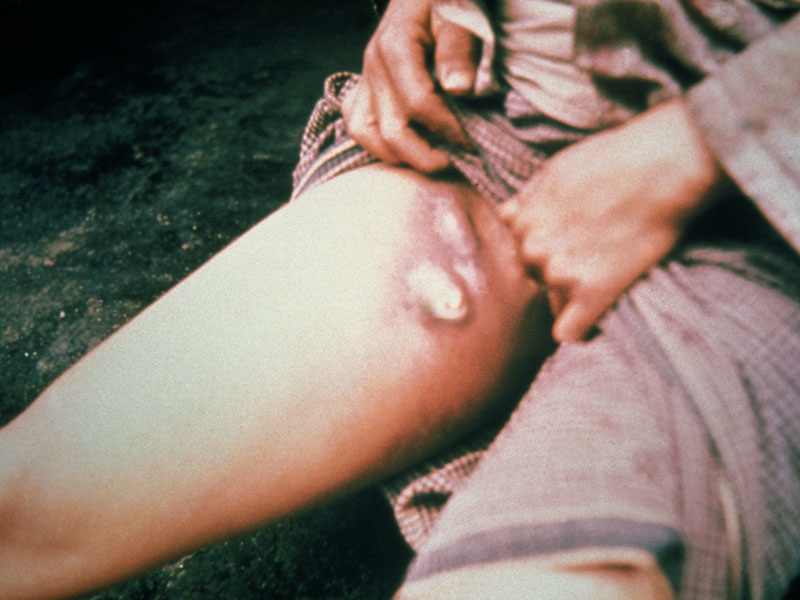
Bubonic plague, the deadly scourge that wiped out half of Europe during the Middle Ages, still lurks in pockets of the globe, new research suggests.
Although plague is now rare in Europe, it recently sickened more than 10,000 people in Congo over a decade, and cases still occasionally emerge in the Western United States, according to a study published Sept. 16 in the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.
The plague bacteria, Yersinia pestis, had lain dormant in China's Gobi Desert for centuries. But in the 1300s, it emerged with a vengeance, fanning out via trade routes from Asia to Europe and killing millions of people along the way. The plague was transmitted by fleas harbored by rats, which flourished in the overcrowded, filthy cities of the Middle Ages. By the end of the 1500s, between a third and half of Europe's population had died from the Black Death. [Pictures of a Killer: Plague Gallery]
Even during the 1900s, the plague still killed millions of people, but since then, the advent of better hygiene in cities and swift treatment with antibiotics has reduced this erstwhile killer into a rare disease.
Still present
Still, plague outbreaks still flare up around the world.
According to the new study, which tallied the reported cases of plague around the world between 2000 and 2009, more than 20,000 people became infected during that time. People contracted the disease via rodents, bad camel meat and sick herding dogs, the report said. Cases in Libya and Algeria re-emerged after decades of absence.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The biggest burden was in Africa: in Congo 10,581 people contracted plague, followed by Madagascar with 7,182 cases and Zambia with 1,309 cases.
"These events, although showing progress, suggest that plague will persist in rodent reservoirs mostly in African countries burdened by poverty and civil unrest, causing death when patients fail to receive prompt antimicrobial treatment," the authors wrote in their paper.
In the United States during that time period, 56 people contracted the plague and seven died. The cases occurred mainly because plague has become endemic in squirrels and wild rodents in the American West. Two of the fatalities were scientists: one who had conducted an autopsy on a wild mountain lion, and another who worked with plague bacteria in the lab.
Despite being a hotbed of plague in times past, Europe logged very few cases of the disease in the past decade. That may be because European cities keep their rodent populations in check, so the potential hosts for plague aren't as prevalent, the researchers said.
Follow Tia Ghose on Twitter and Google+. Follow LiveScience @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.

Tia is the managing editor and was previously a senior writer for Live Science. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Wired.com and other outlets. She holds a master's degree in bioengineering from the University of Washington, a graduate certificate in science writing from UC Santa Cruz and a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin. Tia was part of a team at the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel that published the Empty Cradles series on preterm births, which won multiple awards, including the 2012 Casey Medal for Meritorious Journalism.
Flu: Facts about seasonal influenza and bird flu
What is hantavirus? The rare but deadly respiratory illness spread by rodents