Triplet Births Due to Fertility Treatments Are Declining
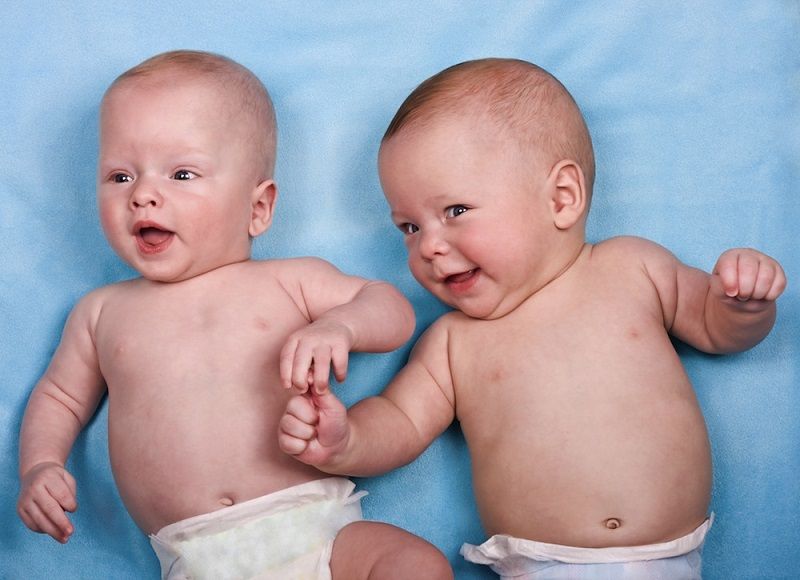

More than one-third of U.S. twins, and more than three-quarters of triplets and other multiple births, are now born as a result of fertility treatments, according to estimates from a new study.
In 2011, 36 percent of twin births and 77 percent of triplet and higher-order births (quadruplets, etc.) were aided by fertility treatments, which include both in vitro fertilization (IVF) and other treatments, such as the use of drugs to stimulate the ovaries and induce ovulation, the study found.
Between 1998 and 2011, the national rate of triplet and higher-order births decreased by nearly 30 percent — a trend that researchers called good news. [8 Fascinating Facts About Twins]
Part of that decline may be related to a 1998 change in guidelines that discouraged doctors from implanting three or more embryos during a single IVF cycle. After that, the proportion of triplet and higher-order births attributable to IVF declined by 33 percent (from 48 percent in 1998 to 32 percent in 2011).
However, there's still a lot of work to be done to reduce the U.S. rate of multiple births, said study researcher Dr. Eli Y. Adashi, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Brown University. The percentage of twin births resulting from IVF and non-IVF fertility treatments is still on the rise.
Why a decline in multiple births is good
Twin and other multiple births increase the risk of complications for the mother and infant, including the risk of premature delivery. An unintended consequence of fertility treatment technology was an increase in the nation's multiple-birth rate, Adashi said.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The new study also suggests that non-IVF fertility treatments deserve greater attention, as they now contribute to a greater proportion of multiple births than IVF does. The percentage of triplet and higher-order births resulting from non-IVF treatments increased from 36 percent in 1998 to 45 percent in 2011, the study found.
"When people hear 'multiple,' they intuitively point at IVF," Adashi said. The study found "IVF is an actor," he said, but "not the leading culprit when it comes to the genesis of multiples."
But unlike multiple births from IVF, which result from the number of embryos that are intentionally implanted, multiple births from non-IVF fertility treatments are difficult to prevent, Adashi said. That's because non-IVF treatments, including oral and injectable drugs, stimulate ovulation in ways that cannot be precisely controlled, Adashi said.
How to reduce multiple births
But there are a few steps doctors can take that may reduce the rate of multiple births from non-IVF fertility treatments, such as lowering the doses of the ovulation-stimulating drugs, Adashi said.
"Increased awareness of multiple births resulting from non-IVF fertility treatments may lead to improved medical practice patterns and a decrease in the rate of multiple births," the researchers wrote in the Dec. 5 issue of The New England Journal of Medicine.
To come up with their estimates, the researchers analyzed information on birth rates between 1962 and 1966 — before the advent of fertility treatments — to get a measure of the natural rate of multiple births. They also used publicly available data on IVF births between 1997 and 2011.
Because no database tracks multiple births due to non-IVF treatment, the researchers estimated this number by factoring in the natural rate of multiple births and IVF births. The researchers also took into account maternal age, which increases the chance of giving birth to multiples, but were not able to account for other factors, like obesity, which some studies suggest increases the chances of giving birth to twins.
Follow Rachael Rettner @RachaelRettner. Follow LiveScience @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.

Rachael is a Live Science contributor, and was a former channel editor and senior writer for Live Science between 2010 and 2022. She has a master's degree in journalism from New York University's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program. She also holds a B.S. in molecular biology and an M.S. in biology from the University of California, San Diego. Her work has appeared in Scienceline, The Washington Post and Scientific American.
'Love hormone' oxytocin can pause pregnancy, animal study finds
'Mini placentas' in a dish reveal key gene for pregnancy