweather.com.
The particles from another CME could deliver a glancing blow to our planet a few hours earlier on Wednesday, Spaceweather.com reported.
The two impacts will likely spawn minor and/or moderate geomagnetic storms at high latitudes on Wednesday and Thursday. If they're powerful enough, geomagnetic storms can temporarily disrupt GPS signals, radio communications and power grids.
"Category G1 (Minor) geomagnetic storms are expected 28 and 29 December due to multiple coronal mass ejection arrivals," the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Space Weather Prediction Center wrote in an update Tuesday (Dec. 27). "R1 (Minor) radio blackouts are expected until 31 December."
Geomagnetic storms can also trigger dramatic aurora displays, which are also known as the northern and southern lights. So skywatchers at higher latitudes may want to look up after sunset over the next few days.
The sun's recent eruptions are part of a pattern.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
After remaining surprisingly quiet from 2005 through 2010, our star has come alive in 2011, spouting off numerous powerful flares and CMEs. An August flare, for example, was the strongest one seen in more than four years.
Most experts expect such outbursts to continue over the next few years. Solar activity waxes and wanes on an 11-year cycle, and scientists think the current one — known as Solar Cycle 24 — will peak in 2013.
This story was provided by SPACE.com, a sister site to OurAmazingPlanet. You can follow SPACE.com senior writer Mike Wall on Twitter: @michaeldwall. Follow SPACE.com for the latest in space science and exploration news on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.