Canal Carved Through Nicaragua Will Destroy Rainforests, Communities and Wildlife (Op-Ed)
This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Live Science's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights.
The Nicaraguan government has granted a concession to a mysterious Chinese company owned by Jing Wang, a little-known Hong-Kong based businessman, to build an inter-oceanic canal. This would provide an alternative to the Panama Canal that, 99 years after it first opened, is struggling to cope with shipping.
Despite being one of the most important decisions in Nicaragua’s history, the legislative bill in question appeared virtually overnight and was approved as law only three days after it was sent to the parliament, with no serious national consultation or opportunity to hear the opposition from some of the country’s leading scientists.
The company is the Hong Kong Nicaraguan Development Group (HKND), which has no experience with major construction projects. With an estimated cost of US$40 billion, the canal was slated to start in June 2014, but has been delayed to the end of the year
The Nicaraguan government claims the project will pull the country, in which 45% of the population live on less than US$2 day, out of poverty. But so far no feasibility studies have been revealed, and serious economists have expressed their concern that the canal will just be another enclave economy as it was for Panama. Because this private canal will not be a property of Nicaragua for 100 years, and since it will not be linked to the rest of the economy, it will not create wealth nor will it improve Nicaragua’s economy.
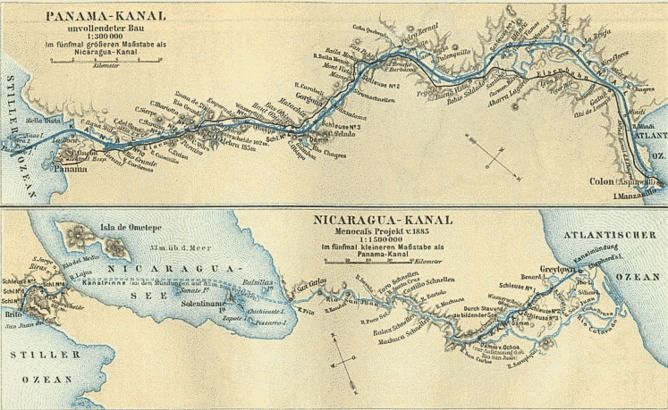
Around 300km of excavations will be required to connect the Pacific Ocean to the Caribbean – three times the length of the Panama Canal. Along the route it will traverse Lake Nicaragua, the largest drinking water reservoir in the region, and cut through rainforests and ecologically valuable swamps.
Although the final route has not been announced, it is clear that all possible routes will use Lake Nicaragua (also known by its indigenous name, Cocibolca). It is the lake and adjacent waterways, together with the area’s rich biodiversity, that are the most pressing environmental concerns.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
No environmental impact assessment was carried out as required by law before the canal concession was granted, and the face of the bill requires environmental assessments after the fact, at the discretion of the firm – an obvious conflict of interest.
Environmental concerns
The project threatens some of the most fragile ecosystems in the country, on land, at sea, and in the lake, causing potentially irreversible damage.
We fear that, should the plans proceed, there may be some devastating impact on the region’s ecology, such as the chemical and biological properties of the watercourses, due to the major excavation, dredging, sedimentation that construction will bring, as well as the inevitable pollution and invasive species that marine shipping brings.
This could ultimately lead to the extinction of many fish species important to surrounding fishing communities, and characteristic aquatic fauna such as freshwater bull sharks, sawfish and tarpon could also be affected.
In addition to the canal infrastructure itself, other related projects include oil pipelines, airports, and industrial zones, which will negatively affect the migration patterns and biological dynamics of terrestrial animals.
Direct and indirect damage to natural reserves such as the Indio-Maiz reserve and others will threaten Nicaragua’s endangered species. Drastic changes in land use and the displacement of indigenous communities will put even greater pressures on natural protected areas as villages are relocated and begin clearing rainforest for food and shelter.
Social and economic concerns
Dozens of villages and indigenous communities will have to be moved out of their ancestral homes, a serious concern for indigenous groups with a deep religious connection to their ancestral lands.
Communities, facing a loss of land and food insecurity, have filed lawsuits asserting that they were not consulted and that it violates their legitimate territorial rights.
The Academy of Sciences of Nicaragua along with other civil organisations has organised a series of forums to promote a better-informed debate on the possible threats posed by the canal, and alternatives. A document of all the scientific and technical forum presentations has been prepared and will be published soon (in Spanish).
The academy has called for an independent and external evaluation of the canal, in particular an environmental assessment, and is seeking help from the international community. It is surprising, given the magnitude of the project, how little attention it has been given abroad.
As it stands the project is neither environmentally sustainable nor scientifically sound, but will proceed no matter what. International action is needed to provide expert advice to local scientists to prevent the tragic destruction of biodiversity and precious ecosystems in Central America.
Jorge Huete-Perez does not work for, consult to, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has no relevant affiliations.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article. The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the publisher. This version of the article was originally published on Live Science.