'Jellyroll' Ice Sculptures Discovered Under Greenland Ice Sheet
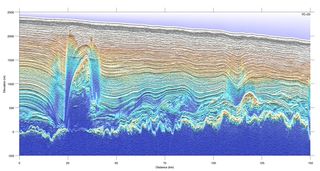
The Greenland ice sheet may look like a vast expanse of white, but scientists peering beneath the smooth veil have found a fun house of sorts, full of giant jellyroll-like ice sculptures that could rival city skyscrapers in height and the whole of Manhattan in width.
The newfound wonderland not only reveals Mother Nature as artist, but also gives scientists a better picture of how Greenland's ice behaves and how that might change as the planet warms.
"If we could peel away each layer of snow at a time, eventually we would see that the layers were no longer coming off flat, like a layer cake," study researcher Robin Bell, of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory in New York, told Live Science in an email. "If we could see them, they would look more like an odd, icy jelly roll. The ice is bent, twisted and folded," so that 120,000-year-old ice generally found at some 1.5 miles (2.5 kilometers) down is now found just 0.6 miles (1 km) from the surface. [Images: Greenland's Gorgeous Glaciers in Stunning Photos]
Bell added that the structures would be like "giant ice sculptures made by nature."
Until now, scientists relying on airborne radar thought the structures, which Bell and colleagues estimate cover about a tenth of northern Greenland, were rocky hills. With newer, ice-penetrating radar instruments used during NASA's Operation IceBridge mission — which aimed to map ice loss at the North and South Poles — researchers realized those hilly structures were actually made of ice.
As for how these sculptures are formed, the researchers built their theory partly on past findings from Antarctica, where Bell and others had found that ice sheets can grow from the bottom up, not just from the accumulation of snowing piling up on top of the ice. That growth, the scientists found, occurs as melt water at the bottom of the ice sheet thaws and refreezes.

Here's what the researchers think is occurring: Water that comes from melting at the bottom of the ice sheet, or water that streams down from the surface along crevasses and tubular shafts called moulins, refreezes at the bottom of the ice sheet. Over hundreds to thousands of years, the refreezing process warms, softens and warps the ice above the base of the ice sheet, creating the giant jellyroll-like structures discovered using radar. These structures could be up to 3,280 feet (1,000 m) in height, Bell said. They get bigger and are more common as the ice sheet narrows into the ice streams headed out to sea.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
These rolled-up ice sculptures may also explain a weird behavior of Petermann Glacier, which made headlines in 2010 when a Manhattan-size chunk of ice broke off and slid into the sea. The researchers found one of these "sculptures" lying at a spot on the glacier that is moving along at about twice the speed of nearby ice. They suggest the refreezing process, by softening the ice, may accelerate the flow of glaciers.
Bell and her colleagues detailed their research in the June 15 issue of the journal Nature Geoscience.
Follow Jeanna Bryner on Twitter and Google+. Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on Live Science.
Jeanna Bryner is managing editor of Scientific American. Previously she was editor in chief of Live Science and, prior to that, an editor at Scholastic's Science World magazine. Bryner has an English degree from Salisbury University, a master's degree in biogeochemistry and environmental sciences from the University of Maryland and a graduate science journalism degree from New York University. She has worked as a biologist in Florida, where she monitored wetlands and did field surveys for endangered species, including the gorgeous Florida Scrub Jay. She also received an ocean sciences journalism fellowship from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. She is a firm believer that science is for everyone and that just about everything can be viewed through the lens of science.
Most Popular

