Gallery: First Red List of Endangered Ecosystems
Seagrass meadows — South Australia

Status: endangered-critically endangered
Like an underwater meadow, seagrass covers the sandy seafloor off South Australia. Seagrass is a habitat and a nursery for a variety of marine life.
German tamarisk pioneer vegetation — Europe

Status: endangered
Tamarisk are wispy but tough shrubs that pioneer new spots to grow in wet, sandy sites such as ever-shifting riverbanks.
Coolibah-Black Box woodland — Australia

Coolibah-Black Box woodland — Australia
Status: endangered
This mature woodland features large eucalyptus, coolibah and black box trees, fed by floods.
Tapia forest — Madagascar
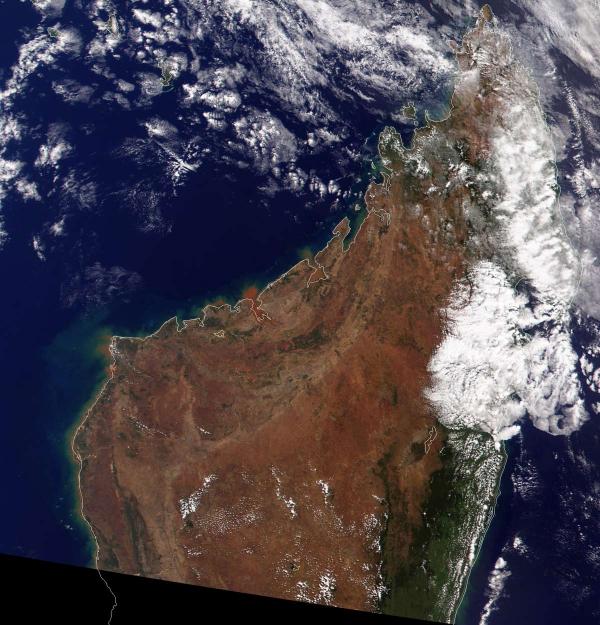

Status: endangered
The remarkable Tapia tree forests of Madagascar are named for one of the island's many unique species, evolved in near-isolation over millennia.
Semi-evergreen vine thicket — Australia

Status: endangered
The dense vegetation of this vine thicket was home to one of the few southern Australia sightings of the black-striped wallaby. Much of the habitat has been cleared to grow wheat.
Great Lakes Alvar — U.S. and Canada
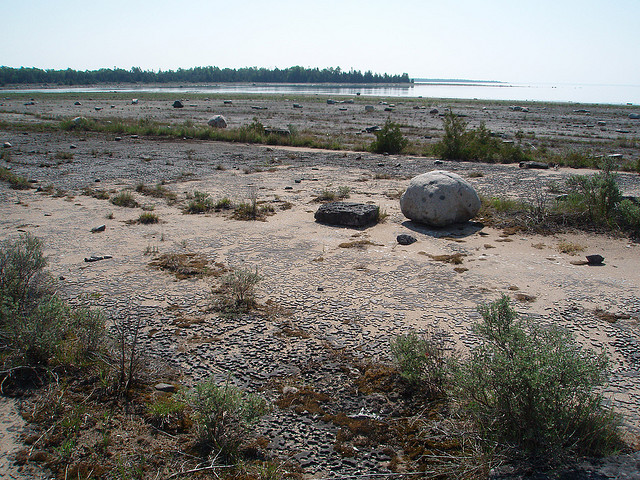

Status: vulnerable-endangered
Alvars are flat expanses of limestone bedrock, ground smooth by glaciers and covered with a thin scrim of soil. Almost all of North America's alvars are found near the Great Lakes.
Reedbeds — Europe
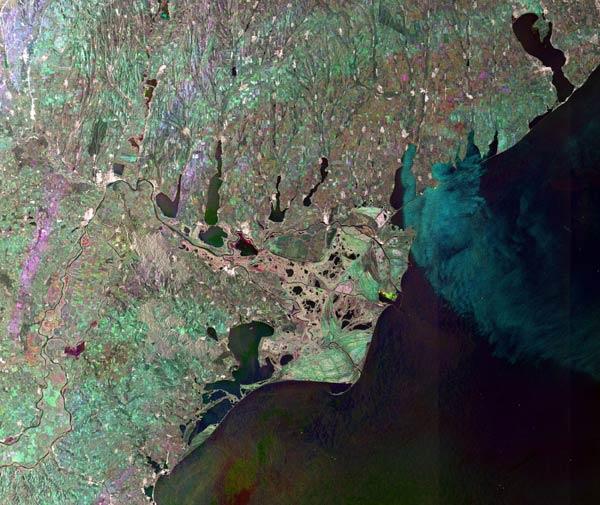

Status: vulnerable
In Europe, reedbeds provide vital breeding habitat for several vulnerable and endangered bird species. The reeds, dominated by one species, Phragmites australis, grow in wetlands, marshes, river deltas and even ditches — any marginal habitat with stagnant, brackish water.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Floodplain ecosystem of river red gum and black box — southeastern Australia
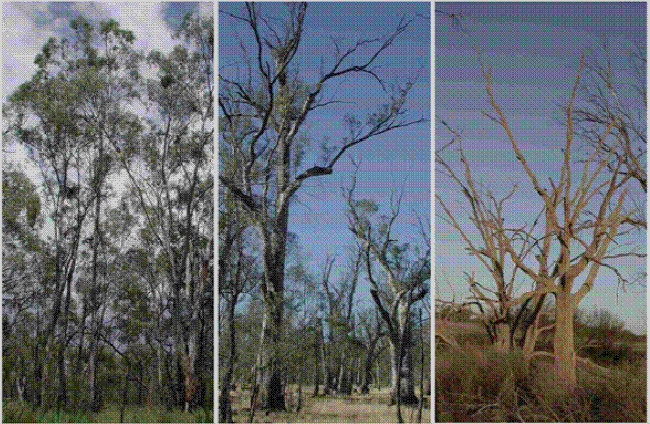

Status: vulnerable
Both the river red gum and black box trees thrive along the banks of rivers crossing the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia's largest floodplain. Several rare species call the forest home, and live nowhere else on Earth.
Tepui shrubland — Venezuela

Status: least concern
The Tepui shrubland is a lofty province of table mountains elevated above 4,900 feet (1,500 meters). Tepui, the local word for table mountains, now also refers to the distinctive vegetation growing on the flat-topped peaks.
Granite gravel fields and sandplains — New Zealand

Status: least concern
The granite gravels and sand dunes of New Zealand's spectacular Fiordlands, on the South Islands, are a rare example of sediments formed entirely from granite. The pink, white and black speckled igneous rock dominates the local geology, creating the unique piles of sediment as it erodes.