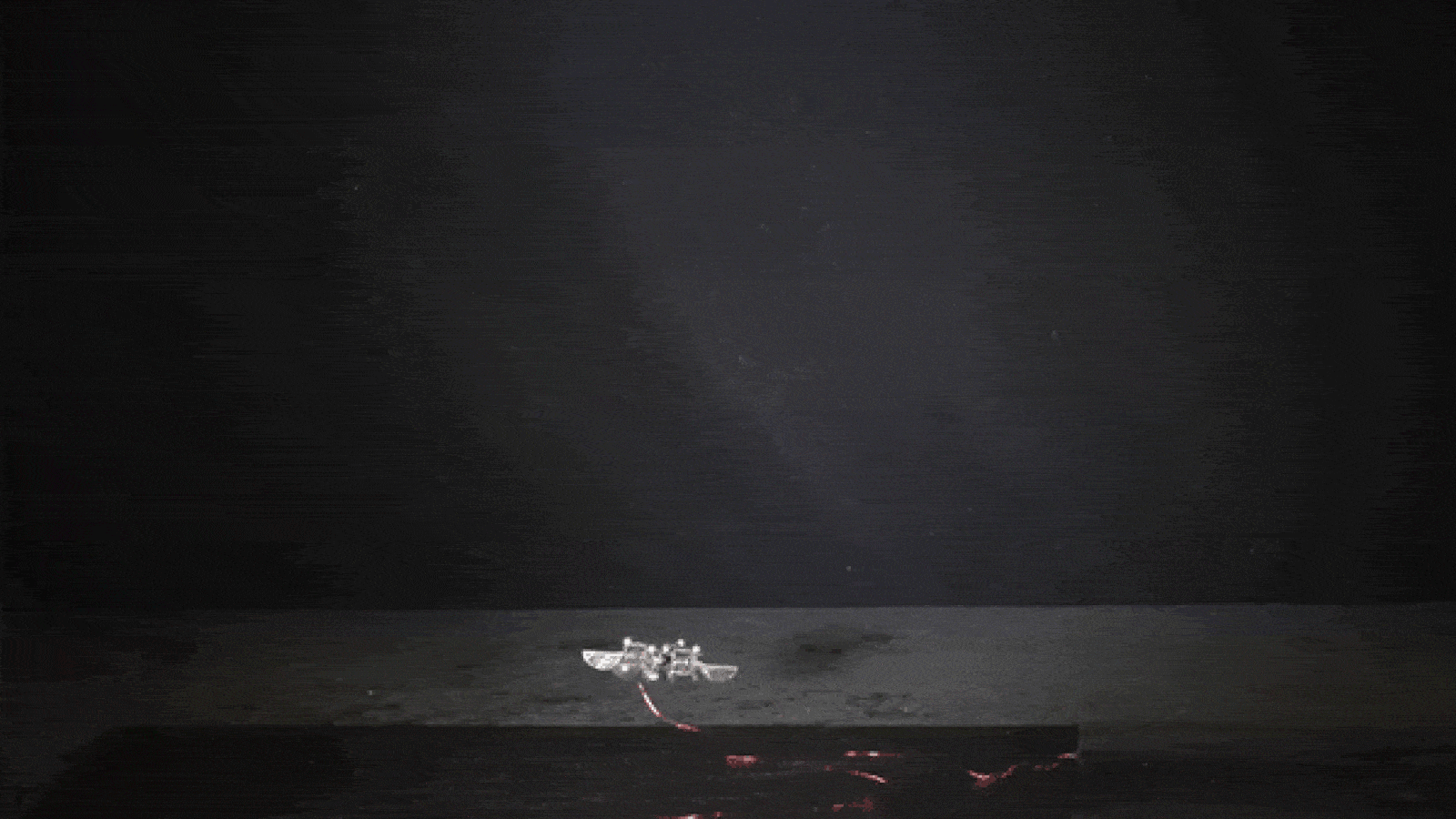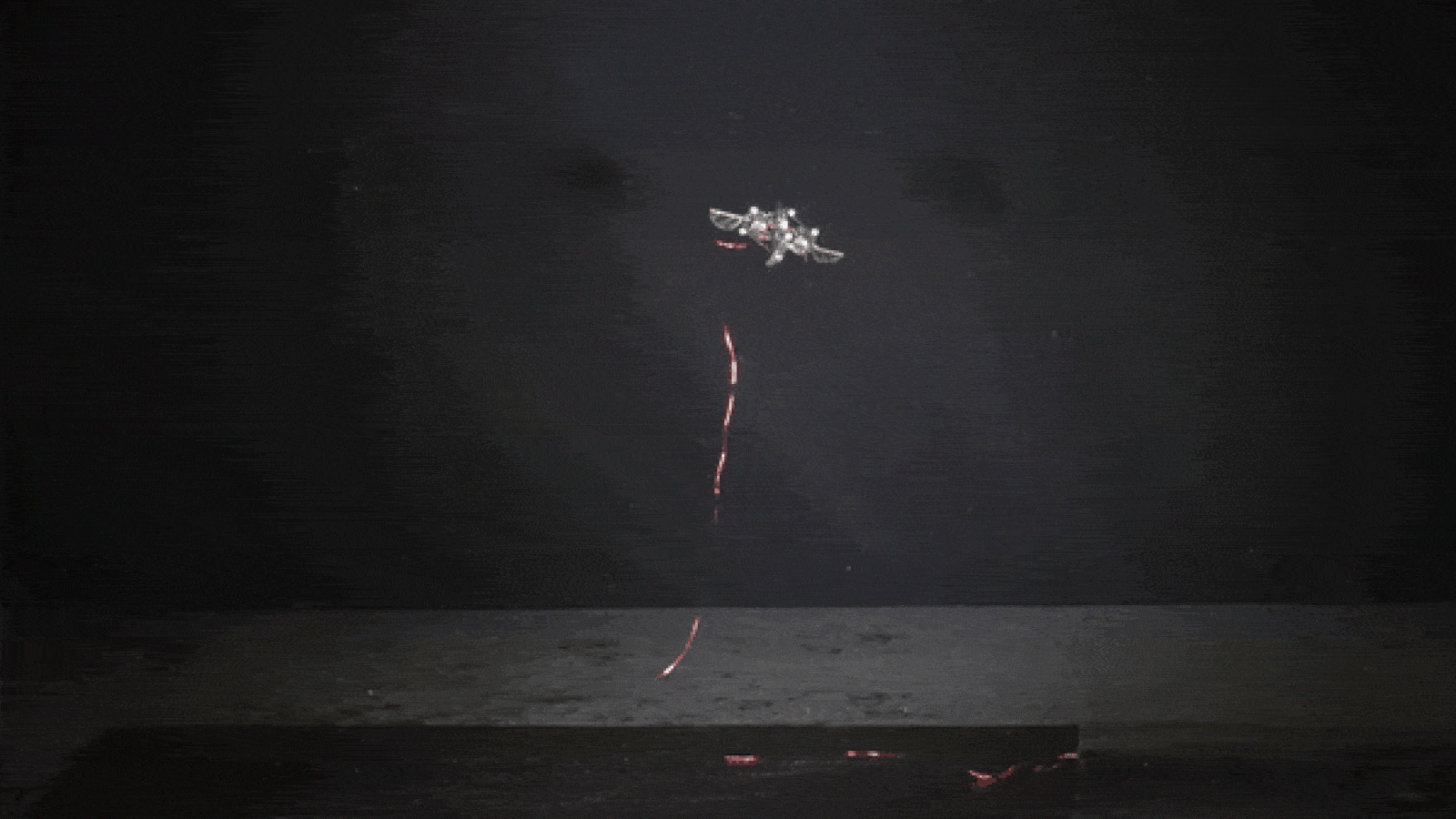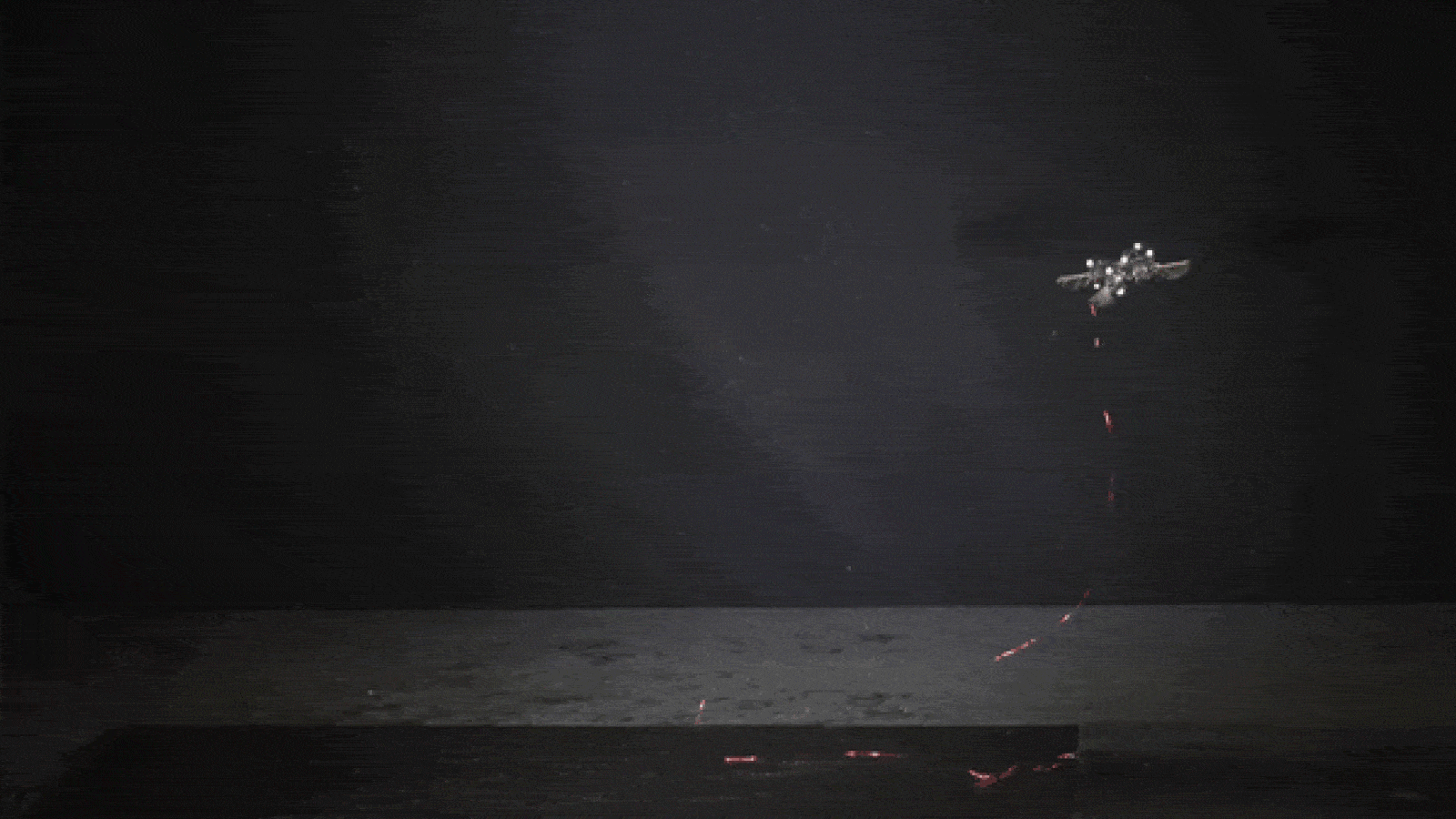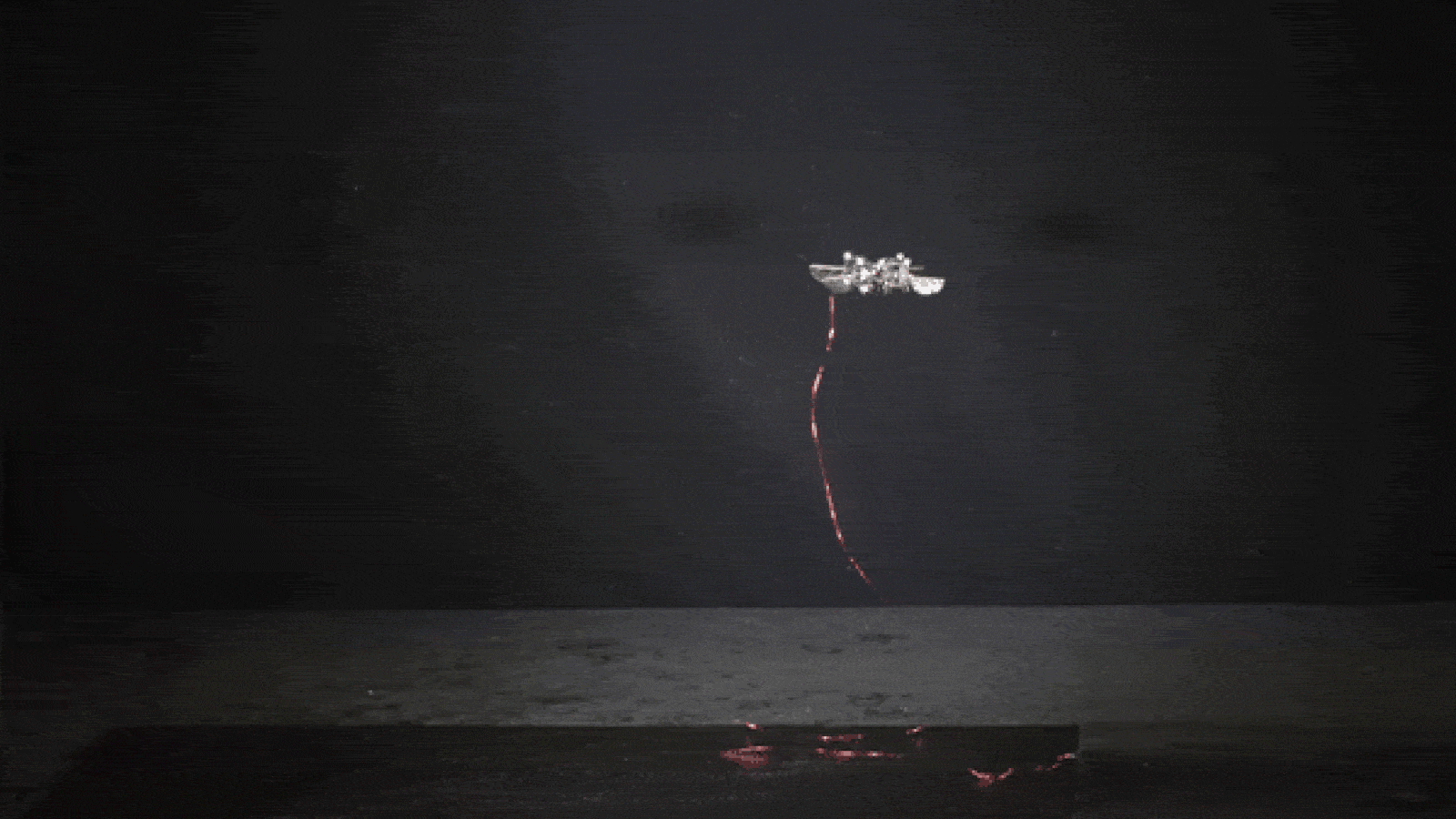Your Pee Could Power Future Robots

There's a new use for artificial hearts, and it involves a more taboo bodily fluid than blood.
A device that mimics the squeezing action of the human heart has been used to pump urine into a microbial fuel cell, which could power robots that convert the waste into electricity.
"In the future, we hope the robots might be used in city environments for remote sensing," where they could help to monitor pollution, said study researcher Peter Walters, an industrial designer at the University of the West of England. "It could refuel from public lavatories, or urinals, " Walters said.
Walters and colleagues at the University of Bristol have created four generations of these so-called EcoBots over the past decade. Previous versions of the robots ran off energy from rotten produce, dead flies, wastewater and sludge. [Super-Intelligent Machines: 7 Robotic Futures]
Each is powered by a microbial fuel cell, containing live microorganisms like those found in the human gut or sewage treatment plants. The microbes digest the waste (or urine) and produce electrons, which can be harvested to produce electrical current, Walters said.
The researchers have already proved the microbial fuel cells can use urine power to charge a mobile phone.
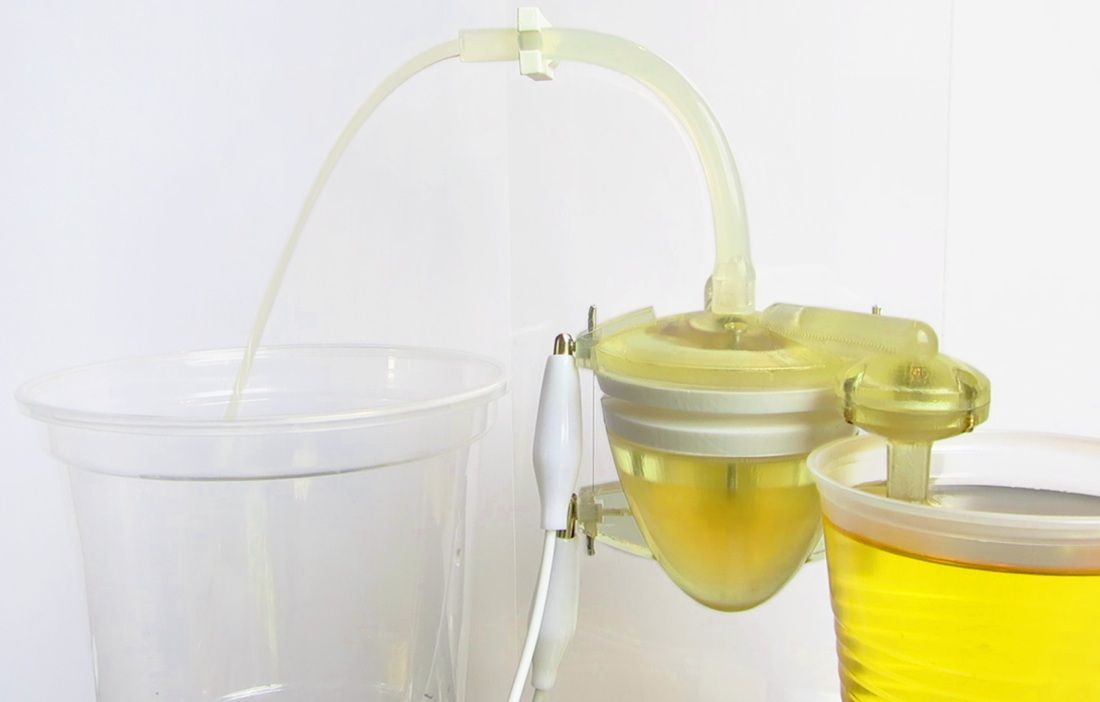
Now, the team has developed a device, made of artificial muscles, that delivers real human urine to the robot's microbial power stations. The pump is constructed from smart materials, called shape memory alloys, which remember their shape after being deformed.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Heating the artificial muscles with an electric current causes them to compress the soft center of the pump, forcing urine through an outlet that pumps it up to the height of the robot's fuel cells. Removing the heat allows the muscles to revert to their original shape, allowing more fluid to enter the pump — much as a heart relaxes to suck in more blood.
Twenty-four of these fuel cells stacked together were able to produce enough electricity to charge a capacitor, which was used to trigger contractions of the artificial heart pump, the researchers report today (Nov. 8) in the journal Bioinspiration and Biomimetics.
Whereas conventional motor-powered pumps tend to get clogged, the artificial muscle pump has larger internal orifices, Walters said.
While the new pump does produce more electricity than it consumes (since some of the electricity comes from urine that's converted to electrons), it's still not extremely efficient. The researchers hope to improve the pump's efficiency for use in future generations of the EcoBot.
Follow Tanya Lewis on Twitterand Google+. Follow us @livescience, Facebook& Google+. Original article on LiveScience.

Most Popular