Found! First Earth-Size Planet That Could Support Life
For the first time, scientists have discovered an Earth-size alien planet in the habitable zone of its host star, an "Earth cousin" that just might have liquid water and the right conditions for life.
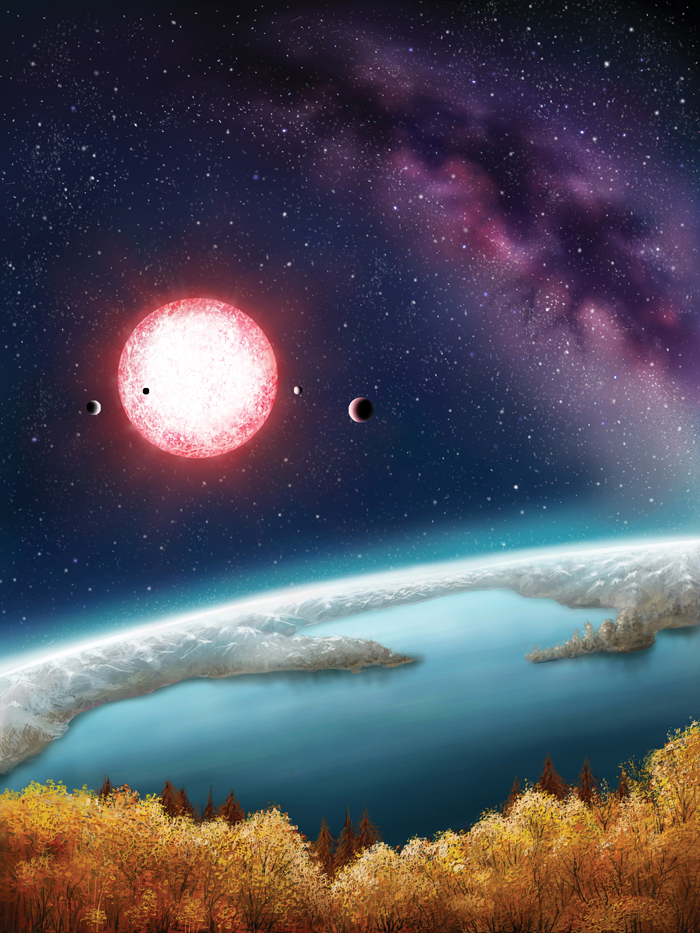

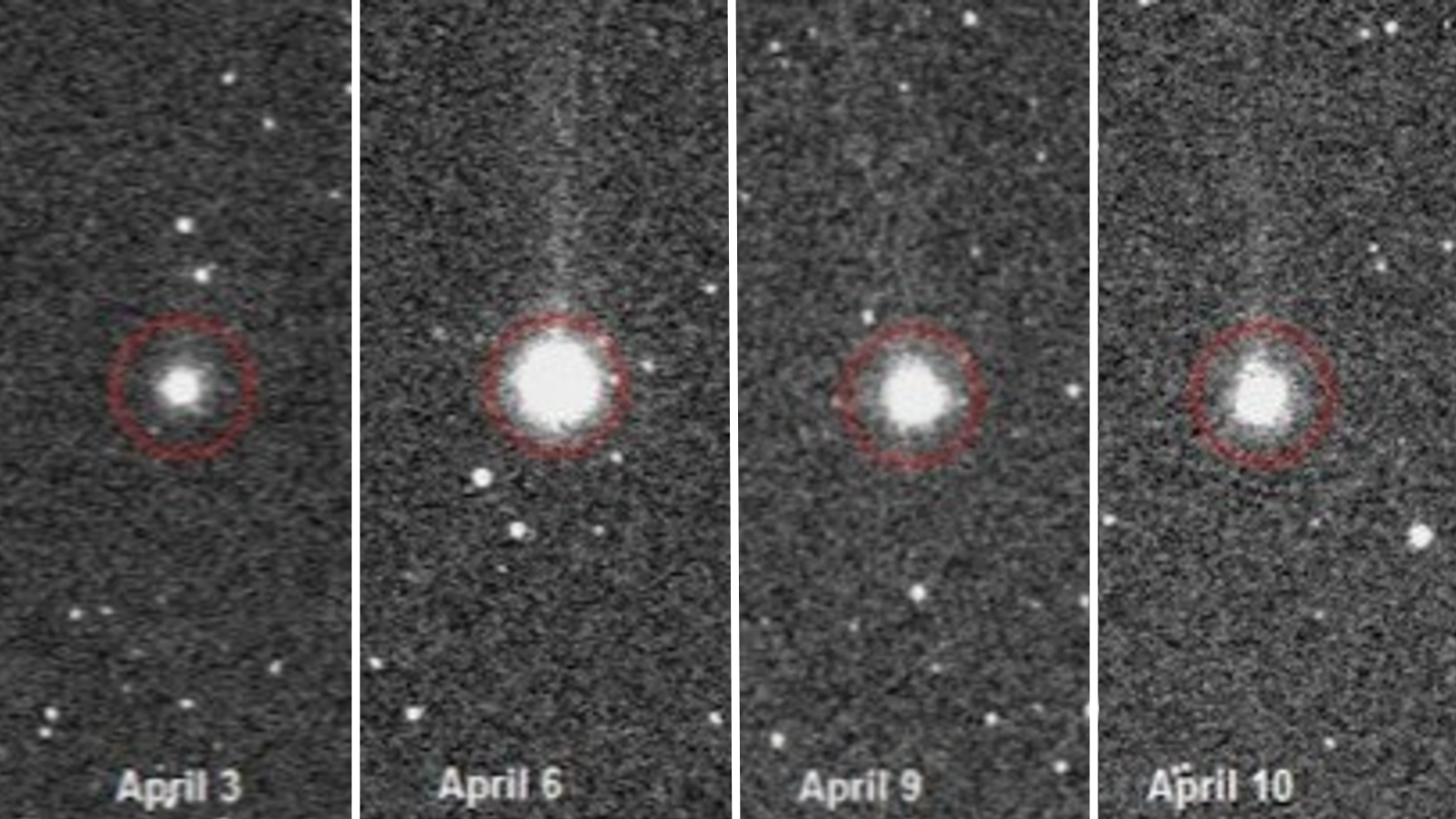
The newfound planet, called Kepler-186f, was first spotted by NASA's Kepler space telescope and circles a dim red dwarf star about 490 light-years from Earth. While the host star is dimmer than Earth's sun and the planet is slightly bigger than Earth, the positioning of the alien world coupled with its size suggests that Kepler-186f could have water on its surface, scientists say. You can learn more about the amazing alien planet find in a video produced by Space.com.
"One of the things we've been looking for is maybe an Earth twin, which is an Earth-size planet in the habitable zone of a sunlike star," Tom Barclay, Kepler scientist and co-author of the new exoplanet research, told Space.com. "This [Kepler-186f] is an Earth-size planet in the habitable zone of a cooler star. So, while it's not an Earth twin, it is perhaps an Earth cousin. It has similar characteristics, but a different parent." [10 Exoplanets That Could Host Alien Life]

Potentially habitable planet
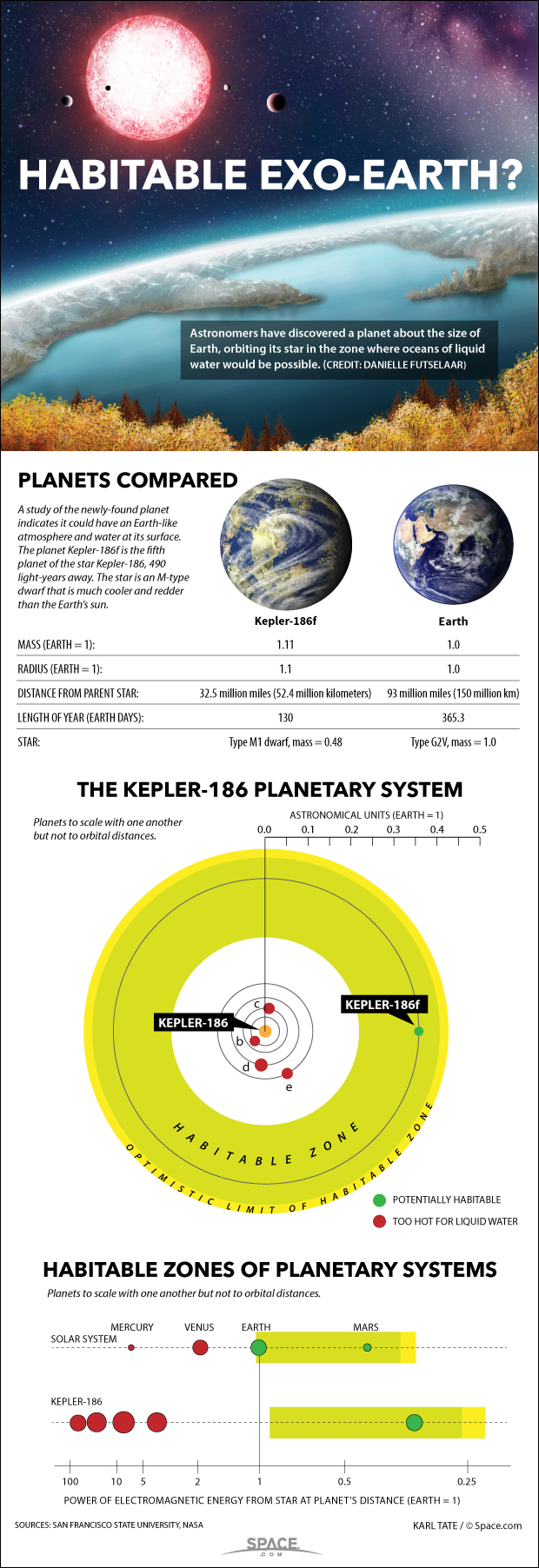
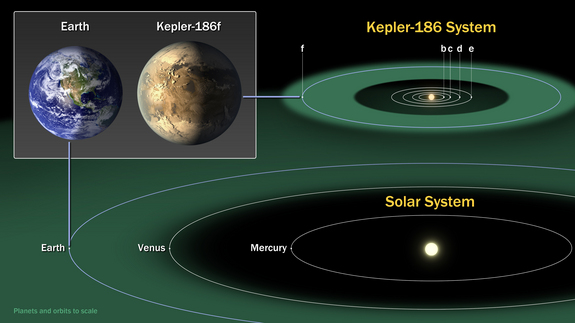
Scientists think that Kepler-186f — the outermost of five planets found to be orbiting the star Kepler-186 — orbits at a distance of 32.5 million miles (52.4 million kilometers), theoretically within the habitable zone for a red dwarf.
Earth orbits the sun from an average distance of about 93 million miles (150 million km), but the sun is larger and brighter than the Kepler-186 star, meaning that the sun's habitable zone begins farther out from the star by comparison to Kepler-186.
"This is the first definitive Earth-sized planet found in the habitable zone around another star," Elisa Quintana, of the SETI Institute and NASA's Ames Research Center and the lead author of a new study detailing the findings, said in a statement.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Other planets of various sizes have been found in the habitable zones of their stars. However, Kepler-186f is the first alien planet this close to Earth in size found orbiting in that potentially life-supporting area of an extrasolar system, according to exoplanet scientists.
'An historic discovery'
"This is an historic discovery of the first truly Earth-size planet found in the habitable zone around its star," Geoff Marcy, an astronomer at the University of California, Berkeley, who is unaffiliated with the research, told Space.com via email. "This is the best case for a habitable planet yet found. The results are absolutely rock-solid. The planet itself may not be, but I'd bet my house on it. In any case, it's a gem."
The newly discovered planet measures about 1.1 Earth radii, making it slightly larger than Earth, but researchers still think the alien world may be rocky like Earth. Researchers still aren't sure what Kepler-186f's atmosphere is made of, a key element that could help scientists understand if the planet is hospitable to life. [Kepler-186f: Earth-Size World Could Support Oceans, Maybe Life (Infographic)]
"What we've learned, just over the past few years, is that there is a definite transition which occurs around about 1.5 Earth radii," Quintana said in a statement. "What happens there is that for radii between 1.5 and 2 Earth radii, the planet becomes massive enough that it starts to accumulate a very thick hydrogen and helium atmosphere, so it starts to resemble the gas giants of our solar system rather than anything else that we see as terrestrial."
The edge of habitability
Kepler-186f actually lies at the edge of the Kepler-186 star's habitable zone, meaning that liquid water on the planet's surface could freeze, according to study co-author Stephen Kane of San Francisco State University.
Because of its position in the outer part of the habitable zone, the planet's larger size could actually help keep its water liquid, Kane said in a statement. Since it is slightly bigger than Earth, Kepler-186f could have a thicker atmosphere, which would insulate the planet and potentially keep its water in liquid form, Kane added.
"It [Kepler-186f] goes around its star over 130 days, but because its star is a lower mass than our sun, the planet orbits slightly inner of where Mercury orbits in our own solar system," Barclay said. "It's on the cooler edge of the habitable zone. It's still well within it, but it receives less energy than Earth receives. So, if you're on this planet [Kepler-186f], the star would appear dimmer."
Astronomers have confirmed more than 700 planets beyond our own solar system, and the discoveries keep rolling in. How much do you know about these exotic worlds?
Alien Planet Quiz: Are You an Exoplanet Expert?


Exoplanet hunting in the future
Kepler-186f could be too dim for follow-up studies that would probe the planet's atmosphere. NASA's James Webb Space Telescope — Hubble's successor, expected to launch to space in 2018 — is designed to image planets around relatively nearby stars; however, the Kepler-186 system might be too far off for the powerful telescope to investigate, Barclay said.
Scientists using the Kepler telescope discovered Kepler-186f using the transit method: When the planet moved across the face of its star from the telescope's perspective, Kepler recorded a slight dip in the star's brightness, allowing researchers to learn more about the planet itself. Kepler suffered a major malfunction last year and is no longer working in the same fashion, but scientists are still going through the spacecraft's trove of data searching for new alien worlds.
"I find it simply awesome that we live in a time when finding potentially habitable planets is common, and the method to find them is standardized," MIT exoplanet hunter and astrophysicist Sara Seager, who is unaffiliated with the research, told Space.com via email.
The new research was published online today (April 17) in the journal Science.
Follow Miriam Kramer @mirikramer and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.