Why Do I Bruise Easily?
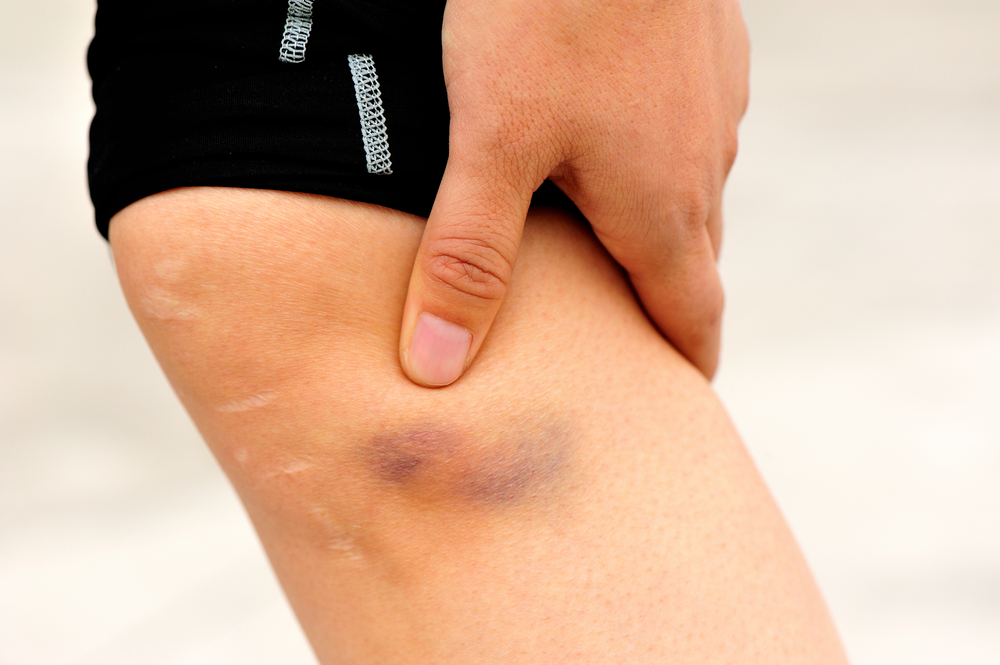
A contusion, or bruise, is a reddish-purple discoloration of the skin that doesn't blanch, or turn white or pale, when pressed upon.
Bruises typically form when a localized injury, such a blow or impact, causes capillaries to break open and leak red blood cells under the skin.
A person may start to bruise more easily than before for a number of different reasons, though bruising doesn't necessarily indicate a serious health issue.
To start, bruising easily is a normal part of getting older. As you age, your capillaries weaken, becoming more prone to rupture. Your skin also thins and loses some of the fat that would otherwise protect your blood vessels from impacts.
Various medications can also cause you to bruise more easily. These include aspirin, the corticosteroids prednisone and prednisolone, anticoagulants, antibiotics, and blood thinners (including certain dietary supplements, such as fish oil and ginkgo).
Easy bruising can sometimes be a symptom of a disease or health issue. For instance, sepsis (a bacterial infection), chronic inflammatory disease, liver disease and certain types of cancer can all cause you to bruise easily.
Disorders that reduce your ability to clot blood, such as hemophilia and von Willebrand disease, may also affect your bruising frequency.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Finally, if you bruise easily, it may be a sign of malnutrition or a lack of adequate amounts of certain nutrients, including folic acid and vitamins B12, C and K.
Follow Joseph Castro on Twitter. Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+.