GlobalFlyer Seeks Round-the-World Record
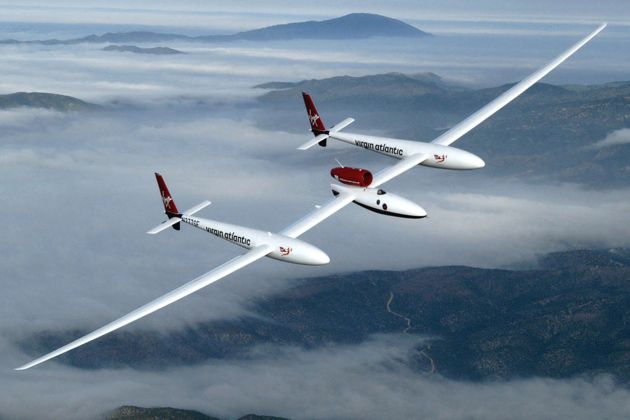

If all goes according to flight plan, an exotic looking aircraft will be piloted into the history books this month. An attempt will be made to set the record for the first solo non-stop flight around the Earth.
The uplifting motto behind the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer project seems to say it all: "One man...One plane...One world."
Designed by the visionary aerospace engineer Burt Rutan of Scaled Composites in Mojave, California -- the mind behind the SpaceShipOne rocket plane -- the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer is to be piloted by millionaire businessman and aerial adventurer Steve Fossett. Sir Richard Branson, chairman of Virgin Atlantic, is bankrolling the GlobalFlyer effort, and is also the project's reserve pilot.
Launch site for the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer's record attempt will be the Salina Municipal Airport in Salina, Kansas. If Mother Nature cooperates, the aircraft will depart company with the ground in early January. The specific date will depend on weather conditions locally and on the airplane's track.
Rolling down one of the longest runways in North America, GlobalFlyer's itinerary is nothing short of non-stop. That is, stay airborne using onboard fuel and circumnavigate the world. Winging through the skies at speeds of over 285 miles per hour (250 knots), the craft's flight should be completed inside 80 hours.
Tight quarters
The GlobalFlyer mission builds on the December 1986 flight of the two-seater Voyager aircraft that flew around the globe non-stop, non-refueled. That milestone flight took 9 days, 3 minutes and 44 seconds, co-piloted by Jeana Yeager and Dick Rutan, brother of Burt who designed Voyager, too.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Early sketch by aircraft designer Burt Rutan led to building GlobalFlyer. Credit: Virgin Atlantic/Scaled Composites
Solo pilot Fossett will be sitting in tight quarters. GlobalFlyer's cockpit is a mere 7 feet (2.1 meters) long within the main fuselage, just behind the nose landing gear and below the engine.
GlobalFlyer is powered by a single turbofan jet engine, fed by thirteen separate fuel tanks on the aircraft.
The plane's unique structure is all graphite/epoxy. The stiffest carbon fibers are used in the construction of the craft's long wings, and the skin is a sandwich of graphite/epoxy and Aramid honeycomb.
Optimized aerodynamics
Burt Rutan told LiveScience that unlike SpaceShipOne, which in 2004 won the Ansari X Prize for the first private craft to fly into space twice in two weeks, the GlobalFlyer does not immediately lead to some big follow-on industry, like space tourism.
"What we did here was to use some optimized aerodynamics (high lift/drag), combined with a configuration that can carry a very unusually high amount of fuel as a percentage of takeoff weight -- 82 percent, with Voyager being 73 percent -- and thus show that the non-refueled world flight range performance could be done even with a relatively inefficient turbofan engine," Rutan explained.
"Probably the only real effect for the commercial airline arena might be to preclude some future airliner design from claiming it has the best range in the world," Rutan added. "No airliner with turbofans will exceed the GlobalFlyer range performance."
GlobalFlyer effort might spur airline designers to get more courageous and use 100 percent composites in their structures. "They continue to use a poor combination of metal and composites that results in a lot of structural problems at the composite-metal interfaces," Rutan said.
Soaring sojourn
Mission control for the GlobalFlyer attempt will be based at a Kansas State University facility at the Salina Municipal Airport in Kansas.
The flight path will take GlobalFlyer across the Atlantic to the United Kingdom, flying southeast across the Mediterranean and the Gulf before turning east towards Pakistan, India, China and Japan. The final leg of the soaring sojourn takes the plane out over the Pacific towards Hawaii before crossing the west coast of the United States and touching down at the Salina, Kansas airport.
"I hope that we can add Salina to the roll call of sites like Kitty Hawk which have been the setting for milestones in aviation history," Branson said.

Leonard David is an award-winning space journalist who has been reporting on space activities for more than 50 years.