Black Hole's Guts Modeled in Supercomputer Simulation

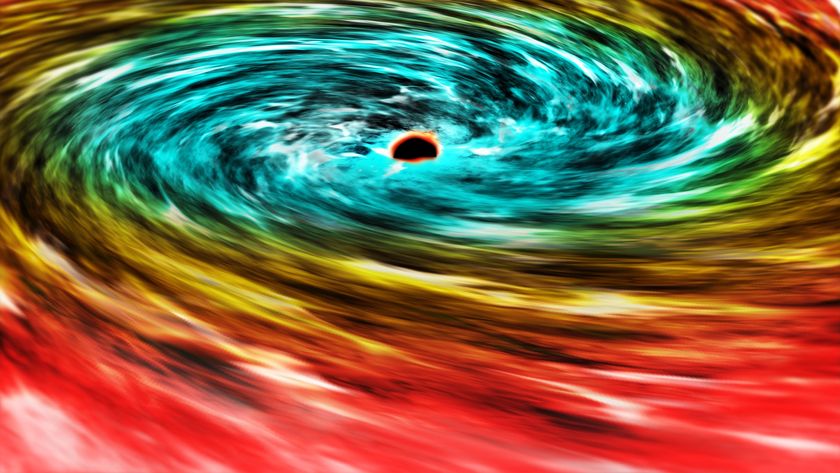
The inner workings of black holes are a bit clearer thanks to a supercomputer simulation that showed how matter falling into black holes emits light.
By analyzing a simulation of a black hole about the size of a star, researchers saw how two kinds of X-rays can be emitted by the stuff falling into the densest objects in the known universe.
"Our work traces the complex motions, particle interactions and turbulent magnetic fields in billion-degree gas on the threshold of a black hole, one of the most extreme physical environments in the universe," lead researcher Jeremy Schnittman, an astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., said in a statement.
Stellar-mass black holes are created when massive stars run out of fuel, collapsing into extremely dense objects with strong gravitational pulls.
Gas orbiting a black hole eventually builds up into a flattened disk as it falls toward the black hole's center. The gas can reach temperatures of up to 20 million degrees Fahrenheit (12 million degrees Celsius) — about 2,000 times hotter than the sun's surface — as it nears the center. The hot gas shines in low-energy light known as "soft" X-rays.
"Black holes are truly exotic, with extraordinarily high temperatures, incredibly rapid motions and gravity exhibiting the full weirdness of general relativity," Julian Krolik, a professor at Johns Hopkins University, said in a statement. "But our calculations show we can understand a lot about them using only standard physics principles."
Scientists have also observed black holes producing light with energy tens to hundreds of times greater than soft X-rays. The origin of these "hard" X-rays was a mystery before the research team modeled the process.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Schnittman and his team found that the density, speed and temperature of the gas are increased by magnetic fields in the disk, creating a "turbulent froth orbiting the black hole at speeds approaching the speed of light," NASA officials wrote in a statement.
The magnetic pressures on the disk create a corona above it that leads to the production of hard X-rays.
The scientists used 27 days of data from the Ranger supercomputer located at the University of Texas, Austin to produce these results. The findings were published in the June 1 issue of The Astrophysical Journal.
This story was provided by SPACE.com, a sister site to LiveScience. Follow Miriam Kramer on Twitter and Google+. Follow us on Twitter, Facebook and Google+. Original article on SPACE.com.