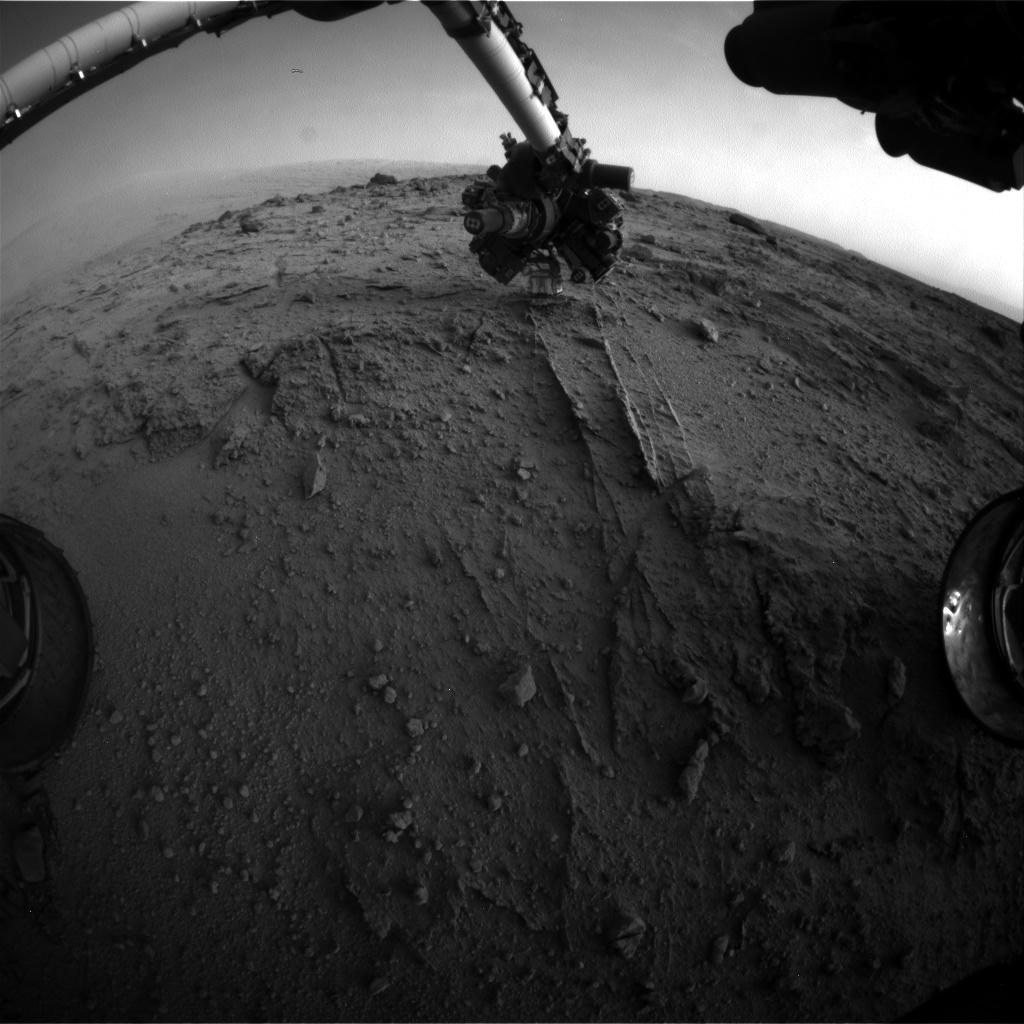
NASA's Curiosity rover has found yet more evidence of ancient Martian water, this time during a recent pit stop along the way toward a huge Red Planet mountain.
The 1-ton Curiosity rover paused to examine a few rocks late last week, making the first of five planned science stops en route to the 3.4-mile-high (5.5 kilometers) Mount Sharp. The break was fruitful, returning further signs of long-ago liquid water, researchers said.
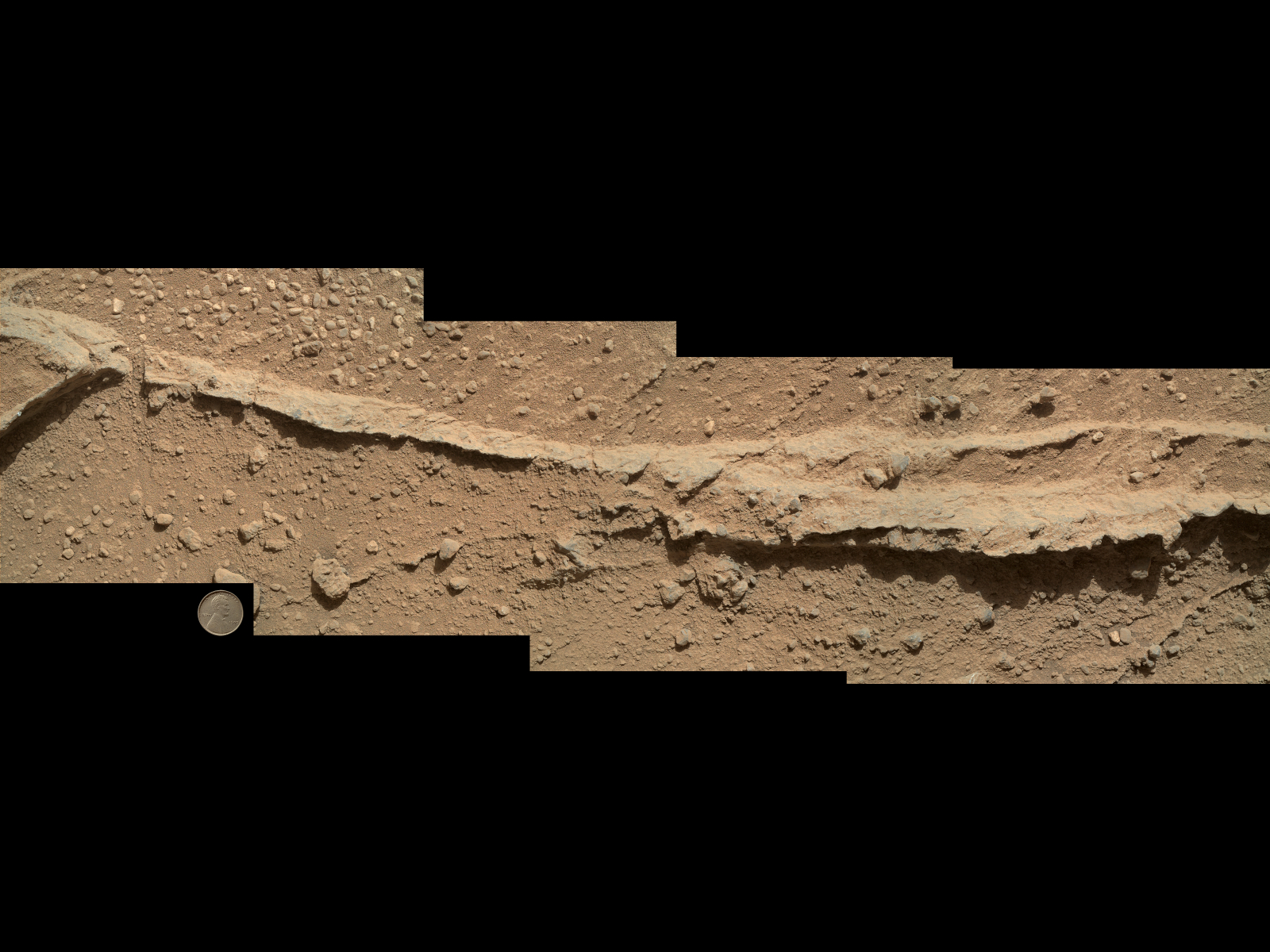
"We examined pebbly sandstone deposited by water flowing over the surface, and veins or fractures in the rock," Curiosity science team member Dawn Sumner, of the University of California, Davis, said in a statement. "We know the veins are younger than the sandstone because they cut through it, but they appear to be filled with grains like the sandstone." [Latest Mars Photos by the Curiosity Rover]

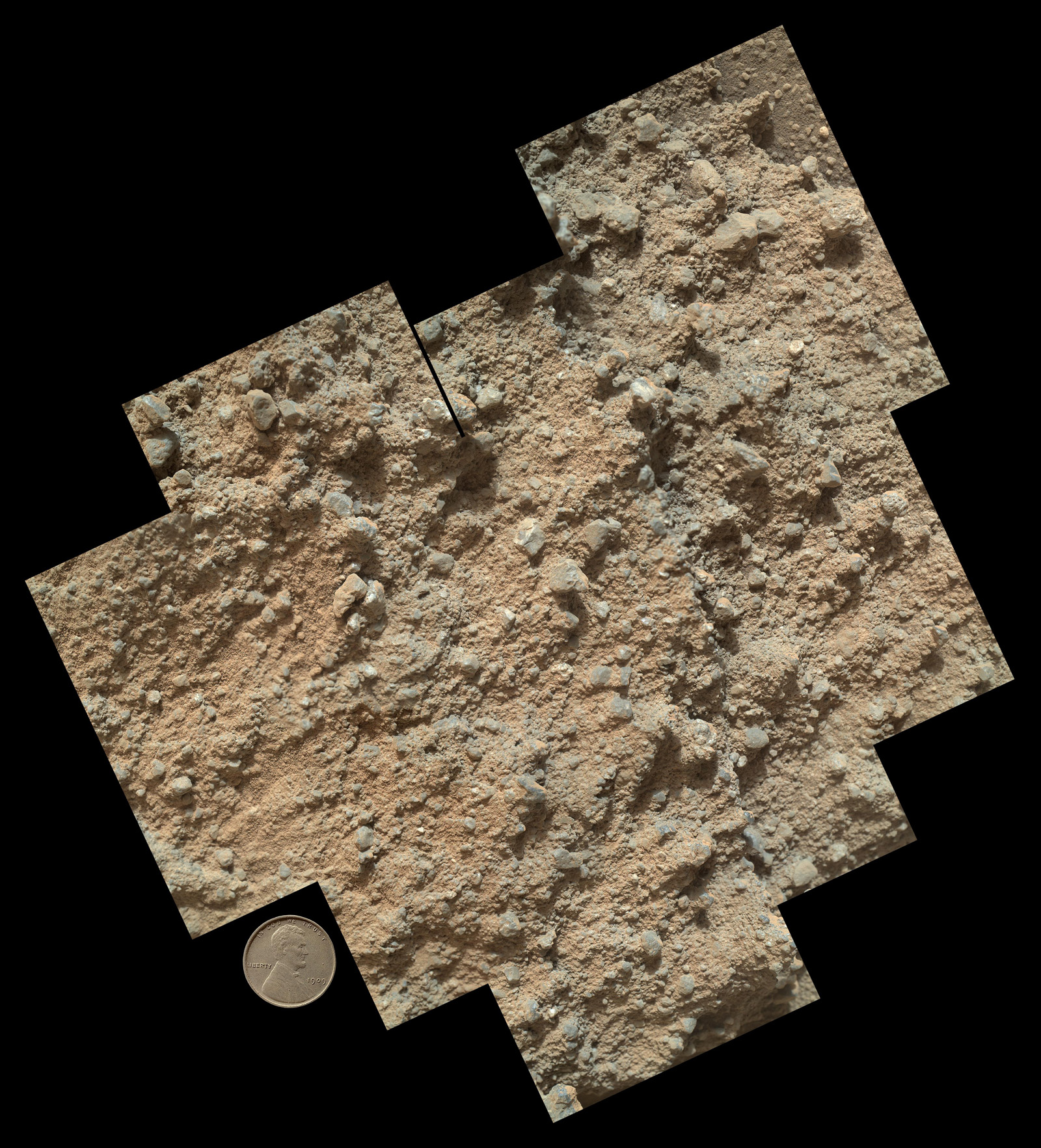
Curiosity landed inside Mars' Gale Crater in August 2012 to determine if the Red Planet has ever been capable of supporting microbial life. The six-wheeled robot checked off that main mission goal this past March, finding that a location near its landing site called Yellowknife Bay was indeed wet and habitable billions of years ago.
In July, Curiosity set out on the 5.3-mile (8.6 km) trek to Mount Sharp, which has been the rover's primary destination since before its November 2011 launch. Researchers want Curiosity to climb up through the mountain's foothills, studying its many layers for clues about the Red Planet's changing environmental conditions.

The rover team also wants to understand the geology of the area between Yellowknife Bay and Mount Sharp, so they planned out investigations at five "waypoints" along the route. The first came Thursday (Sept. 19) at an outcrop scientists dubbed "Darwin."
"We want to understand the history of water in Gale Crater. Did the water flow that deposited the pebbly sandstone at Waypoint 1 occur at about the same time as the water flow at Yellowknife Bay?" Sumner said.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"If the same fluid flow produced the veins here and the veins at Yellowknife Bay, you would expect the veins to have the same composition," Sumner added. "We see that the veins are different, so we know the history is complicated. We use these observations to piece together the long-term history."
Curiosity spent four days studying the rocks at Darwin, then resumed the journey to Mount Sharp on Sunday (Sept. 22) with a 75-foot (22.8 meter) drive. Curiosity has now covered about 20 percent of the distance from Yellowknife Bay to Mount Sharp, researchers said.
"There's a trade-off between wanting to reach Mount Sharp as soon as we can and wanting to chew on rocks all along the way," Curiosity science team member Kenneth Williford, of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., said in a statement. "Our team of more than 450 scientists has set the priority on getting to Mount Sharp, with these few brief waypoint stops."
Follow Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on SPACE.com.