Google Doodle Honors 'Prince of Mathematicians,' Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
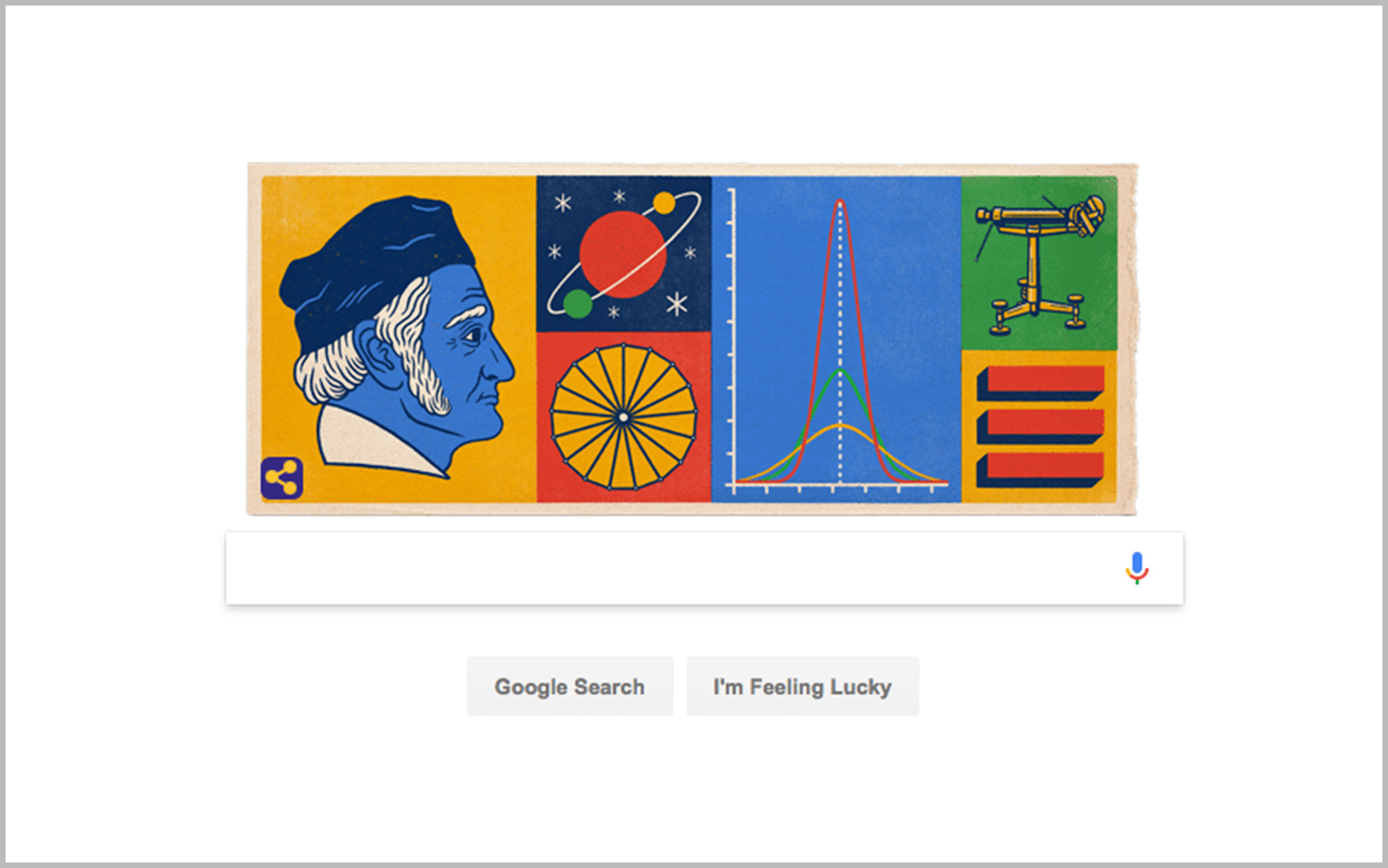
The Google Doodle today (April 30) commemorates the math and science achievements of Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss, widely known as the "prince of mathematicians," on what would have been his 241st birthday.
Born in Germany in 1777, Gauss was recognized as a math prodigy when he was still a young boy; he earned acclaim for the swiftness of his numerical calculations, and later made groundbreaking contributions to the fields of number theory and algebra. He also used mathematics to successfully predict the reappearance of the "missing" Ceres, the largest known asteroid in our solar system, which had disappeared behind the sun shortly after its discovery in 1801, before its orbit could be mapped. [The 11 Most Beautiful Mathematical Equations]
Gauss delivered his astounding calculation about the probable orbit of Ceres when he was only 24 — his efforts marked his introduction to astronomy, which then became a focal point of his career for the next 50 years, according to a paper presented in 1977 at a symposium held on the bicentennial of his birth. The paper was published by the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada.
At age 30, Gauss was appointed professor of astronomy at the University of Göttingen in Germany, and from 1816, he lived and worked at the astronomical observatory building there, according to the university's website.
In his later years, Gauss studied Earth's electromagnetic field, inventing the magnetometer — an instrument for measuring magnetic forces — in 1833. That same year, he also invented one of the first telegraph machines, several years before the telegraph was introduced in America by Samuel Morse, University of Göttingen representatives wrote in a biography of the mathematician and astronomer.
Gauss developed the electromagnetic telegraph with a colleague at the University of Göttingen, the physicist Wilhelm Weber, and they used it to send communications between their two offices, according to the biography. One of the first messages they transmitted was the sentence "Knowing above believing, reality above appearance," and it took about 4 minutes and 30 seconds to transmit.
When Gauss died of a heart attack, in 1855, his contemporaries mourned his loss, describing him as "a prince of science," and in 1856 he was posthumously honored by King George V of Hanover with a medal inscribed to "Mathematicorum Principi" — "the Prince of Mathematicians," the University of Göttingen reported.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Original article on Live Science.

Mindy Weisberger is a science journalist and author of "Rise of the Zombie Bugs: The Surprising Science of Parasitic Mind-Control" (Hopkins Press). She formerly edited for Scholastic and was a channel editor and senior writer for Live Science. She has reported on general science, covering climate change, paleontology, biology and space. Mindy studied film at Columbia University; prior to LS, she produced, wrote and directed media for the American Museum of Natural History in NYC. Her videos about dinosaurs, astrophysics, biodiversity and evolution appear in museums and science centers worldwide, earning awards such as the CINE Golden Eagle and the Communicator Award of Excellence. Her writing has also appeared in Scientific American, The Washington Post, How It Works Magazine and CNN.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










