Superstitions Collide: Full Moon Rises on Friday the 13th
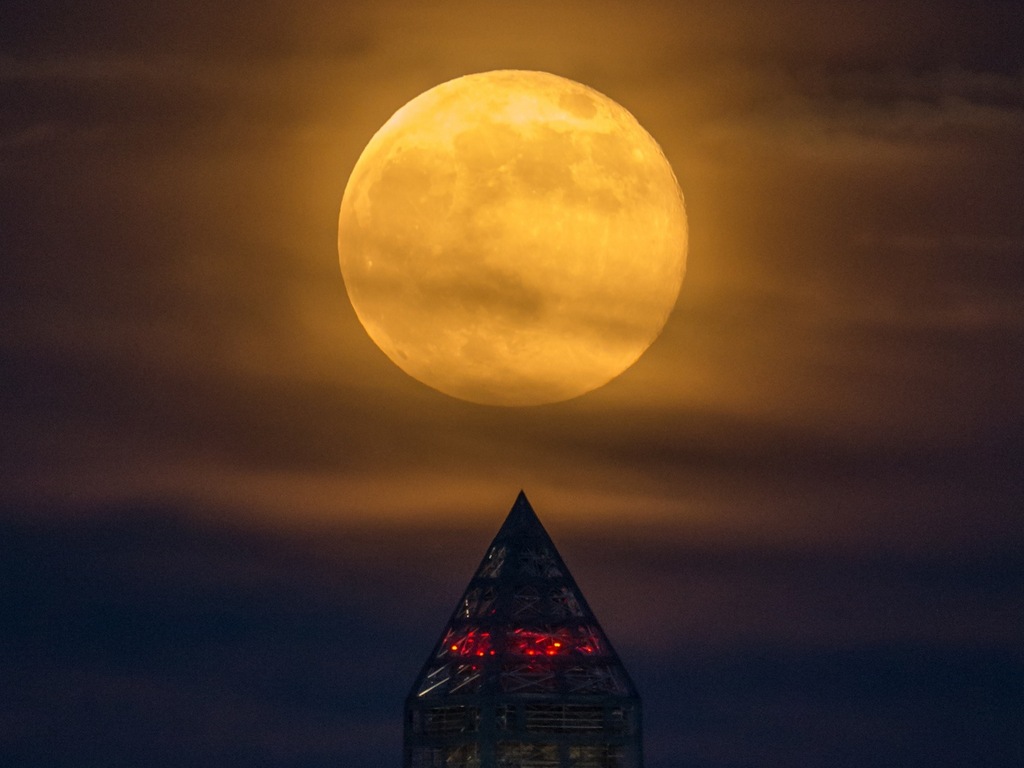

This month, the full moon falls on Friday the 13th.
Freaky? Nah, probably not.
Despite many myths, the full moon does not actually embolden criminals, bring about births or make people mad, studies show. And while Friday the 13th superstitions may be well entrenched, there's nothing particularly special about a full moon falling on this date.
This Friday's full moon will be the lowest in the sky this year, however, since it will occur so close to the summer solstice. You can watch this freaky full moon rising in a live webcast on Live Science, beginning at 9:30 p.m. EDT tonight (June 12). [Gallery: Fantastic Photos of Full Moons]
Strawberry moon
The June full moon is nicknamed the "Strawberry Moon," a moniker that goes back to the Algonquin Native American tribe, according to the Farmer's Almanac. June is strawberry season, and the full moon would have traditionally coincided with the harvest.
The June full moon is frequently the one nearest to the summer solstice, which falls on June 21 this year. Because of a neat bit of galactic geometry, this means the full moon on Friday will be the lowest in the sky of any in 2014.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Here's how it works: The Earth rotates on a tilted axis; in June — summer in the Northern Hemisphere — the North Pole is tilted about 23.5 degrees toward the sun, while the South Pole is tilted 23.5 degrees away from the sun. On the solstice, the sun reaches its farthest point north of the equator.
Full moons happen when Earth's satellite is opposite the sun; that's why viewers on Earth see the entire face of the moon illuminated. Thus, when the full moon is directly opposite the sun when our host star appears at its highest point, the moon is at its lowest point with respect to the equator. That's why winter full moons rise higher above the horizon than summer full moons.
Moon myths
June's moon reaches its fullest point at 12:11 a.m. EDT (0411 GMT) on Friday, June 13. Of course, this means that for people in the Central, Mountain and Pacific time zones in the United States, this full moon isn't a Friday the 13th full moon at all: It technically falls on June 12.
Friday the 13th full moons occur sporadically. The last one fell on Aug. 13, 2011. The next Friday the 13th full moon will be on Aug. 13, 2049.
Even those who live in the Eastern time zone should not stress over the confluence of the full moon with Friday the 13th. Contrary to myth, the full moon does not affect human behavior or health. For example, a 1985 review published in the journal Psychological Bulletin tracked hospital admissions, psychiatric disturbances, homicides and other crime over several months and found no uptick in any of those variables around the time of the full moon.
Alas for heavily pregnant women, a 2001 study in the Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society looked at about 70 million births in the United States and found no link between the phase of the moon and labor starting. So don't expect to finish your pregnancy just because the moon is full.
Studies have also shown that other phenomena, including seizures, crime and heart surgery outcomes, have no link to the full moon.
Pet owners might want to avoid walking their black cats under the full moon on Friday, however. One 2007 study of pet injuries published in the Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association found that emergency vet visits for cats were 23 percent higher on days around the full moon. (Dog visits spiked 28 percent on those days.) Researchers speculated that people might use the extra light of the full moon to stay out after dark with their pets, perhaps boosting the likelihood of injury.
Editor's Note: If you have an amazing moon or general science photo you'd like to share for a possible story or image gallery, please contact managing editor Jeanna Bryner at LSphotos@livescience.com.
Follow Stephanie Pappas on Twitter and Google+. Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on Live Science.

Stephanie Pappas is a contributing writer for Live Science, covering topics ranging from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and behavior. She was previously a senior writer for Live Science but is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and regularly contributes to Scientific American and The Monitor, the monthly magazine of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie received a bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.