Metals in Your Smartphone Have No Substitutes (Op-Ed)
This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to LiveScience's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights.
A few centuries ago, there were just a few widely used materials: wood, brick, iron, copper, gold and silver. Today’s material diversity is astounding. A chip in your smartphone, for instance, contains 60 different elements. Our lives are so dependent on these materials that a scarcity of a handful of elements could send us back in time by decades.
If we do ever face such scarcity, what can be done? Thomas Graedel of Yale University and his colleagues decided to investigate. He chose to restrict his analysis to metals and metalloids, which could face more critical constraints because many of them are relatively rare.
The authors’ first task was to make a comprehensive list of uses for these 62 elements. This is a surprisingly difficult task. Much of the modern use of metals happens behind closed doors of corporations, under the veil of trade secrets. Even if we can find out how certain metals are used, it may not always be possible to determine the proportions they are used in. Their compromise was to account for the use of 80% of the material that is made available each year through extraction and recycling.
The next task was to determine if there were any substitutes for these uses. But, as Graedel writes, “the best substitute for a metal in a particular use is not always readily apparent.” Elemental properties are quite unique and substitution will often reduce the performance of the product. But it can be done.
Two examples stand testament to that. In the 1970s, cobalt was commonly used in magnets. When a civil war in Zaire caused scarcity of cobalt, scientists at General Motors and elsewhere were forced to develop magnets that used no cobalt. More recently, a shortage of rhenium, which is used in superalloys for gas turbines, forced General Electric to develop alternatives that use little or no rhenium.
Graedel’s analysis of substitutes involved ploughing through scientific literature and interviewing product designers and material scientists. The results are a sobering reminder of how critical some metals are. On seeing the data, Andrea Sella of University College London said, “This is an important wake up call.”
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
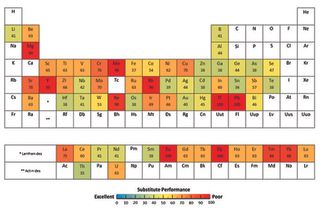
None of the 62 elements have substitutes that perform equally well. And 12 out of the 62 have no substitutes at all (or if there are substitutes, then they are inadequate). These 12 elements are: rhenium, rhodium, lanthanum, europium, dysprosium, thulium, ytterbium, yttrium, strontium, thallium, magnesium and manganese.
Economists have long assumed that a shortage of anything will promptly lead to the development of suitable substitutes, an attitude fostered in part because there have been successful substitutions in the past, such as the cobalt and rhenium examples. But metals are special, Graedel said: “We have shown that metal substitution is very problematic. Substitution would need to mimic these special properties – a real challenge in many applications.”
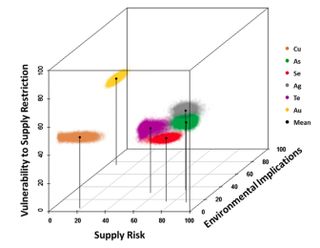
“The clarity of Graedel’s thinking is impressive,” said Sella. “No one has analysed metal criticality in such detail.” One of Graedel’s biggest contributions has been developing a visual way of understanding how critical metals are. They created a 3D map, where the three axes represent supply risk, environmental implications and vulnerability to supply restriction.
The scarcity of metals came to public attention in 2010 when China suddenly decided to restrict its export of a group of metals called the rare earths. Prices of these metals shot up by as much as five times and caused companies around the world to consider reopening their rare earth mines. This had knock-on effects on the prices of everything from gadgets to wind turbines.
Some comfort may be drawn from the fact that consumptions of some metals can peak. For example, the use of iron has reached saturation in many countries. And, in the US, this seems to have happened for aluminium too. This, however, is the case only for bulk metals. Scarcer metals, even with superior recycling, may never reach saturation.
Apart from China, a handful of countries, including the US, South Africa, Australia, Congo, and Canada, hold the most diverse and largest metal reserves. “A national disaster or extended political turmoil in any of them would significantly ripple throughout the material world in which we live,” said Graedel.
As Sella puts it, Graedel’s measured analysis, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is a warning of a serious issue. “But he has a thoughtful way of putting it.”
This article was originally published at The Conversation. Read the original article. The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the publisher. This version of the article was originally published on LiveScience.