NASA's hobbled Kepler space telescope may be able to detect alien planets again, thanks to some creative troubleshooting.
Kepler's original planet hunt ended this past May when the second of its four orientation-maintaining reaction wheels failed, robbing the spacecraft of its ultraprecise pointing ability. But mission team members may have found a way to restore much of this lost capacity, suggesting that a proposed new mission called K2 could be doable for Kepler.
Engineers with the Kepler mission and Ball Aerospace, which built the telescope, have oriented the spacecraft such that it's nearly parallel to its path around the sun. In this position, the pressure exerted by sunlight is spread evenly across Kepler's surfaces, minimizing drift. [Gallery: A World of Kepler Planets]
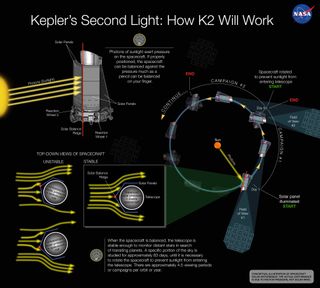
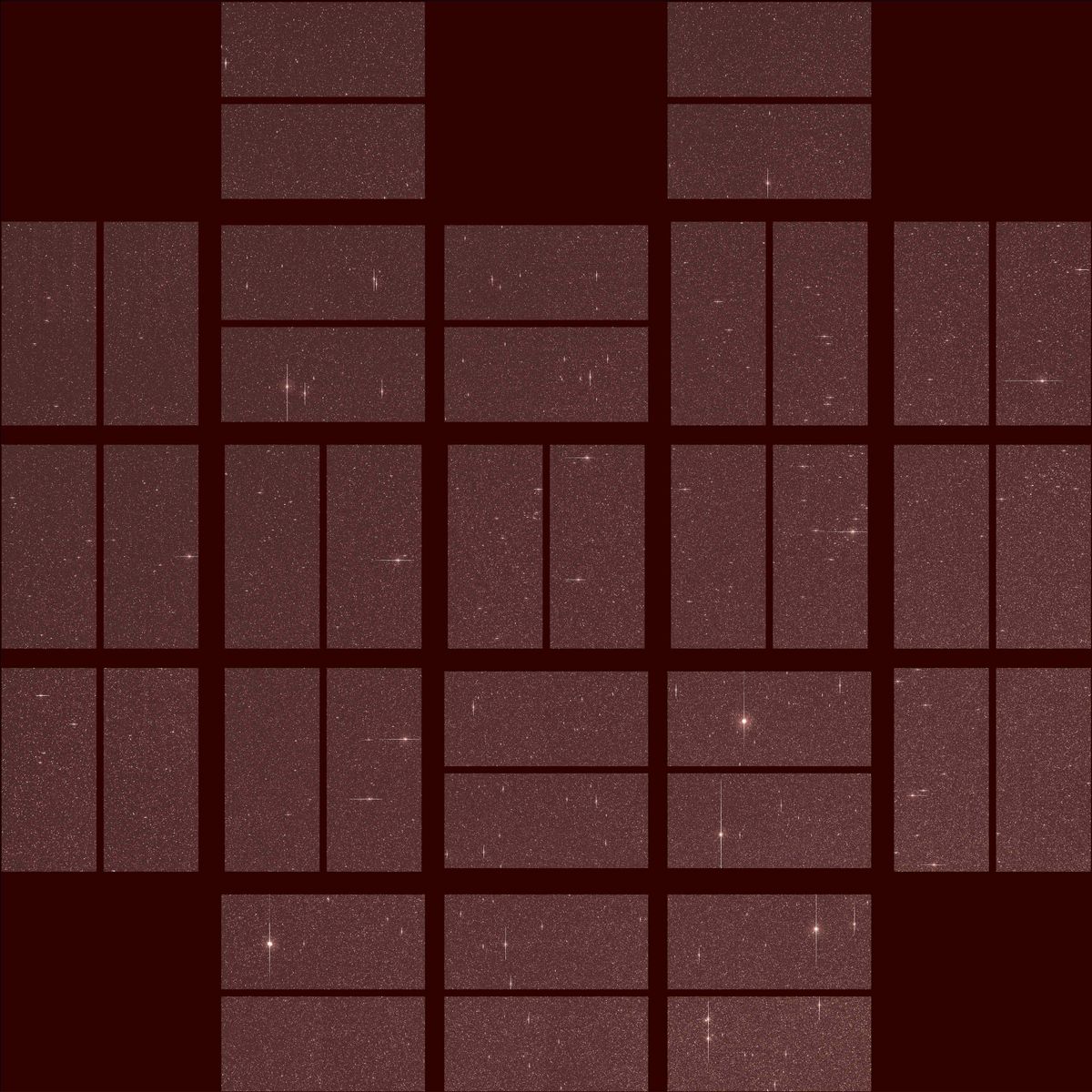
This strategy is returning some promising results, mission officials say. During a 30-minute pointing test in late October, for example, Kepler captured an image of a distant star field that was within 5 percent of the image quality achieved during Kepler's original mission.
"This 'second light' image provides a successful first step in a process that may yet result in new observations and continued discoveries from the Kepler space telescope," Charlie Sobeck, Kepler deputy project manager at NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif., said in a statement.
The Kepler team is currently conducting tests to see if the spacecraft can maintain such pointing stability over periods of days and weeks — a necessity for discovering exoplanets.
Kepler launched in March 2009 on a mission to determine how frequently Earth-like planets occur around the Milky Way galaxy. The spacecraft finds exoplanets via the "transit method," noting the telltale brightness dips caused when an alien world crosses the face of, or transits, its host star from the instrument's perspective.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Kepler has been remarkably successful, spotting more than 3,500 planet candidates to date. Just 167 of them have been confirmed so far by follow-up observations, but mission scientists think 90 percent or so will end up being the real deal.
Researchers are still sifting through the mountains of data Kepler returned during its four years of science operations. Kepler team members have expressed confidence that they'll find Earth analogs in these databases, allowing the mission's primary goal to be achieved.
The proposed K2 mission would continue Kepler's exoplanet hunt, albeit in a modified fashion. K2 would also gather data about supernova explosions, star formation and solar-system bodies such as asteroids and comets, among other things, team members have said.
The Kepler team has officially presented the K2 mission concept to NASA Headquarters, which is expected to decide by the end of the year if the idea progresses to a vetting stage called "senior review." The ultimate fate of K2, and the Kepler spacecraft, will likely be known by the middle of next year, Kepler officials have said.
Follow Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on SPACE.com.