New Year's 'Detox' Lands Woman in the ER
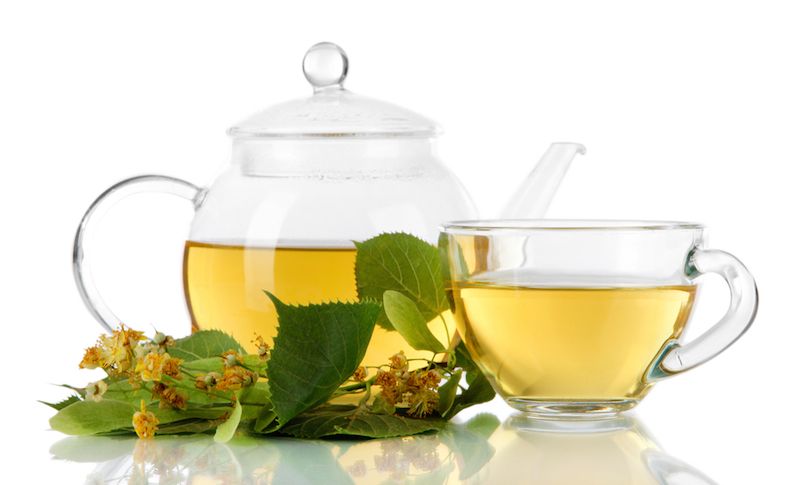

Undertaking a New Year's "detox" can sometimes be dangerous, according to a new report.
The report described the case of a woman in England who developed a potentially life-threatening condition after she drank lots of fluids and took a slew of herbal remedies at the start of the new year.
"Patients should be advised of the potential detriment done to their health of undertaking a new year 'detox,' especially if it involves consuming excessive amounts of fluid or alternative remedies," the report said.
The 47-year-old woman was healthy when she began consuming more fluids and herbal remedies than usual, the report said. She was admitted to the emergency room after she appeared confused and showed changes in behavior, including teeth grinding, and then suffered a seizure.
Her family said she had been drinking more water and tea over the last few days and consuming a number of supplements, including milk thistle, molkosan, l-theanine, glutamine, vitamin B compound, vervain, sage tea, green tea and valerian root. [7 Foods You Can Overdose On]
When the patient was able to speak, she said that she had been under increased stress lately and had experienced mood problems, and had been increasingly taking all of these supplements at the same time, the report said.
Doctors diagnosed the patient with hyponatremia, a condition in which a person has abnormally low levels of sodium in his or her blood. Drinking too much water can lead to hyponatremia, but for this to happen, people usually need to consume more than 2.5 gallons (10 liters) of water per day. Although the woman had been drinking more water than usual, she didn't appear to be drinking the high amounts needed to trigger hyponatremia, the report authors said.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
While trying to determine what caused the woman's problems, her doctors came across a report of a similar case, in which a man developed hyponatremia after taking valerian root, along with several other herbal remedies. In that case, too, the patient did not appear to have drunk an excessive amount of fluid. [27 Oddest Medical Cases]
Because of the findings in these two cases, the doctors in the new report hypothesized that consuming valerian root may lower the threshold of fluid intake needed for hyponatremia to develop.
"It may well be that the valerian root altered this threshold [of fluid intake], allowing severe hyponatremia to develop at an earlier stage," the doctors wrote.
However, they noted that with only two cases, they cannot draw a definite conclusion about whether valerian root played a role in these health problems.
Still, the doctors warned that "despite marketing suggesting otherwise, all-natural products are not without side effects."
Doctors treated the woman with replacement sodium in the intensive care unit, and she was soon discharged from the hospital. At a follow-up visit, she had normal sodium levels and did not experience any neurological complications as a result of her hyponatremia. The doctors also arranged for a mental health team to help the woman with her reported mood problems.
The report of the case was published online Sept. 28, 2016.
Original article on Live Science.

Rachael is a Live Science contributor, and was a former channel editor and senior writer for Live Science between 2010 and 2022. She has a master's degree in journalism from New York University's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program. She also holds a B.S. in molecular biology and an M.S. in biology from the University of California, San Diego. Her work has appeared in Scienceline, The Washington Post and Scientific American.