Malignant Mesothelioma: Symptoms and Treatments
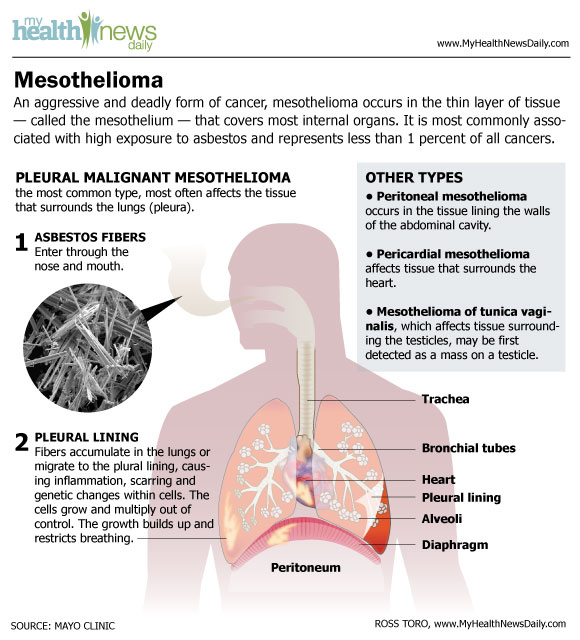
Malignant mesothelioma is a rare type of cancer that grows in the thin layer of tissue that covers the heart, lungs and other internal organs. This membrane, called mesothelium, protects organs by making fluid that allows, say, the lungs to move while breathing.
According to the Mesothelioma Cancer Alliance, there are three varieties of malignant mesothelioma: pleural mesothelioma, which occurs in the the lung's lining, or pleura; peritoneal mesothelioma, which occurs in the abdominal cavity wall, or peritoneum; and pericardial mesothelioma, which occurs in the lining of the heart, or the pericardium.
Malignant pleural mesothelioma is the most common type, with about 70 percent of mesothelioma diagnoses. Another 15 percent to 20 percent of diagnoses are for peritoneal mesothelioma, while pericardial mesothelioma represents about 10 percent of diagnoses.
Causes
Mesothelioma, no matter the type, is rare, with about 2,000 or 3,000 people in the United States getting a diagnosis each year, according to the American Lung Association.
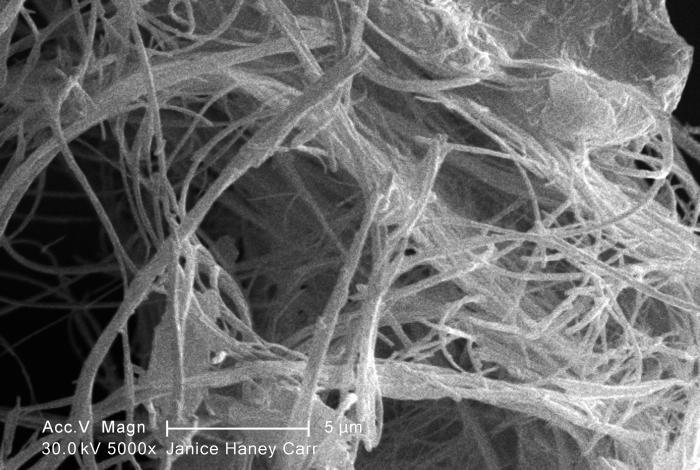
The main risk factor for malignant mesothelioma is contact with asbestos. Asbestos is a natural, fibrous silicate mineral found in rock and soil that is heat resistant and very durable. It was once used in everything from insulation to car parts until its danger became better understood in the 1970s. According the American Lung Association, 70 percent to 80 percent of those diagnosed with mesothelioma had heavy contact with asbestos.
"Asbestos exposure through work with insulation, construction, shipbuilding or textiles or exposure to soiled clothes of an asbestos worker results in a six-fold increase in the risk of developing lung cancer and mesothelioma," said Dr. Megan Baumgart, an assistant professor in the department of medicine, hematology/oncology at the Wilmot Cancer Institute in Rochester, New York."This risk is significantly higher in those who smoke in addition to asbestos exposure.”
What makes asbestos so dangerous is that its fibers are microscopic, up to 1,200 times smaller than a human hair, according to the Environmental Protection Agency. The small particulate size makes asbestos easily inhaled. The tiny fibers enter the body, and then lodge in the internal tissue of the respiratory system, such as the lining of the lungs and inner cavity tissue. The body has a hard time getting rid of the particles once they are lodged into tissue.
Symptoms
Symptoms typically show up 35 to 50 years after asbestos exposure, according to the American Lung Association. So, by the time a person is affected by mesothelioma they are typically over the age of 65.
Symptoms differ depending on where in the body the cancer grows. In pleural mesothelioma, which affects the tissue around the lungs, symptoms include chest pain under the rib cage, shortness of breath, painful coughing, unexplained weight loss and lumps of tissue under the skin on the chest, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Peritoneal mesothelioma, which is when the condition occurs in the abdomen, has symptoms of pain, swelling or lumps in the abdomen and unexplained weight loss, according to the Mayo Clinic.

Diagnosis and treatment
Though there are many symptoms of mesothelioma, it is hard to diagnose because many of the symptoms are shared by other diseases. A doctor will typically check for lumps during a physical checkup and may also order X-ray and computerized tomography (CT) scans to determine if the patient's body has any abnormalities consistent with mesothelioma. If the doctor suspects mesothelioma, a biopsy of the affected area may also be ordered, according to the Mayo Clinic.
If mesothelioma is diagnosed, then the doctor will "stage" the diagnosis, meaning the cancer will be defined by severity. According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), staging is broken up into three categories called TNM. The "T" stands for the extent that the primary tumor has spread. The "N" stands for how much of the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. "M" stands for whether the cancer has metastasized, which means the cancer spread to other organs.
Once the doctor understands the staging of the case, then a plan of treatment can be made. Though there is no cure for mesothelioma, treatments can help increase a patient's life expectancy.
Radiation, surgery and chemotherapy are treatment options for those diagnosed with mesothelioma, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine. Surgery as a cure has been tried in rare cases where the patient is otherwise healthy, but often by the time it's diagnosed, malignant mesothelioma has spread to other organs, according to the Cancer Society.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved two medications for the treatment of malignant mesothelioma. According to the National Cancer Institute, these are pemetrexed disodium (sold in the United States under the brand name Alimta) and cisplatin (sold as Platinol and Platinol-AQ).
Additional resources
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.











