Spectacular Aurora Seen Over Jupiter
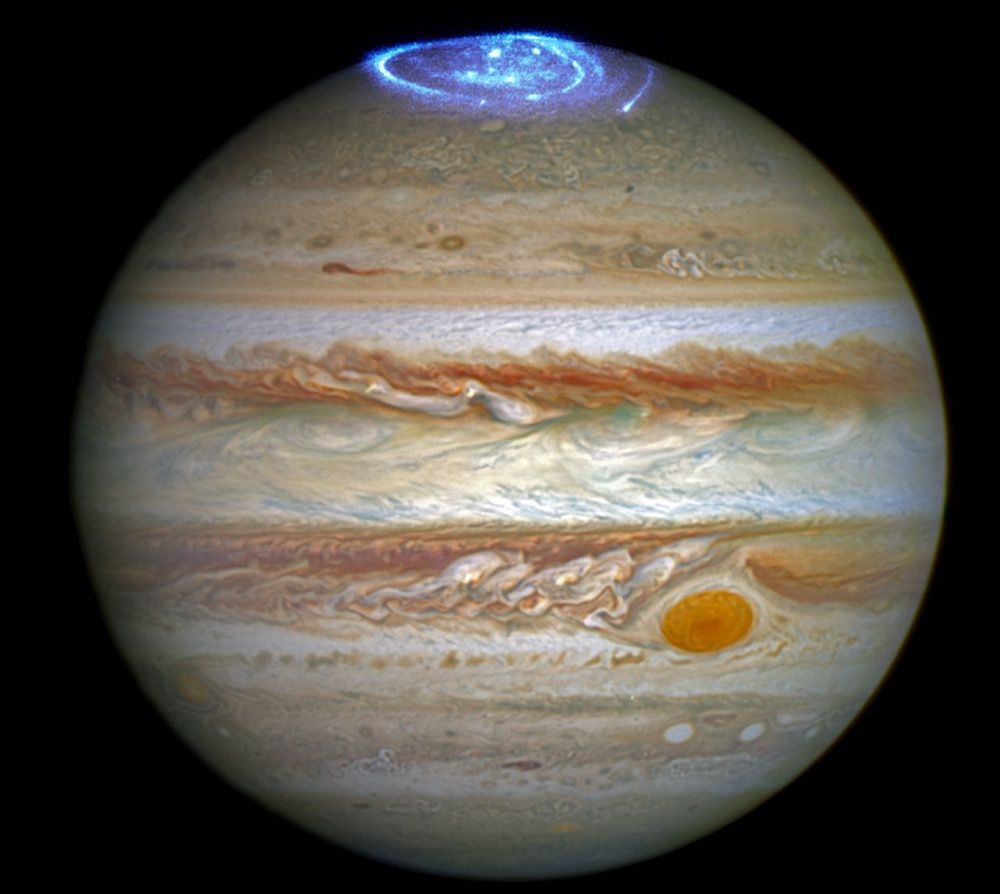

Bright blue auroras at Jupiter's north and south poles are putting on a veritable fireworks show just before the July 4 arrival of the Juno probe.
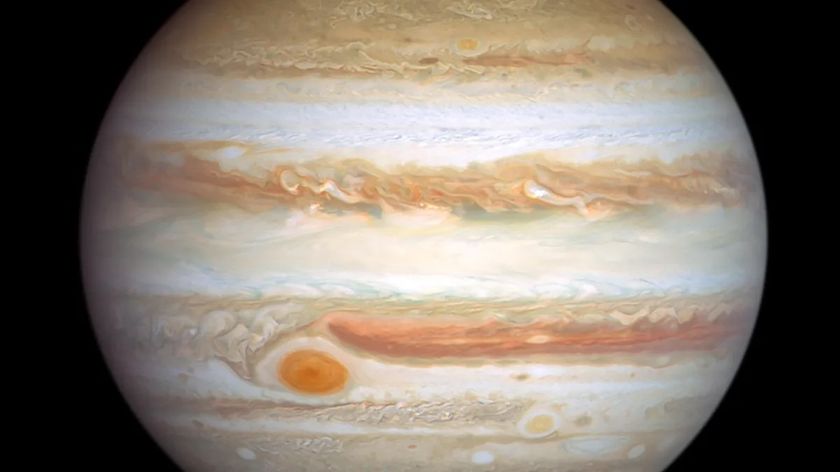
Jupiter's colorful auroras have been imaged before, but a month of daily observations of Jupiter by the Hubble Space Telescope has allowed scientists to put together a time-lapse video showing how the auroras evolve.
"These auroras are very dramatic and among the most active I have ever seen," Jonathan Nichols, a researcher at the University of Leicester in England who is using Hubble's observations to study auroras on Jupiter, said in a statement. "It almost seems as if Jupiter is throwing a fireworks party for the imminent arrival of Juno."
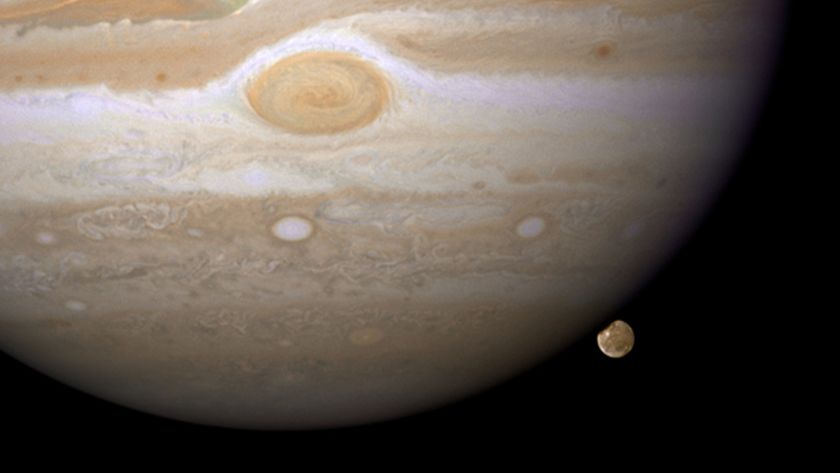
The auroras cover large sections of the planet's poles and are "hundreds of times more energetic" than Earth's auroras, according to the statement from the European Space Agency's (ESA) Hubble Telescope group. Earth's auroras are created when charged particles from the sun (called the solar wind) interact with the Earth's magnetic field and atmosphere. On Jupiter, auroras are created by the energetic particles that come from the sun, but also from one of the planet's moons, Io. Jupiter has an incredibly strong magnetic field, and, unlike on Earth, the auroras on Jupiter never stop, according to the statement.
Jupiter's auroras were first spotted by the Voyager 1 probe, and have been studied by additional observatories ever since.
The Juno probe will arrive at Jupiter on July 4, and turn on its thrusters in order to slow down and enter into orbit around the planet. Juno will make a total of 37 loops around Jupiter (traveling into the narrow space between the cloud tops and the radiation belt that surrounds the planet), over the course of about 20 months. With its mission complete, Juno will make a death dive into Jupiter in February 2018.
Follow Calla Cofield @callacofield. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.